Morteza Romoozi
An Innovative Framework for Breast Cancer Detection Using Pyramid Adaptive Atrous Convolution, Transformer Integration, and Multi-Scale Feature Fusion
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women worldwide, and its accurate and timely diagnosis plays a critical role in improving treatment outcomes. This thesis presents an innovative framework for detecting malignant masses in mammographic images by integrating the Pyramid Adaptive Atrous Convolution (PAAC) and Transformer architectures. The proposed approach utilizes Multi-Scale Feature Fusion to enhance the extraction of features from benign and malignant tissues and combines Dice Loss and Focal Loss functions to improve the model's learning process, effectively reducing errors in binary breast cancer classification and achieving high accuracy and efficiency. In this study, a comprehensive dataset of breast cancer images from INbreast, MIAS, and DDSM was preprocessed through data augmentation and contrast enhancement and resized to 227x227 pixels for model training. Leveraging the Transformer's ability to manage long-range dependencies with Self-Attention mechanisms, the proposed model achieved high accuracy in detecting cancerous masses, outperforming foundational models such as BreastNet, DeepMammo, Multi-Scale CNN, Swin-Unet, and SegFormer. The final evaluation results for the proposed model include an accuracy of 98.5\%, sensitivity of 97.8\%, specificity of 96.3\%, F1-score of 98.2\%, and overall precision of 97.9\%. These metrics demonstrate a significant improvement over traditional methods and confirm the model's effectiveness in identifying cancerous masses in complex scenarios and large datasets. This model shows potential as a reliable and efficient tool for breast cancer diagnosis and can be effectively integrated into medical diagnostic systems.
A Fuzzy Realistic Mobility Model For Ad hoc Networks
Nov 29, 2011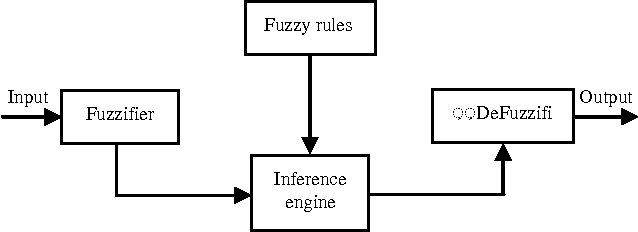
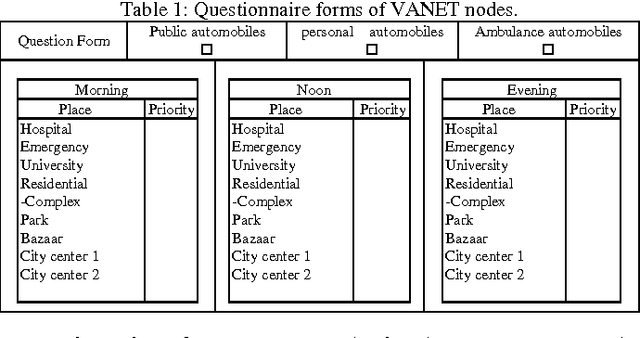
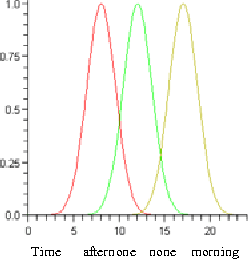
Abstract:Realistic mobility models can demonstrate more precise evaluation results because their parameters are closer to the reality. In this paper a realistic Fuzzy Mobility Model has been proposed. This model has rules which is changeable depending on nodes and environment conditions. This model is more complete and precise than the other mobility models and this is the advantage of this model. After simulation, it was found out that not only considering nodes movement as being imprecise (fuzzy) has a positive effects on most of ad hoc network parameters, but also, more importantly as they are closer to the real world condition, they can have a more positive effect on the implementation of ad hoc network protocols.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge