Naoki Takashima
Cross-modal Music Emotion Recognition Using Composite Loss-based Embeddings
Dec 14, 2021
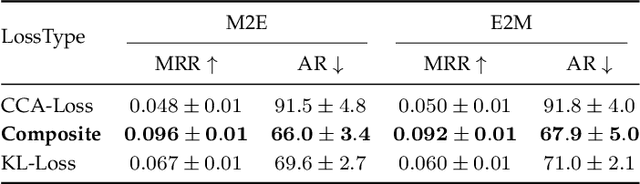

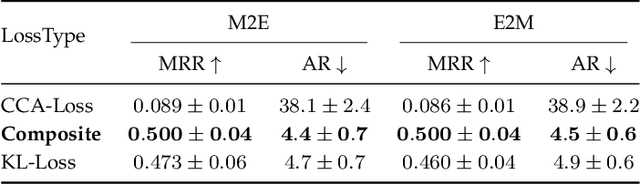
Abstract:Most music emotion recognition approaches use one-way classification or regression that estimates a general emotion from a distribution of music samples, but without considering emotional variations (e.g., happiness can be further categorised into much, moderate or little happiness). We propose a cross-modal music emotion recognition approach that associates music samples with emotions in a common space by considering both of their general and specific characteristics. Since the association of music samples with emotions is uncertain due to subjective human perceptions, we compute composite loss-based embeddings obtained to maximise two statistical characteristics, one being the correlation between music samples and emotions based on canonical correlation analysis, and the other being a probabilistic similarity between a music sample and an emotion with KL-divergence. Experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our approach over one-way baselines. In addition, detailed analysis show that our approach can accomplish robust cross-modal music emotion recognition that not only identifies music samples matching with a specific emotion but also detects emotions expressed in a certain music sample.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge