Nivethitha Somu
EnsembleNTLDetect: An Intelligent Framework for Electricity Theft Detection in Smart Grid
Oct 09, 2021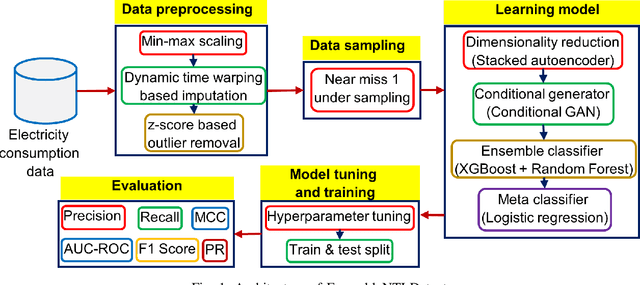
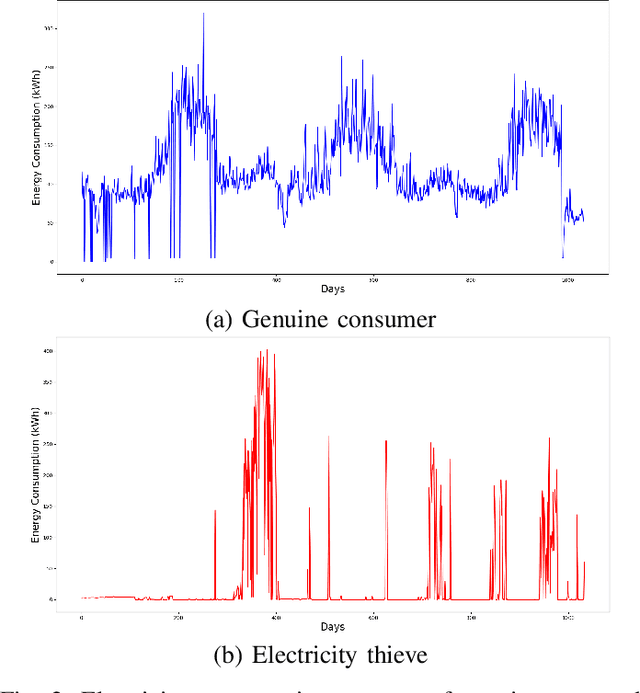
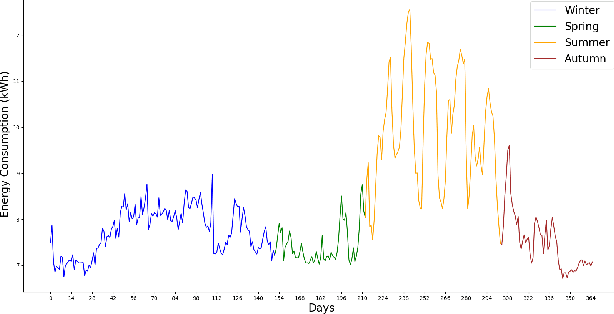
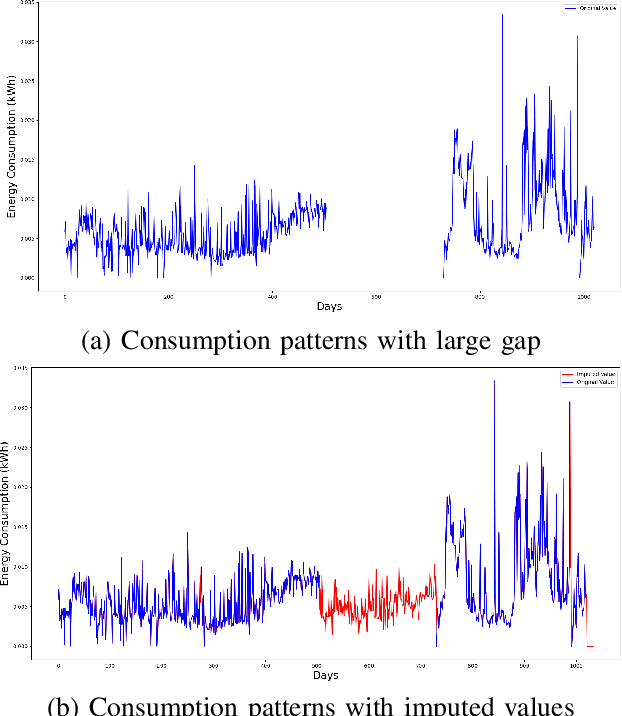
Abstract:Artificial intelligence-based techniques applied to the electricity consumption data generated from the smart grid prove to be an effective solution in reducing Non Technical Loses (NTLs), thereby ensures safety, reliability, and security of the smart energy systems. However, imbalanced data, consecutive missing values, large training times, and complex architectures hinder the real time application of electricity theft detection models. In this paper, we present EnsembleNTLDetect, a robust and scalable electricity theft detection framework that employs a set of efficient data pre-processing techniques and machine learning models to accurately detect electricity theft by analysing consumers' electricity consumption patterns. This framework utilises an enhanced Dynamic Time Warping Based Imputation (eDTWBI) algorithm to impute missing values in the time series data and leverages the Near-miss undersampling technique to generate balanced data. Further, stacked autoencoder is introduced for dimensionality reduction and to improve training efficiency. A Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (CTGAN) is used to augment the dataset to ensure robust training and a soft voting ensemble classifier is designed to detect the consumers with aberrant consumption patterns. Furthermore, experiments were conducted on the real-time electricity consumption data provided by the State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC) to validate the reliability and efficiency of EnsembleNTLDetect over the state-of-the-art electricity theft detection models in terms of various quality metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge