Olga Graf
Toxicity Assessment in Preclinical Histopathology via Class-Aware Mahalanobis Distance for Known and Novel Anomalies
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Drug-induced toxicity remains a leading cause of failure in preclinical development and early clinical trials. Detecting adverse effects at an early stage is critical to reduce attrition and accelerate the development of safe medicines. Histopathological evaluation remains the gold standard for toxicity assessment, but it relies heavily on expert pathologists, creating a bottleneck for large-scale screening. To address this challenge, we introduce an AI-based anomaly detection framework for histopathological whole-slide images (WSIs) in rodent livers from toxicology studies. The system identifies healthy tissue and known pathologies (anomalies) for which training data is available. In addition, it can detect rare pathologies without training data as out-of-distribution (OOD) findings. We generate a novel dataset of pixelwise annotations of healthy tissue and known pathologies and use this data to fine-tune a pre-trained Vision Transformer (DINOv2) via Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) in order to do tissue segmentation. Finally, we extract features for OOD detection using the Mahalanobis distance. To better account for class-dependent variability in histological data, we propose the use of class-specific thresholds. We optimize the thresholds using the mean of the false negative and false positive rates, resulting in only 0.16\% of pathological tissue classified as healthy and 0.35\% of healthy tissue classified as pathological. Applied to mouse liver WSIs with known toxicological findings, the framework accurately detects anomalies, including rare OOD morphologies. This work demonstrates the potential of AI-driven histopathology to support preclinical workflows, reduce late-stage failures, and improve efficiency in drug development.
Improved Uncertainty Quantification in Physics-Informed Neural Networks Using Error Bounds and Solution Bundles
May 09, 2025



Abstract:Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) have been widely used to obtain solutions to various physical phenomena modeled as Differential Equations. As PINNs are not naturally equipped with mechanisms for Uncertainty Quantification, some work has been done to quantify the different uncertainties that arise when dealing with PINNs. In this paper, we use a two-step procedure to train Bayesian Neural Networks that provide uncertainties over the solutions to differential equation systems provided by PINNs. We use available error bounds over PINNs to formulate a heteroscedastic variance that improves the uncertainty estimation. Furthermore, we solve forward problems and utilize the obtained uncertainties when doing parameter estimation in inverse problems in cosmology.
Error-Aware B-PINNs: Improving Uncertainty Quantification in Bayesian Physics-Informed Neural Networks
Dec 14, 2022



Abstract:Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) are gaining popularity as a method for solving differential equations. While being more feasible in some contexts than the classical numerical techniques, PINNs still lack credibility. A remedy for that can be found in Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) which is just beginning to emerge in the context of PINNs. Assessing how well the trained PINN complies with imposed differential equation is the key to tackling uncertainty, yet there is lack of comprehensive methodology for this task. We propose a framework for UQ in Bayesian PINNs (B-PINNs) that incorporates the discrepancy between the B-PINN solution and the unknown true solution. We exploit recent results on error bounds for PINNs on linear dynamical systems and demonstrate the predictive uncertainty on a class of linear ODEs.
Uncertainty Quantification in Neural Differential Equations
Nov 08, 2021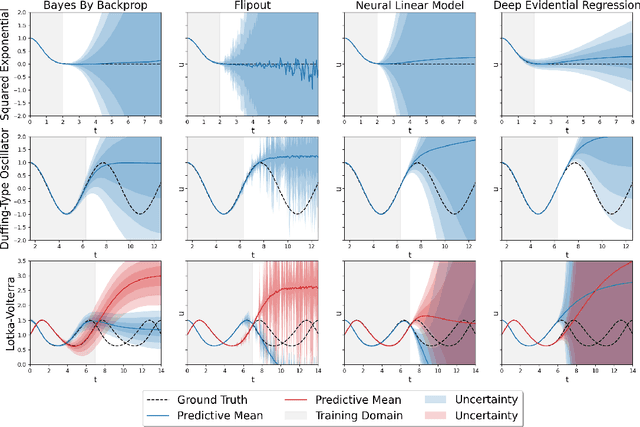
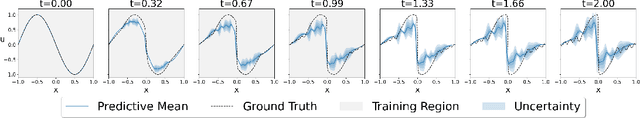
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) helps to make trustworthy predictions based on collected observations and uncertain domain knowledge. With increased usage of deep learning in various applications, the need for efficient UQ methods that can make deep models more reliable has increased as well. Among applications that can benefit from effective handling of uncertainty are the deep learning based differential equation (DE) solvers. We adapt several state-of-the-art UQ methods to get the predictive uncertainty for DE solutions and show the results on four different DE types.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge