Montse Pardàs
Hybridnet for depth estimation and semantic segmentation
Feb 09, 2024



Abstract:Semantic segmentation and depth estimation are two important tasks in the area of image processing. Traditionally, these two tasks are addressed in an independent manner. However, for those applications where geometric and semantic information is required, such as robotics or autonomous navigation,depth or semantic segmentation alone are not sufficient. In this paper, depth estimation and semantic segmentation are addressed together from a single input image through a hybrid convolutional network. Different from the state of the art methods where features are extracted by a sole feature extraction network for both tasks, the proposed HybridNet improves the features extraction by separating the relevant features for one task from those which are relevant for both. Experimental results demonstrate that HybridNet results are comparable with the state of the art methods, as well as the single task methods that HybridNet is based on.
Color Deconvolution applied to Domain Adaptation in HER2 histopathological images
May 12, 2023



Abstract:Breast cancer early detection is crucial for improving patient outcomes. The Institut Catal\`a de la Salut (ICS) has launched the DigiPatICS project to develop and implement artificial intelligence algorithms to assist with the diagnosis of cancer. In this paper, we propose a new approach for facing the color normalization problem in HER2-stained histopathological images of breast cancer tissue, posed as an style transfer problem. We combine the Color Deconvolution technique with the Pix2Pix GAN network to present a novel approach to correct the color variations between different HER2 stain brands. Our approach focuses on maintaining the HER2 score of the cells in the transformed images, which is crucial for the HER2 analysis. Results demonstrate that our final model outperforms the state-of-the-art image style transfer methods in maintaining the cell classes in the transformed images and is as effective as them in generating realistic images.
Graph based Dynamic Segmentation of Generic Objects in 3D
Apr 17, 2019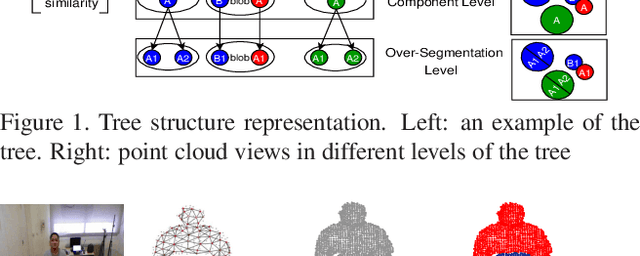
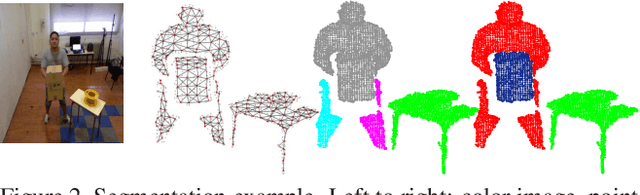
Abstract:We propose a novel 3D segmentation method for RBGD stream data to deal with 3D object segmentation task in a generic scenario with frequent object interactions. It mainly contributes in two aspects, while being generic and not requiring initialization: firstly, a novel tree structure representation for the point cloud of the scene is proposed. Then, a dynamic manangement mechanism for connected component splits and merges exploits the tree structure representation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge