Moritz Sackmann
Conditional Prediction by Simulation for Automated Driving
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Modular automated driving systems commonly handle prediction and planning as sequential, separate tasks, thereby prohibiting cooperative maneuvers. To enable cooperative planning, this work introduces a prediction model that models the conditional dependencies between trajectories. For this, predictions are generated by a microscopic traffic simulation, with the individual traffic participants being controlled by a realistic behavior model trained via Adversarial Inverse Reinforcement Learning. By assuming various candidate trajectories for the automated vehicle, we generate predictions conditioned on each of them. Furthermore, our approach allows the candidate trajectories to adapt dynamically during the prediction rollout. Several example scenarios are available at https://conditionalpredictionbysimulation.github.io/.
Distribution Preserving Multiple Hypotheses Prediction for Uncertainty Modeling
Oct 06, 2021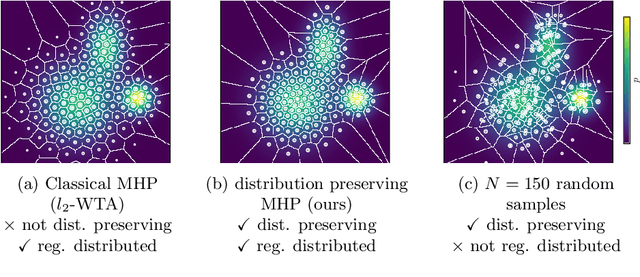
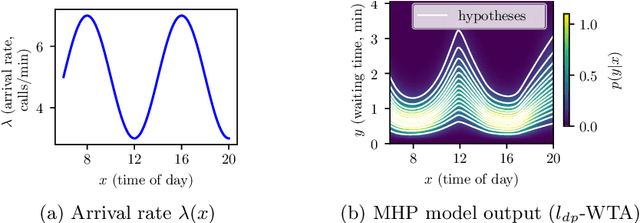
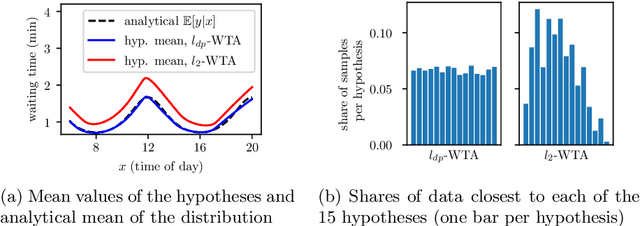
Abstract:Many supervised machine learning tasks, such as future state prediction in dynamical systems, require precise modeling of a forecast's uncertainty. The Multiple Hypotheses Prediction (MHP) approach addresses this problem by providing several hypotheses that represent possible outcomes. Unfortunately, with the common $l_2$ loss function, these hypotheses do not preserve the data distribution's characteristics. We propose an alternative loss for distribution preserving MHP and review relevant theorems supporting our claims. Furthermore, we empirically show that our approach yields more representative hypotheses on a synthetic and a real-world motion prediction data set. The outputs of the proposed method can directly be used in sampling-based Monte-Carlo methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge