Omar Abdelaziz
GNN-MoE: Context-Aware Patch Routing using GNNs for Parameter-Efficient Domain Generalization
Nov 06, 2025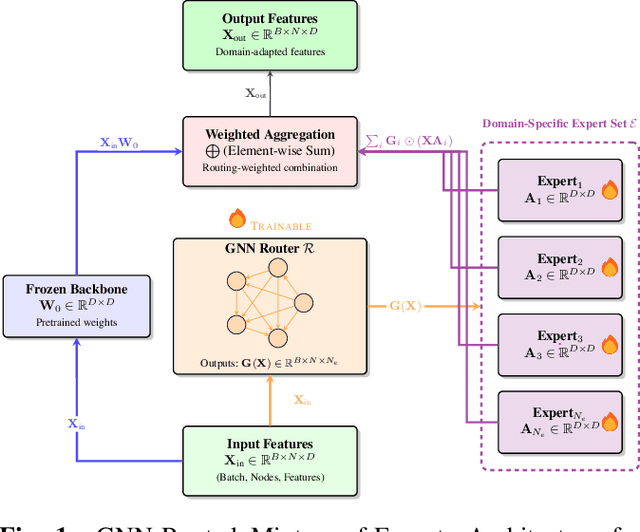
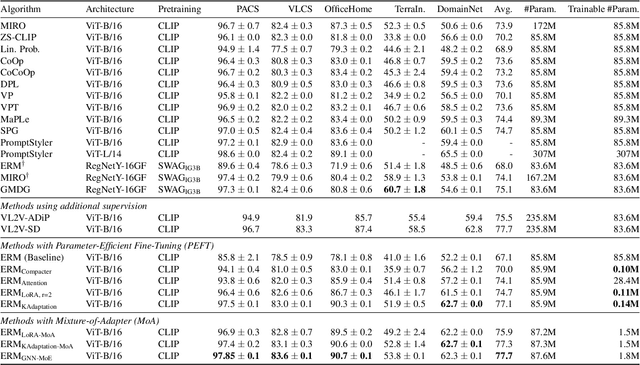

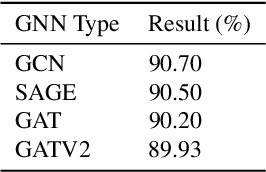
Abstract:Domain generalization (DG) seeks robust Vision Transformer (ViT) performance on unseen domains. Efficiently adapting pretrained ViTs for DG is challenging; standard fine-tuning is costly and can impair generalization. We propose GNN-MoE, enhancing Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) for DG with a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) framework using efficient Kronecker adapters. Instead of token-based routing, a novel Graph Neural Network (GNN) router (GCN, GAT, SAGE) operates on inter-patch graphs to dynamically assign patches to specialized experts. This context-aware GNN routing leverages inter-patch relationships for better adaptation to domain shifts. GNN-MoE achieves state-of-the-art or competitive DG benchmark performance with high parameter efficiency, highlighting the utility of graph-based contextual routing for robust, lightweight DG.
Beyond Traditional Single Object Tracking: A Survey
May 16, 2024



Abstract:Single object tracking is a vital task of many applications in critical fields. However, it is still considered one of the most challenging vision tasks. In recent years, computer vision, especially object tracking, witnessed the introduction or adoption of many novel techniques, setting new fronts for performance. In this survey, we visit some of the cutting-edge techniques in vision, such as Sequence Models, Generative Models, Self-supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, Reinforcement Learning, Meta-Learning, Continual Learning, and Domain Adaptation, focusing on their application in single object tracking. We propose a novel categorization of single object tracking methods based on novel techniques and trends. Also, we conduct a comparative analysis of the performance reported by the methods presented on popular tracking benchmarks. Moreover, we analyze the pros and cons of the presented approaches and present a guide for non-traditional techniques in single object tracking. Finally, we suggest potential avenues for future research in single-object tracking.
A Novel Bounding Box Regression Method for Single Object Tracking
May 16, 2024



Abstract:Locating an object in a sequence of frames, given its appearance in the first frame of the sequence, is a hard problem that involves many stages. Usually, state-of-the-art methods focus on bringing novel ideas in the visual encoding or relational modelling phases. However, in this work, we show that bounding box regression from learned joint search and template features is of high importance as well. While previous methods relied heavily on well-learned features representing interactions between search and template, we hypothesize that the receptive field of the input convolutional bounding box network plays an important role in accurately determining the object location. To this end, we introduce two novel bounding box regression networks: inception and deformable. Experiments and ablation studies show that our inception module installed on the recent ODTrack outperforms the latter on three benchmarks: the GOT-10k, the UAV123 and the OTB2015.
Multiple configurations for puncturing robot positioning
Mar 06, 2019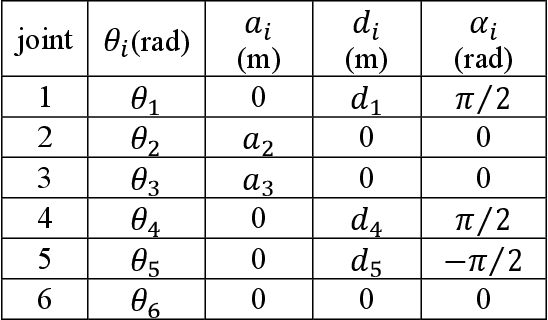
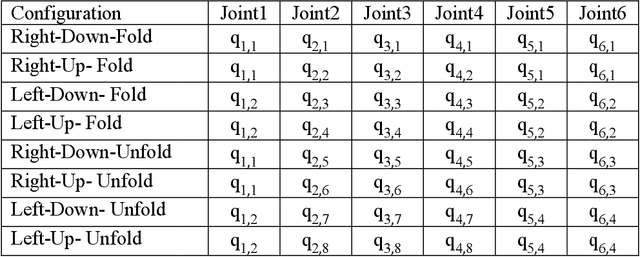
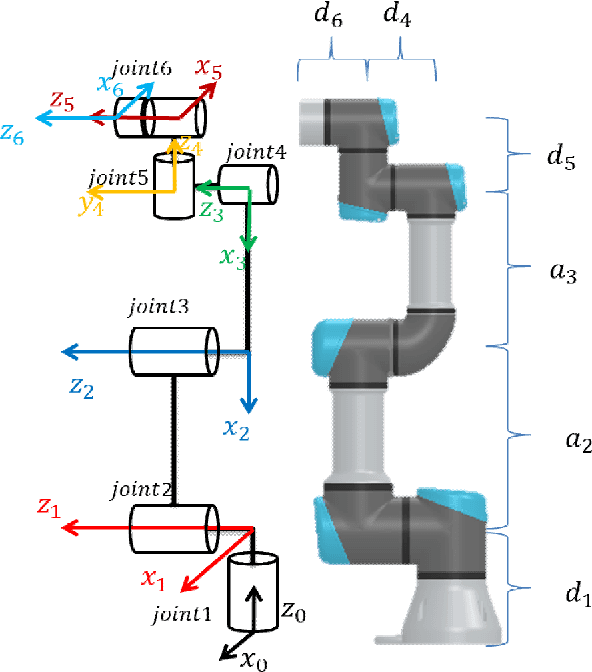
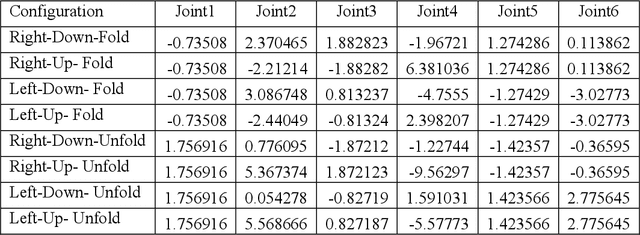
Abstract:The paper presents the Inverse Kinematics (IK) close form derivation steps using combination of analytical and geometric techniques for the UR robot. The innovative application of this work is used in the precise positioning of puncture robotics system. The end effector is a puncture needle guide tube, which needs precise positioning over the puncture insertion point. The IK closed form solutions bring out maximum 8 solutions represents 8 different robot joints configurations. These multiple solutions are helpful in the puncture robotics system, it allow doctors to choose the most suitable configuration during the operation. Therefore the workspace becomes more adequate for the coexistence of human and robot. Moreover IK closed form solutions are more precise in positioning for medical puncture surgery compared to other numerical methods. We include a performance evaluation for both of the IK obtained by the closed form solution and by a numerical method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge