Patrick Delfmann
Event Abstraction for Enterprise Collaboration Systems to Support Social Process Mining
Aug 09, 2023Abstract:One aim of Process Mining (PM) is the discovery of process models from event logs of information systems. PM has been successfully applied to process-oriented enterprise systems but is less suited for communication- and document-oriented Enterprise Collaboration Systems (ECS). ECS event logs are very fine-granular and PM applied to their logs results in spaghetti models. A common solution for this is event abstraction, i.e., converting low-level logs into more abstract high-level logs before running discovery algorithms. ECS logs come with special characteristics that have so far not been fully addressed by existing event abstraction approaches. We aim to close this gap with a tailored ECS event abstraction (ECSEA) approach that trains a model by comparing recorded actual user activities (high-level traces) with the system-generated low-level traces (extracted from the ECS). The model allows us to automatically convert future low-level traces into an abstracted high-level log that can be used for PM. Our evaluation shows that the algorithm produces accurate results. ECSEA is a preprocessing method that is essential for the interpretation of collaborative work activity in ECS, which we call Social Process Mining.
Inter-case Predictive Process Monitoring: A candidate for Quantum Machine Learning?
Jun 30, 2023Abstract:Regardless of the domain, forecasting the future behaviour of a running process instance is a question of interest for decision makers, especially when multiple instances interact. Fostered by the recent advances in machine learning research, several methods have been proposed to predict the next activity, outcome or remaining time of a process automatically. Still, building a model with high predictive power requires both - intrinsic knowledge of how to extract meaningful features from the event log data and a model that captures complex patterns in data. This work builds upon the recent progress in inter-case Predictive Process Monitoring (PPM) and comprehensively benchmarks the impact of inter-case features on prediction accuracy. Moreover, it includes quantum machine learning models, which are expected to provide an advantage over classical models with a scaling amount of feature dimensions. The evaluation on real-world training data from the BPI challenge shows that the inter-case features provide a significant boost by more than four percent in accuracy and quantum algorithms are indeed competitive in a handful of feature configurations. Yet, as quantum hardware is still in its early stages of development, this paper critically discusses these findings in the light of runtime, noise and the risk to overfit on the training data. Finally, the implementation of an open-source plugin demonstrates the technical feasibility to connect a state-of-the-art workflow engine such as Camunda to an IBM quantum computing cloud service.
Ontology-Based Process Modelling -- Will we live to see it?
Jul 12, 2021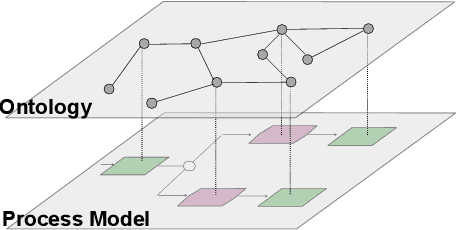
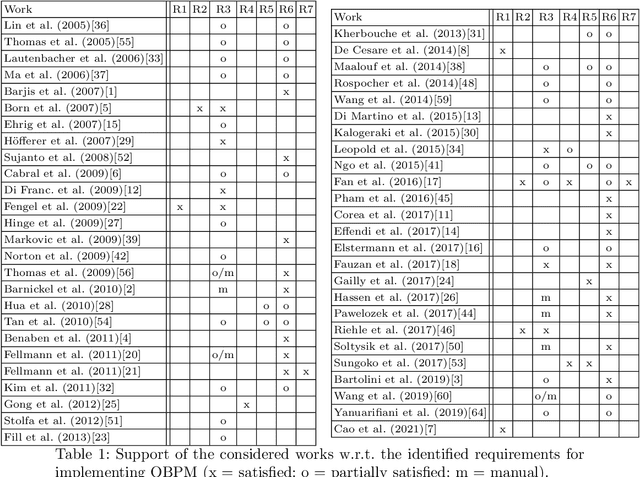
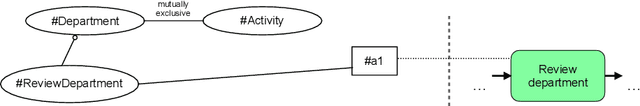
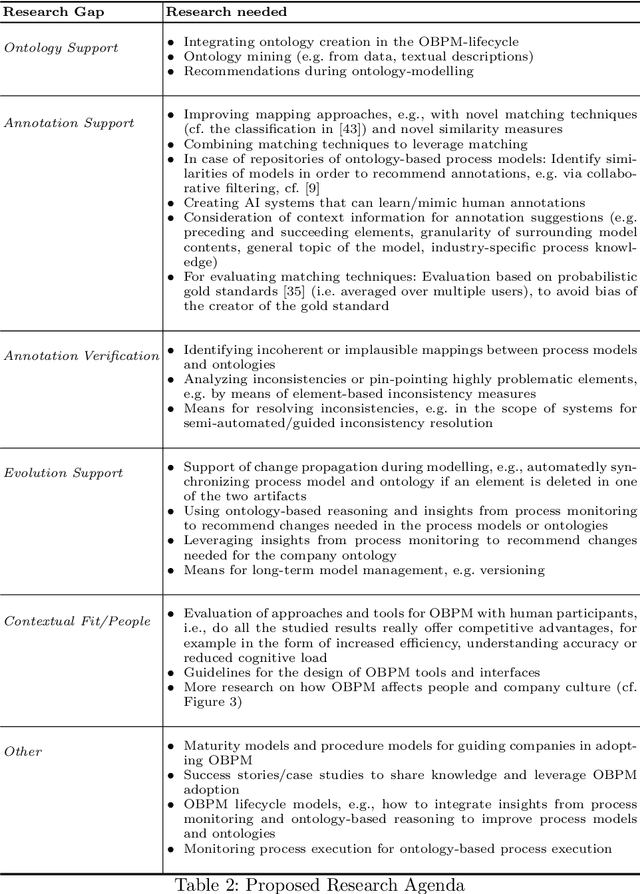
Abstract:In theory, ontology-based process modelling (OBPM) bares great potential to extend business process management. Many works have studied OBPM and are clear on the potential amenities, such as eliminating ambiguities or enabling advanced reasoning over company processes. However, despite this approval in academia, a widespread industry adoption is still nowhere to be seen. This can be mainly attributed to the fact, that it still requires high amounts of manual labour to initially create ontologies and annotations to process models. As long as these problems are not addressed, implementing OBPM seems unfeasible in practice. In this work, we therefore identify requirements needed for a successful implementation of OBPM and assess the current state of research w.r.t. these requirements. Our results indicate that the research progress for means to facilitate OBPM are still alarmingly low and there needs to be urgent work on extending existing approaches.
Measuring Inconsistency over Sequences of Business Rule Cases
Mar 01, 2021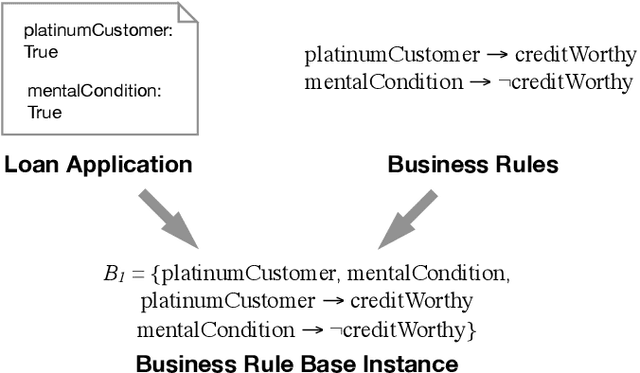
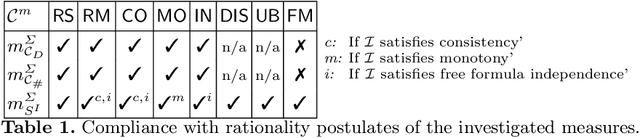
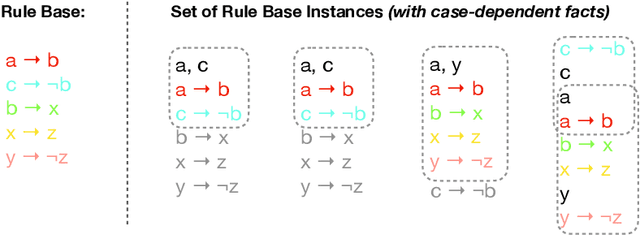
Abstract:In this report, we investigate (element-based) inconsistency measures for multisets of business rule bases. Currently, related works allow to assess individual rule bases, however, as companies might encounter thousands of such instances daily, studying not only individual rule bases separately, but rather also their interrelations becomes necessary, especially in regard to determining suitable re-modelling strategies. We therefore present an approach to induce multiset-measures from arbitrary (traditional) inconsistency measures, propose new rationality postulates for a multiset use-case, and investigate the complexity of various aspects regarding multi-rule base inconsistency measurement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge