Pavel Rychlý
A survey of neural-network-based methods utilising comparable data for finding translation equivalents
Oct 19, 2024
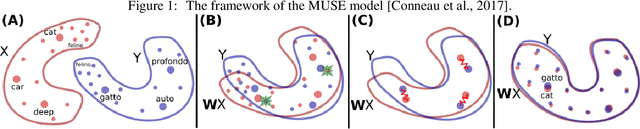


Abstract:The importance of inducing bilingual dictionary components in many natural language processing (NLP) applications is indisputable. However, the dictionary compilation process requires extensive work and combines two disciplines, NLP and lexicography, while the former often omits the latter. In this paper, we present the most common approaches from NLP that endeavour to automatically induce one of the essential dictionary components, translation equivalents and focus on the neural-network-based methods using comparable data. We analyse them from a lexicographic perspective since their viewpoints are crucial for improving the described methods. Moreover, we identify the methods that integrate these viewpoints and can be further exploited in various applications that require them. This survey encourages a connection between the NLP and lexicography fields as the NLP field can benefit from lexicographic insights, and it serves as a helping and inspiring material for further research in the context of neural-network-based methods utilising comparable data.
Evaluation of Automatically Constructed Word Meaning Explanations
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Preparing exact and comprehensive word meaning explanations is one of the key steps in the process of monolingual dictionary writing. In standard methodology, the explanations need an expert lexicographer who spends a substantial amount of time checking the consistency between the descriptive text and corpus evidence. In the following text, we present a new tool that derives explanations automatically based on collective information from very large corpora, particularly on word sketches. We also propose a quantitative evaluation of the constructed explanations, concentrating on explanations of nouns. The methodology is to a certain extent language independent; however, the presented verification is limited to Czech and English. We show that the presented approach allows to create explanations that contain data useful for understanding the word meaning in approximately 90% of cases. However, in many cases, the result requires post-editing to remove redundant information.
* preprint of a chapter published by College Publications at https://www.collegepublications.co.uk/tributes/?00049
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge