Mubin Ul Haque
Detection of Animal Movement from Weather Radar using Self-Supervised Learning
Aug 08, 2024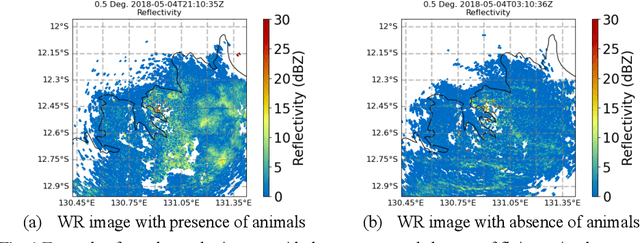
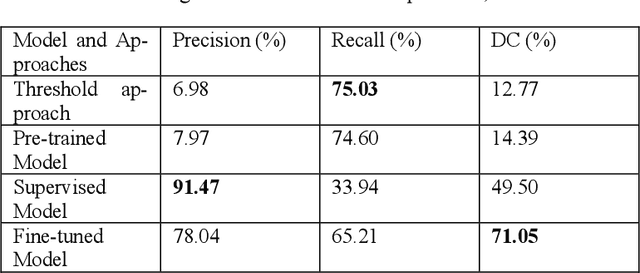
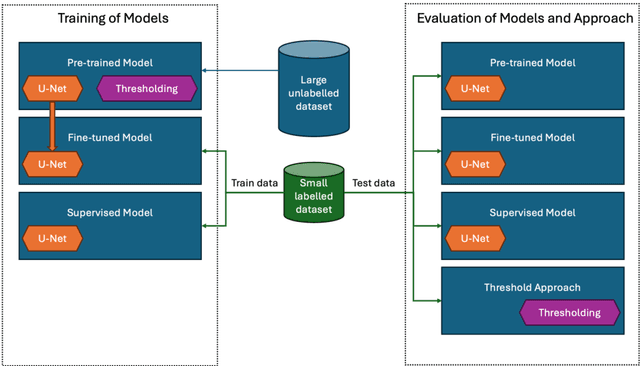
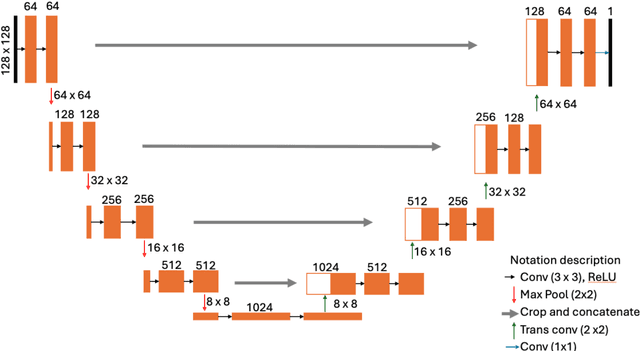
Abstract:Detecting flying animals (e.g., birds, bats, and insects) using weather radar helps gain insights into animal movement and migration patterns, aids in management efforts (such as biosecurity) and enhances our understanding of the ecosystem.The conventional approach to detecting animals in weather radar involves thresholding: defining and applying thresholds for the radar variables, based on expert opinion. More recently, Deep Learning approaches have been shown to provide improved performance in detection. However, obtaining sufficient labelled weather radar data for flying animals to build learning-based models is time-consuming and labor-intensive. To address the challenge of data labelling, we propose a self-supervised learning method for detecting animal movement. In our proposed method, we pre-train our model on a large dataset with noisy labels produced by a threshold approach. The key advantage is that the pre-trained dataset size is limited only by the number of radar images available. We then fine-tune the model on a small human-labelled dataset. Our experiments on Australian weather radar data for waterbird segmentation show that the proposed method outperforms the current state-of-the art approach by 43.53% in the dice co-efficient statistic.
"I think this is the most disruptive technology": Exploring Sentiments of ChatGPT Early Adopters using Twitter Data
Dec 12, 2022



Abstract:Large language models have recently attracted significant attention due to their impressive performance on a variety of tasks. ChatGPT developed by OpenAI is one such implementation of a large, pre-trained language model that has gained immense popularity among early adopters, where certain users go to the extent of characterizing it as a disruptive technology in many domains. Understanding such early adopters' sentiments is important because it can provide insights into the potential success or failure of the technology, as well as its strengths and weaknesses. In this paper, we conduct a mixed-method study using 10,732 tweets from early ChatGPT users. We first use topic modelling to identify the main topics and then perform an in-depth qualitative sentiment analysis of each topic. Our results show that the majority of the early adopters have expressed overwhelmingly positive sentiments related to topics such as Disruptions to software development, Entertainment and exercising creativity. Only a limited percentage of users expressed concerns about issues such as the potential for misuse of ChatGPT, especially regarding topics such as Impact on educational aspects. We discuss these findings by providing specific examples for each topic and then detail implications related to addressing these concerns for both researchers and users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge