Nicolas Gutehrlé
CRIT
Understanding Archives: Towards New Research Interfaces Relying on the Semantic Annotation of Documents
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:The digitisation campaigns carried out by libraries and archives in recent years have facilitated access to documents in their collections. However, exploring and exploiting these documents remain difficult tasks due to the sheer quantity of documents available for consultation. In this article, we show how the semantic annotation of the textual content of study corpora of archival documents allow to facilitate their exploitation and valorisation. First, we present a methodological framework for the construction of new interfaces based on textual semantics, then address the current technological obstacles and their potential solutions. We conclude by presenting a practical case of the application of this framework.
Distantly Supervised Morpho-Syntactic Model for Relation Extraction
Jan 18, 2024



Abstract:The task of Information Extraction (IE) involves automatically converting unstructured textual content into structured data. Most research in this field concentrates on extracting all facts or a specific set of relationships from documents. In this paper, we present a method for the extraction and categorisation of an unrestricted set of relationships from text. Our method relies on morpho-syntactic extraction patterns obtained by a distant supervision method, and creates Syntactic and Semantic Indices to extract and classify candidate graphs. We evaluate our approach on six datasets built on Wikidata and Wikipedia. The evaluation shows that our approach can achieve Precision scores of up to 0.85, but with lower Recall and F1 scores. Our approach allows to quickly create rule-based systems for Information Extraction and to build annotated datasets to train machine-learning and deep-learning based classifiers.
Archive TimeLine Summarization (ATLS): Conceptual Framework for Timeline Generation over Historical Document Collections
Jan 31, 2023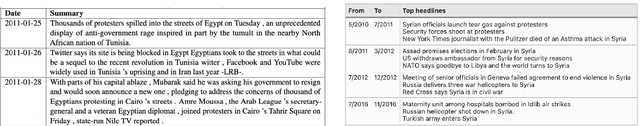

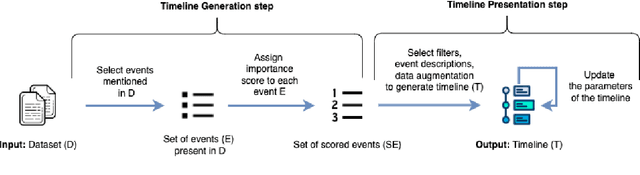
Abstract:Archive collections are nowadays mostly available through search engines interfaces, which allow a user to retrieve documents by issuing queries. The study of these collections may be, however, impaired by some aspects of search engines, such as the overwhelming number of documents returned or the lack of contextual knowledge provided. New methods that could work independently or in combination with search engines are then required to access these collections. In this position paper, we propose to extend TimeLine Summarization (TLS) methods on archive collections to assist in their studies. We provide an overview of existing TLS methods and we describe a conceptual framework for an Archive TimeLine Summarization (ATLS) system, which aims to generate informative, readable and interpretable timelines.
Processing the structure of documents: Logical Layout Analysis of historical newspapers in French
Feb 16, 2022

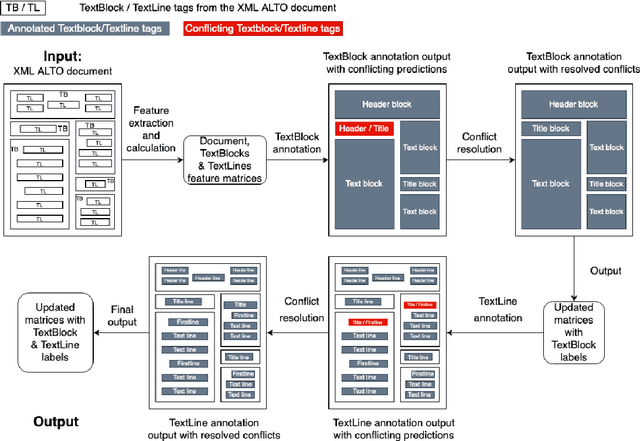
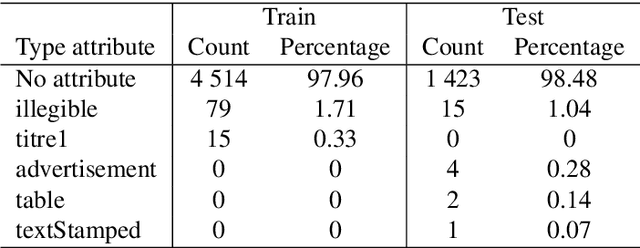
Abstract:Background. In recent years, libraries and archives led important digitisation campaigns that opened the access to vast collections of historical documents. While such documents are often available as XML ALTO documents, they lack information about their logical structure. In this paper, we address the problem of Logical Layout Analysis applied to historical documents in French. We propose a rule-based method, that we evaluate and compare with two Machine-Learning models, namely RIPPER and Gradient Boosting. Our data set contains French newspapers, periodicals and magazines, published in the first half of the twentieth century in the Franche-Comt\'e Region. Results. Our rule-based system outperforms the two other models in nearly all evaluations. It has especially better Recall results, indicating that our system covers more types of every logical label than the other two models. When comparing RIPPER with Gradient Boosting, we can observe that Gradient Boosting has better Precision scores but RIPPER has better Recall scores. Conclusions. The evaluation shows that our system outperforms the two Machine Learning models, and provides significantly higher Recall. It also confirms that our system can be used to produce annotated data sets that are large enough to envisage Machine Learning or Deep Learning approaches for the task of Logical Layout Analysis. Combining rules and Machine Learning models into hybrid systems could potentially provide even better performances. Furthermore, as the layout in historical documents evolves rapidly, one possible solution to overcome this problem would be to apply Rule Learning algorithms to bootstrap rule sets adapted to different publication periods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge