Pavel Janovský
Finding Coordinated Paths for Multiple Holonomic Agents in 2-d Polygonal Environment
Feb 14, 2014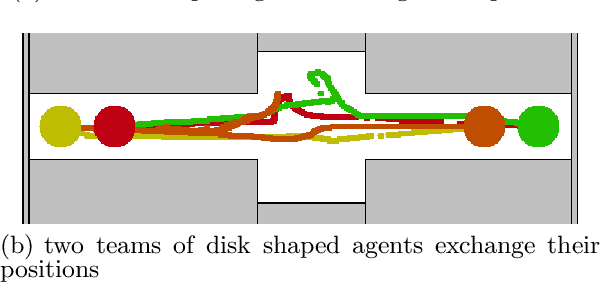


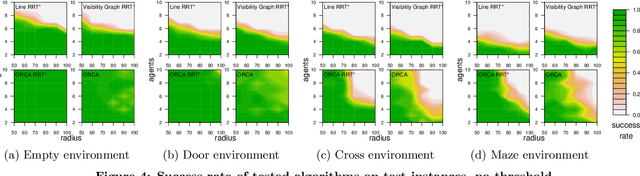
Abstract:Avoiding collisions is one of the vital tasks for systems of autonomous mobile agents. We focus on the problem of finding continuous coordinated paths for multiple mobile disc agents in a 2-d environment with polygonal obstacles. The problem is PSPACE-hard, with the state space growing exponentially in the number of agents. Therefore, the state of the art methods include mainly reactive techniques and sampling-based iterative algorithms. We compare the performance of a widely-used reactive method ORCA with three variants of a popular planning algorithm RRT* applied to multi-agent path planning and find that an algorithm combining reactive collision avoidance and RRT* planning, which we call ORCA-RRT* can be used to solve instances that are out of the reach of either of the techniques. We experimentally show that: 1) the reactive part of the algorithm can efficiently solve many multi-agent path finding problems involving large number of agents, for which RRT* algorithm is often unable to find a solution in limited time and 2) the planning component of the algorithm is able to solve many instances containing local minima, where reactive techniques typically fail.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge