Parinya Punpongsanon
Directionally Decomposing Structured Light for Projector Calibration
Oct 08, 2021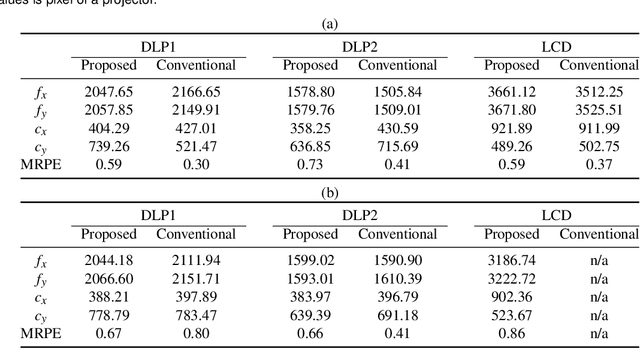
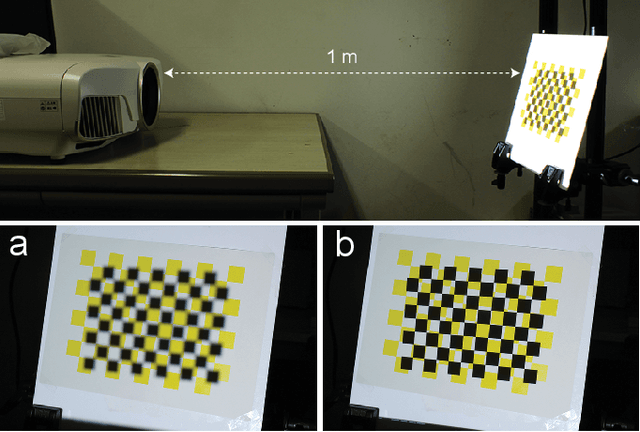
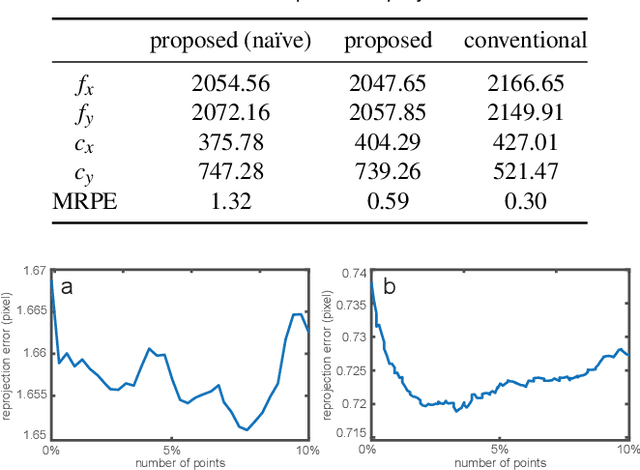
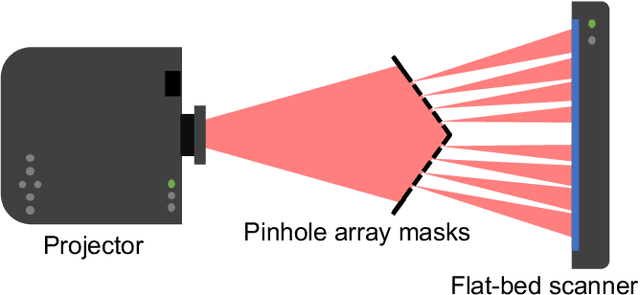
Abstract:Intrinsic projector calibration is essential in projection mapping (PM) applications, especially in dynamic PM. However, due to the shallow depth-of-field (DOF) of a projector, more work is needed to ensure accurate calibration. We aim to estimate the intrinsic parameters of a projector while avoiding the limitation of shallow DOF. As the core of our technique, we present a practical calibration device that requires a minimal working volume directly in front of the projector lens regardless of the projector's focusing distance and aperture size. The device consists of a flat-bed scanner and pinhole-array masks. For calibration, a projector projects a series of structured light patterns in the device. The pinholes directionally decompose the structured light, and only the projected rays that pass through the pinholes hit the scanner plane. For each pinhole, we extract a ray passing through the optical center of the projector. Consequently, we regard the projector as a pinhole projector that projects the extracted rays only, and we calibrate the projector by applying the standard camera calibration technique, which assumes a pinhole camera model. Using a proof-of-concept prototype, we demonstrate that our technique can calibrate projectors with different focusing distances and aperture sizes at the same accuracy as a conventional method. Finally, we confirm that our technique can provide intrinsic parameters accurate enough for a dynamic PM application, even when a projector is placed too far from a projection target for a conventional method to calibrate the projector using a fiducial object of reasonable size.
Multifocal Stereoscopic Projection Mapping
Oct 08, 2021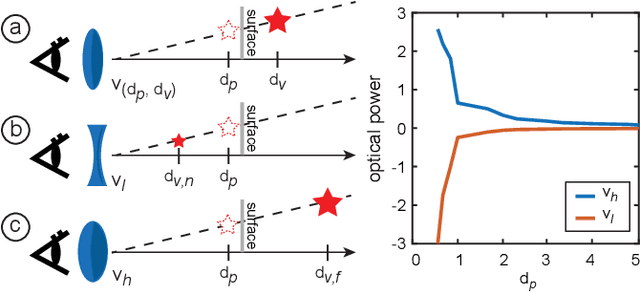
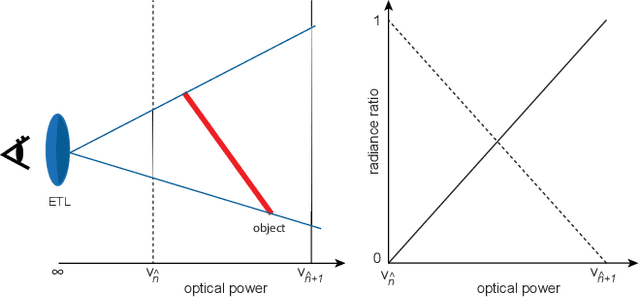
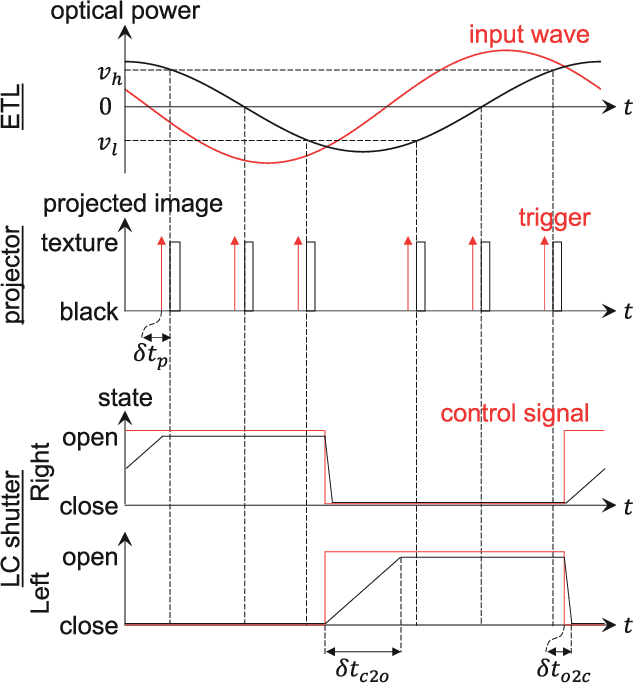
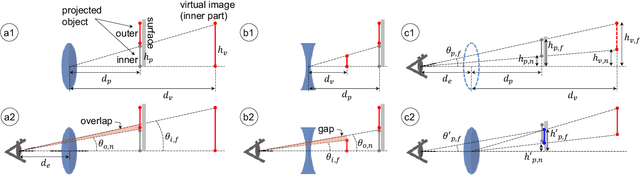
Abstract:Stereoscopic projection mapping (PM) allows a user to see a three-dimensional (3D) computer-generated (CG) object floating over physical surfaces of arbitrary shapes around us using projected imagery. However, the current stereoscopic PM technology only satisfies binocular cues and is not capable of providing correct focus cues, which causes a vergence--accommodation conflict (VAC). Therefore, we propose a multifocal approach to mitigate VAC in stereoscopic PM. Our primary technical contribution is to attach electrically focus-tunable lenses (ETLs) to active shutter glasses to control both vergence and accommodation. Specifically, we apply fast and periodical focal sweeps to the ETLs, which causes the "virtual image'" (as an optical term) of a scene observed through the ETLs to move back and forth during each sweep period. A 3D CG object is projected from a synchronized high-speed projector only when the virtual image of the projected imagery is located at a desired distance. This provides an observer with the correct focus cues required. In this study, we solve three technical issues that are unique to stereoscopic PM: (1) The 3D CG object is displayed on non-planar and even moving surfaces; (2) the physical surfaces need to be shown without the focus modulation; (3) the shutter glasses additionally need to be synchronized with the ETLs and the projector. We also develop a novel compensation technique to deal with the "lens breathing" artifact that varies the retinal size of the virtual image through focal length modulation. Further, using a proof-of-concept prototype, we demonstrate that our technique can present the virtual image of a target 3D CG object at the correct depth. Finally, we validate the advantage provided by our technique by comparing it with conventional stereoscopic PM using a user study on a depth-matching task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge