Nazeeh Ghatasheh
Modified Genetic Algorithm for Feature Selection and Hyper Parameter Optimization: Case of XGBoost in Spam Prediction
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:Recently, spam on online social networks has attracted attention in the research and business world. Twitter has become the preferred medium to spread spam content. Many research efforts attempted to encounter social networks spam. Twitter brought extra challenges represented by the feature space size, and imbalanced data distributions. Usually, the related research works focus on part of these main challenges or produce black-box models. In this paper, we propose a modified genetic algorithm for simultaneous dimensionality reduction and hyper parameter optimization over imbalanced datasets. The algorithm initialized an eXtreme Gradient Boosting classifier and reduced the features space of tweets dataset; to generate a spam prediction model. The model is validated using a 50 times repeated 10-fold stratified cross-validation, and analyzed using nonparametric statistical tests. The resulted prediction model attains on average 82.32\% and 92.67\% in terms of geometric mean and accuracy respectively, utilizing less than 10\% of the total feature space. The empirical results show that the modified genetic algorithm outperforms $Chi^2$ and $PCA$ feature selection methods. In addition, eXtreme Gradient Boosting outperforms many machine learning algorithms, including BERT-based deep learning model, in spam prediction. Furthermore, the proposed approach is applied to SMS spam modeling and compared to related works.
Modeling the Telemarketing Process using Genetic Algorithms and Extreme Boosting: Feature Selection and Cost-Sensitive Analytical Approach
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:Currently, almost all direct marketing activities take place virtually rather than in person, weakening interpersonal skills at an alarming pace. Furthermore, businesses have been striving to sense and foster the tendency of their clients to accept a marketing offer. The digital transformation and the increased virtual presence forced firms to seek novel marketing research approaches. This research aims at leveraging the power of telemarketing data in modeling the willingness of clients to make a term deposit and finding the most significant characteristics of the clients. Real-world data from a Portuguese bank and national socio-economic metrics are used to model the telemarketing decision-making process. This research makes two key contributions. First, propose a novel genetic algorithm-based classifier to select the best discriminating features and tune classifier parameters simultaneously. Second, build an explainable prediction model. The best-generated classification models were intensively validated using 50 times repeated 10-fold stratified cross-validation and the selected features have been analyzed. The models significantly outperform the related works in terms of class of interest accuracy, they attained an average of 89.07\% and 0.059 in terms of geometric mean and type I error respectively. The model is expected to maximize the potential profit margin at the least possible cost and provide more insights to support marketing decision-making.
Robotics Evolution: from Remote Brain to Cloud
Jan 08, 2019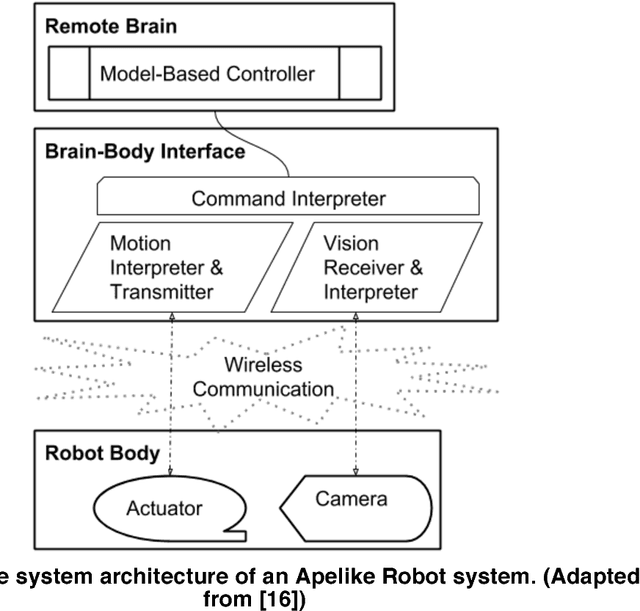
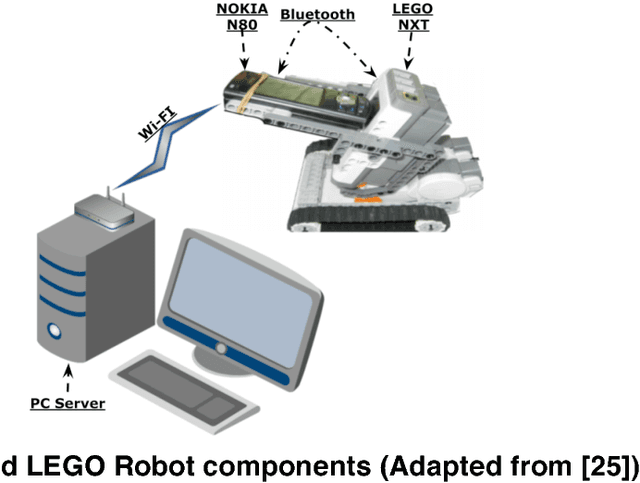

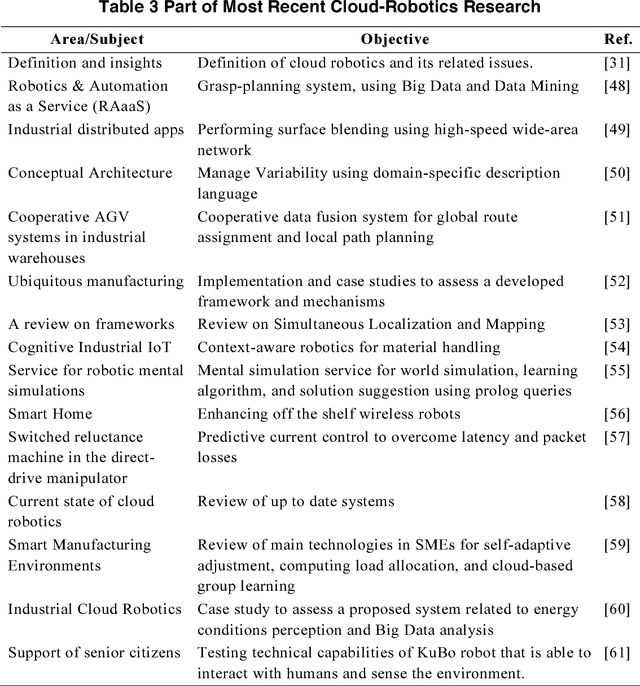
Abstract:Robotic systems have been evolving since decades and touching almost all aspects of life, either for leisure or critical applications. Most of traditional robotic systems operate in well-defined environments utilizing pre-configured on-board processing units. However, modern and foreseen robotic applications ask for complex processing requirements that exceed the limits of on-board computing power. Cloud computing and the related technologies have high potential to overcome on-board hardware restrictions and can improve the performance efficiency. This research highlights the advancements in robotic systems with focus on cloud robotics as an emerging trend. There exists an extensive amount of effort to leverage the potentials of robotic systems and to handle arising shortcomings. Moreover, there are promising insights for future breed of intelligent, flexible, and autonomous robotic systems in the Internet of Things era.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge