Nanda K. Unnikrishnan
LayerPipe2: Multistage Pipelining and Weight Recompute via Improved Exponential Moving Average for Training Neural Networks
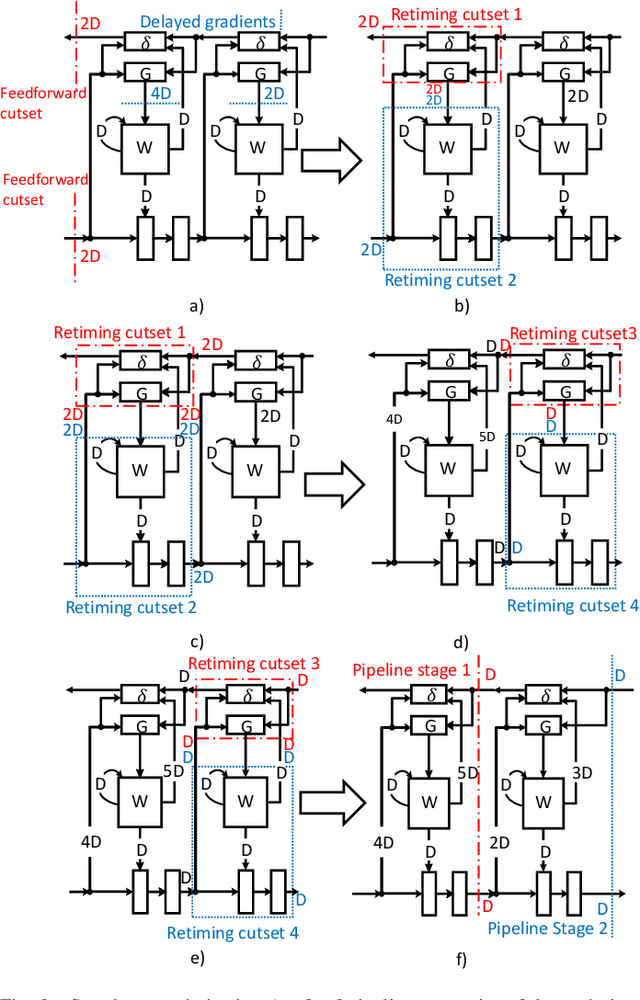
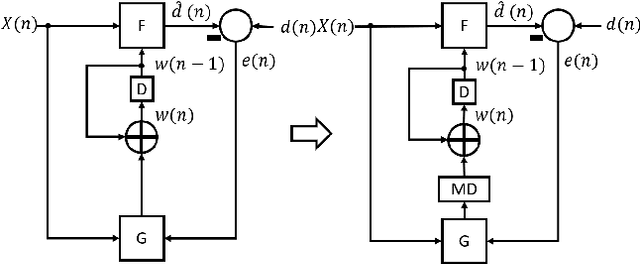
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:In our prior work, LayerPipe, we had introduced an approach to accelerate training of convolutional, fully connected, and spiking neural networks by overlapping forward and backward computation. However, despite empirical success, a principled understanding of how much gradient delay needs to be introduced at each layer to achieve desired level of pipelining was not addressed. This paper, LayerPipe2, fills that gap by formally deriving LayerPipe using variable delayed gradient adaptation and retiming. We identify where delays may be legally inserted and show that the required amount of delay follows directly from the network structure where inner layers require fewer delays and outer layers require longer delays. When pipelining is applied at every layer, the amount of delay depends only on the number of remaining downstream stages. When layers are pipelined in groups, all layers in the group share the same assignment of delays. These insights not only explain previously observed scheduling patterns but also expose an often overlooked challenge that pipelining implicitly requires storage of historical weights. We overcome this storage bottleneck by developing a pipeline--aware moving average that reconstructs the required past states rather than storing them explicitly. This reduces memory cost without sacrificing the accuracy guarantees that makes pipelined learning viable. The result is a principled framework that illustrates how to construct LayerPipe architectures, predicts their delay requirements, and mitigates their storage burden, thereby enabling scalable pipelined training with controlled communication computation tradeoffs.
Multi-Channel FFT Architectures Designed via Folding and Interleaving
Feb 19, 2022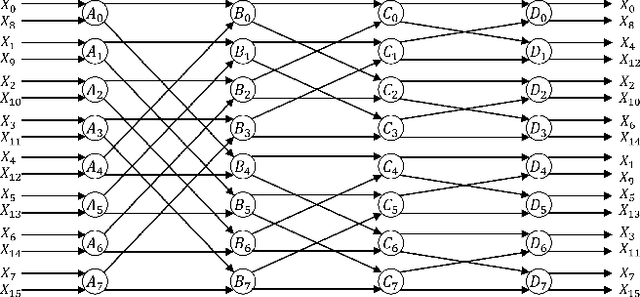
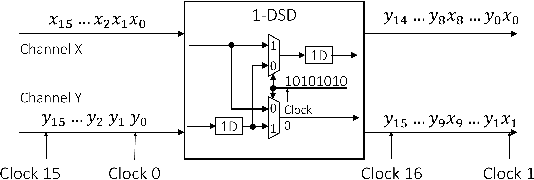
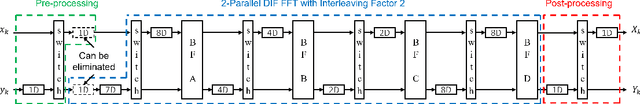
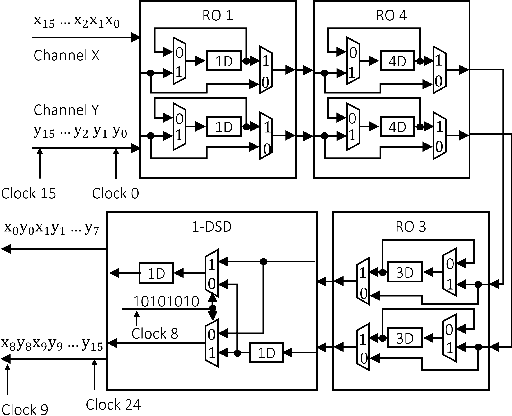
Abstract:Computing the FFT of a single channel is well understood in the literature. However, computing the FFT of multiple channels in a systematic manner has not been fully addressed. This paper presents a framework to design a family of multi-channel FFT architectures using {\em folding} and {\em interleaving}. Three distinct multi-channel FFT architectures are presented in this paper. These architectures differ in the input and output preprocessing steps and are based on different folding sets, i.e., different orders of execution.
LayerPipe: Accelerating Deep Neural Network Training by Intra-Layer and Inter-Layer Gradient Pipelining and Multiprocessor Scheduling
Aug 14, 2021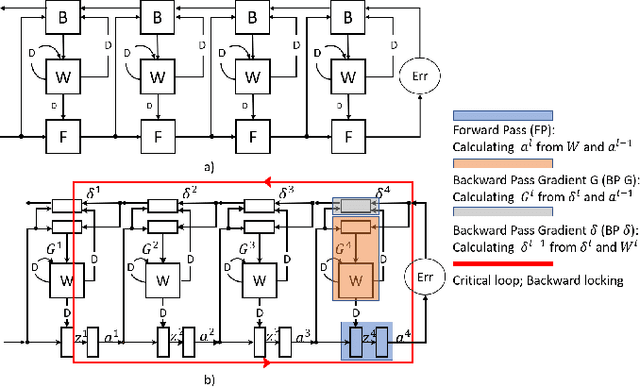
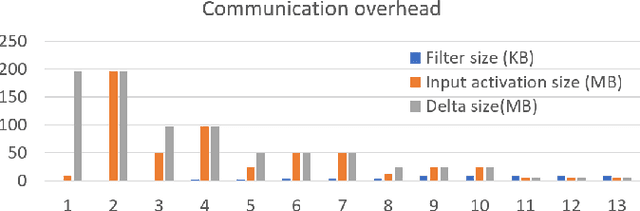
Abstract:The time required for training the neural networks increases with size, complexity, and depth. Training model parameters by backpropagation inherently creates feedback loops. These loops hinder efficient pipelining and scheduling of the tasks within the layer and between consecutive layers. Prior approaches, such as PipeDream, have exploited the use of delayed gradient to achieve inter-layer pipelining. However, these approaches treat the entire backpropagation as a single task; this leads to an increase in computation time and processor underutilization. This paper presents novel optimization approaches where the gradient computations with respect to the weights and the activation functions are considered independently; therefore, these can be computed in parallel. This is referred to as intra-layer optimization. Additionally, the gradient computation with respect to the activation function is further divided into two parts and distributed to two consecutive layers. This leads to balanced scheduling where the computation time of each layer is the same. This is referred to as inter-layer optimization. The proposed system, referred to as LayerPipe, reduces the number of clock cycles required for training while maximizing processor utilization with minimal inter-processor communication overhead. LayerPipe achieves an average speedup of 25% and upwards of 80% with 7 to 9 processors with less communication overhead when compared to PipeDream.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge