Parimala Kancharla
Deep Priors for Video Quality Prediction
Oct 29, 2024

Abstract:In this work, we designed a completely blind video quality assessment algorithm using the deep video prior. This work mainly explores the utility of deep video prior in estimating the visual quality of the video. In our work, we have used a single distorted video and a reference video pair to learn the deep video prior. At inference time, the learned deep prior is used to restore the original videos from the distorted videos. The ability of learned deep video prior to restore the original video from the distorted video is measured to quantify distortion in the video. Our hypothesis is that the learned deep video prior fails in restoring the highly distorted videos. The restoring ability of deep video prior is proportional to the distortion present in the video. Therefore, we propose to use the distance between the distorted video and the restored video as the perceptual quality of the video. Our algorithm is trained using a single video pair and it does not need any labelled data. We show that our proposed algorithm outperforms the existing unsupervised video quality assessment algorithms in terms of LCC and SROCC on a synthetically distorted video quality assessment dataset.
Quality Aware Generative Adversarial Networks
Nov 08, 2019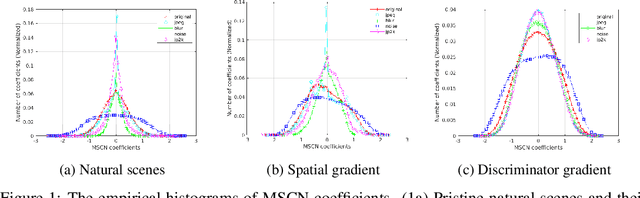
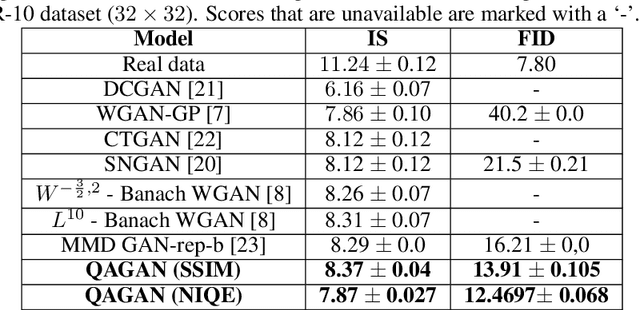
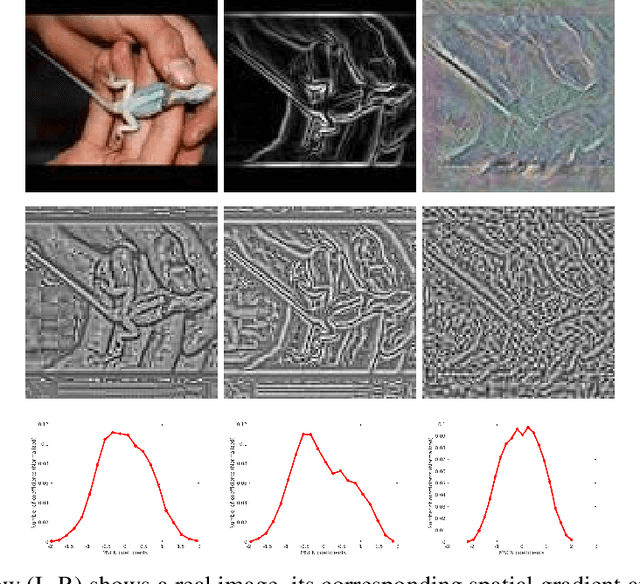
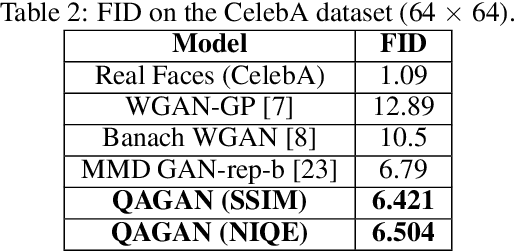
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have become a very popular tool for implicitly learning high-dimensional probability distributions. Several improvements have been made to the original GAN formulation to address some of its shortcomings like mode collapse, convergence issues, entanglement, poor visual quality etc. While a significant effort has been directed towards improving the visual quality of images generated by GANs, it is rather surprising that objective image quality metrics have neither been employed as cost functions nor as regularizers in GAN objective functions. In this work, we show how a distance metric that is a variant of the Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) index (a popular full-reference image quality assessment algorithm), and a novel quality aware discriminator gradient penalty function that is inspired by the Natural Image Quality Evaluator (NIQE, a popular no-reference image quality assessment algorithm) can each be used as excellent regularizers for GAN objective functions. Specifically, we demonstrate state-of-the-art performance using the Wasserstein GAN gradient penalty (WGAN-GP) framework over CIFAR-10, STL10 and CelebA datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge