Mooho Song
An Analysis under a Unified Fomulation of Learning Algorithms with Output Constraints
Jun 03, 2024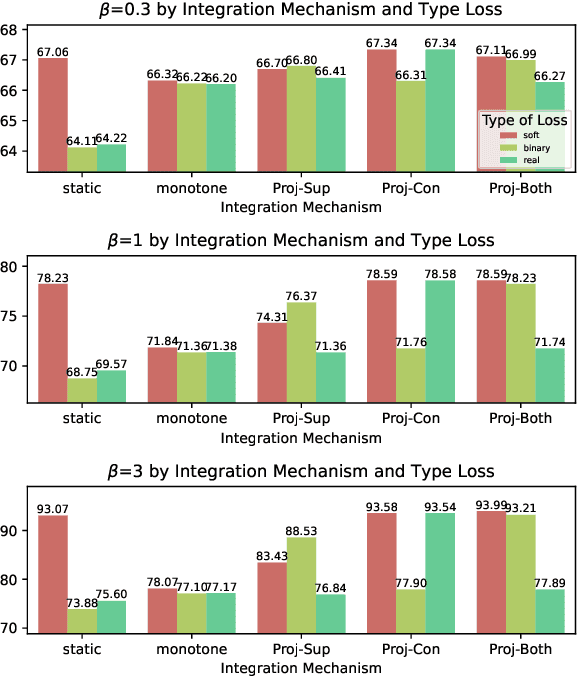
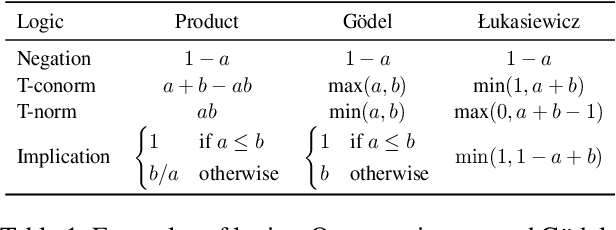
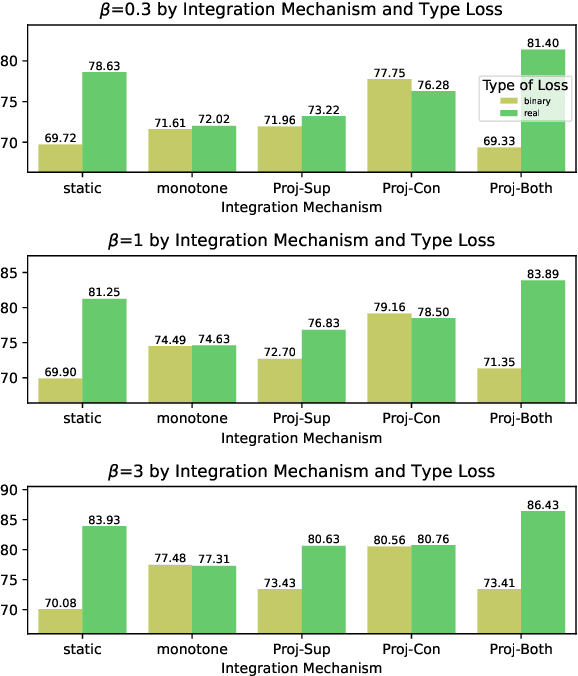
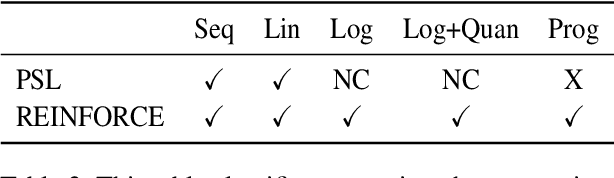
Abstract:Neural networks (NN) perform well in diverse tasks, but sometimes produce nonsensical results to humans. Most NN models "solely" learn from (input, output) pairs, occasionally conflicting with human knowledge. Many studies indicate injecting human knowledge by reducing output constraints during training can improve model performance and reduce constraint violations. While there have been several attempts to compare different existing algorithms under the same programming framework, nonetheless, there has been no previous work that categorizes learning algorithms with output constraints in a unified manner. Our contributions are as follows: (1) We categorize the previous studies based on three axes: type of constraint loss used (e.g. probabilistic soft logic, REINFORCE), exploration strategy of constraint-violating examples, and integration mechanism of learning signals from main task and constraint. (2) We propose new algorithms to integrate the information of main task and constraint injection, inspired by continual-learning algorithms. (3) Furthermore, we propose the $H\beta$-score as a metric for considering the main task metric and constraint violation simultaneously. To provide a thorough analysis, we examine all the algorithms on three NLP tasks: natural language inference (NLI), synthetic transduction examples (STE), and semantic role labeling (SRL). We explore and reveal the key factors of various algorithms associated with achieving high $H\beta$-scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge