Nicolai Hermann
Gabor Fields: Orientation-Selective Level-of-Detail for Volume Rendering
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Gaussian-based representations have enabled efficient physically-based volume rendering at a fraction of the memory cost of regular, discrete, voxel-based distributions. However, several remaining issues hamper their widespread use. One of the advantages of classic voxel grids is the ease of constructing hierarchical representations by either storing volumetric mipmaps or selectively pruning branches of an already hierarchical voxel grid. Such strategies reduce rendering time and eliminate aliasing when lower levels of detail are required. Constructing similar strategies for Gaussian-based volumes is not trivial. Straightforward solutions, such as prefiltering or computing mipmap-style representations, lead to increased memory requirements or expensive re-fitting of each level separately. Additionally, such solutions do not guarantee a smooth transition between different hierarchy levels. To address these limitations, we propose Gabor Fields, an orientation-selective mixture of Gabor kernels that enables continuous frequency filtering at no cost. The frequency content of the asset is reduced by selectively pruning primitives, directly benefiting rendering performance. Beyond filtering, we demonstrate that stochastically sampling from different frequencies and orientations at each ray recursion enables masking substantial portions of the volume, accelerating ray traversal time in single- and multiple-scattering settings. Furthermore, inspired by procedural volumes, we present an application for efficient design and rendering of procedural clouds as Gabor-noise-modulated Gaussians.
Puzzle Similarity: A Perceptually-guided No-Reference Metric for Artifact Detection in 3D Scene Reconstructions
Nov 26, 2024


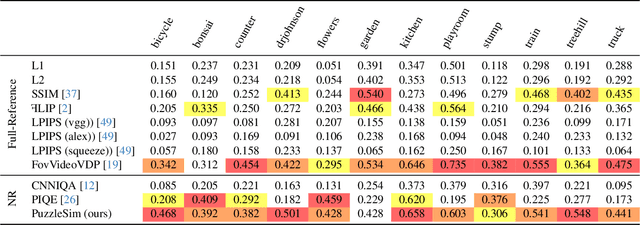
Abstract:Modern reconstruction techniques can effectively model complex 3D scenes from sparse 2D views. However, automatically assessing the quality of novel views and identifying artifacts is challenging due to the lack of ground truth images and the limitations of no-reference image metrics in predicting detailed artifact maps. The absence of such quality metrics hinders accurate predictions of the quality of generated views and limits the adoption of post-processing techniques, such as inpainting, to enhance reconstruction quality. In this work, we propose a new no-reference metric, Puzzle Similarity, which is designed to localize artifacts in novel views. Our approach utilizes image patch statistics from the input views to establish a scene-specific distribution that is later used to identify poorly reconstructed regions in the novel views. We test and evaluate our method in the context of 3D reconstruction; to this end, we collected a novel dataset of human quality assessment in unseen reconstructed views. Through this dataset, we demonstrate that our method can not only successfully localize artifacts in novel views, correlating with human assessment, but do so without direct references. Surprisingly, our metric outperforms both no-reference metrics and popular full-reference image metrics. We can leverage our new metric to enhance applications like automatic image restoration, guided acquisition, or 3D reconstruction from sparse inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge