Moray Kidd
A Tensor-based Structural Health Monitoring Approach for Aeroservoelastic Systems
Dec 11, 2018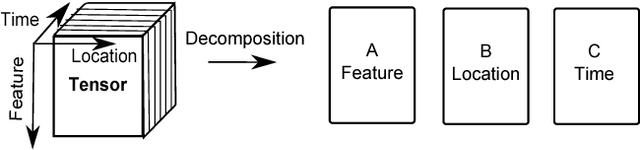
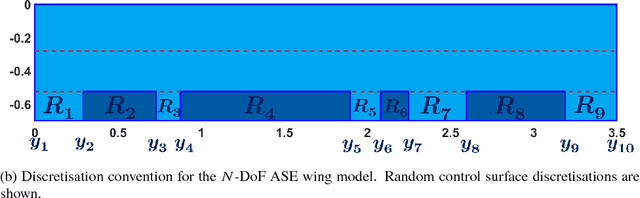
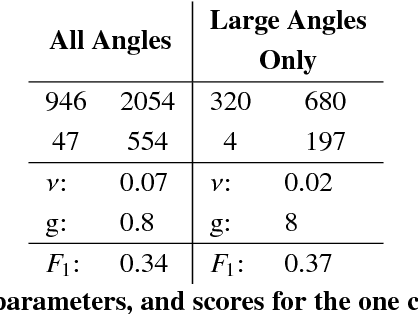
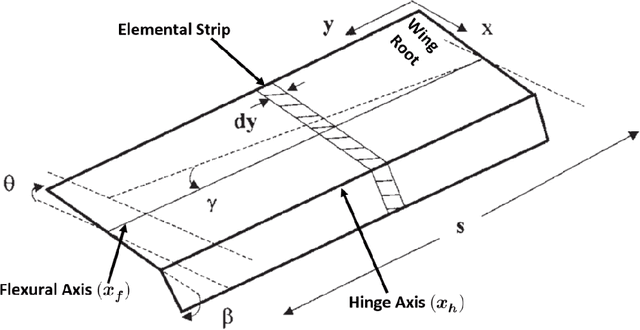
Abstract:Structural health monitoring is a condition-based field of study utilised to monitor infrastructure, via sensing systems. It is therefore used in the field of aerospace engineering to assist in monitoring the health of aerospace structures. A difficulty however is that in structural health monitoring the data input is usually from sensor arrays, which results in data which are highly redundant and correlated, an area in which traditional two-way matrix approaches have had difficulty in deconstructing and interpreting. Newer methods involving tensor analysis allow us to analyse this multi-way structural data in a coherent manner. In our approach, we demonstrate the usefulness of tensor-based learning coupled with for damage detection, on a novel $N$-DoF Lagrangian aeroservoelastic model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge