Motolani Olarinre
Beyond the Mud: Datasets and Benchmarks for Computer Vision in Off-Road Racing
Feb 12, 2024



Abstract:Despite significant progress in optical character recognition (OCR) and computer vision systems, robustly recognizing text and identifying people in images taken in unconstrained \emph{in-the-wild} environments remain an ongoing challenge. However, such obstacles must be overcome in practical applications of vision systems, such as identifying racers in photos taken during off-road racing events. To this end, we introduce two new challenging real-world datasets - the off-road motorcycle Racer Number Dataset (RND) and the Muddy Racer re-iDentification Dataset (MUDD) - to highlight the shortcomings of current methods and drive advances in OCR and person re-identification (ReID) under extreme conditions. These two datasets feature over 6,300 images taken during off-road competitions which exhibit a variety of factors that undermine even modern vision systems, namely mud, complex poses, and motion blur. We establish benchmark performance on both datasets using state-of-the-art models. Off-the-shelf models transfer poorly, reaching only 15% end-to-end (E2E) F1 score on text spotting, and 33% rank-1 accuracy on ReID. Fine-tuning yields major improvements, bringing model performance to 53% F1 score for E2E text spotting and 79% rank-1 accuracy on ReID, but still falls short of good performance. Our analysis exposes open problems in real-world OCR and ReID that necessitate domain-targeted techniques. With these datasets and analysis of model limitations, we aim to foster innovations in handling real-world conditions like mud and complex poses to drive progress in robust computer vision. All data was sourced from PerformancePhoto.co, a website used by professional motorsports photographers, racers, and fans. The top-performing text spotting and ReID models are deployed on this platform to power real-time race photo search.
MUDD: A New Re-Identification Dataset with Efficient Annotation for Off-Road Racers in Extreme Conditions
Nov 14, 2023



Abstract:Re-identifying individuals in unconstrained environments remains an open challenge in computer vision. We introduce the Muddy Racer re-IDentification Dataset (MUDD), the first large-scale benchmark for matching identities of motorcycle racers during off-road competitions. MUDD exhibits heavy mud occlusion, motion blurring, complex poses, and extreme lighting conditions previously unseen in existing re-id datasets. We present an annotation methodology incorporating auxiliary information that reduced labeling time by over 65%. We establish benchmark performance using state-of-the-art re-id models including OSNet and ResNet-50. Without fine-tuning, the best models achieve only 33% Rank-1 accuracy. Fine-tuning on MUDD boosts results to 79% Rank-1, but significant room for improvement remains. We analyze the impact of real-world factors including mud, pose, lighting, and more. Our work exposes open problems in re-identifying individuals under extreme conditions. We hope MUDD serves as a diverse and challenging benchmark to spur progress in robust re-id, especially for computer vision applications in emerging sports analytics. All code and data can be found at https://github.com/JacobTyo/MUDD.
Reading Between the Mud: A Challenging Motorcycle Racer Number Dataset
Nov 14, 2023
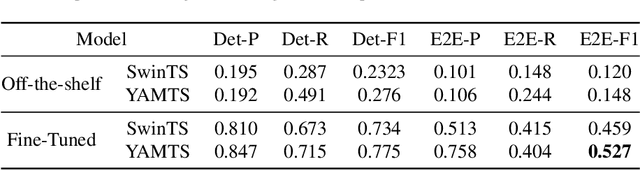

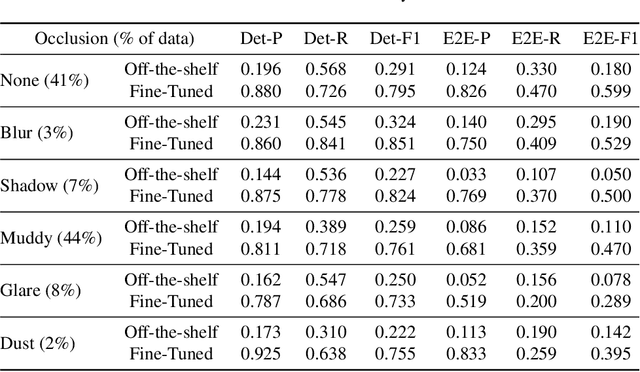
Abstract:This paper introduces the off-road motorcycle Racer number Dataset (RnD), a new challenging dataset for optical character recognition (OCR) research. RnD contains 2,411 images from professional motorsports photographers that depict motorcycle racers in off-road competitions. The images exhibit a wide variety of factors that make OCR difficult, including mud occlusions, motion blur, non-standard fonts, glare, complex backgrounds, etc. The dataset has 5,578 manually annotated bounding boxes around visible motorcycle numbers, along with transcribed digits and letters. Our experiments benchmark leading OCR algorithms and reveal an end-to-end F1 score of only 0.527 on RnD, even after fine-tuning. Analysis of performance on different occlusion types shows mud as the primary challenge, degrading accuracy substantially compared to normal conditions. But the models struggle with other factors including glare, blur, shadows, and dust. Analysis exposes substantial room for improvement and highlights failure cases of existing models. RnD represents a valuable new benchmark to drive innovation in real-world OCR capabilities. The authors hope the community will build upon this dataset and baseline experiments to make progress on the open problem of robustly recognizing text in unconstrained natural environments. The dataset is available at https://github.com/JacobTyo/SwinTextSpotter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge