Montse Civit
Semantic Parsing based on Verbal Subcategorization
Jun 29, 2000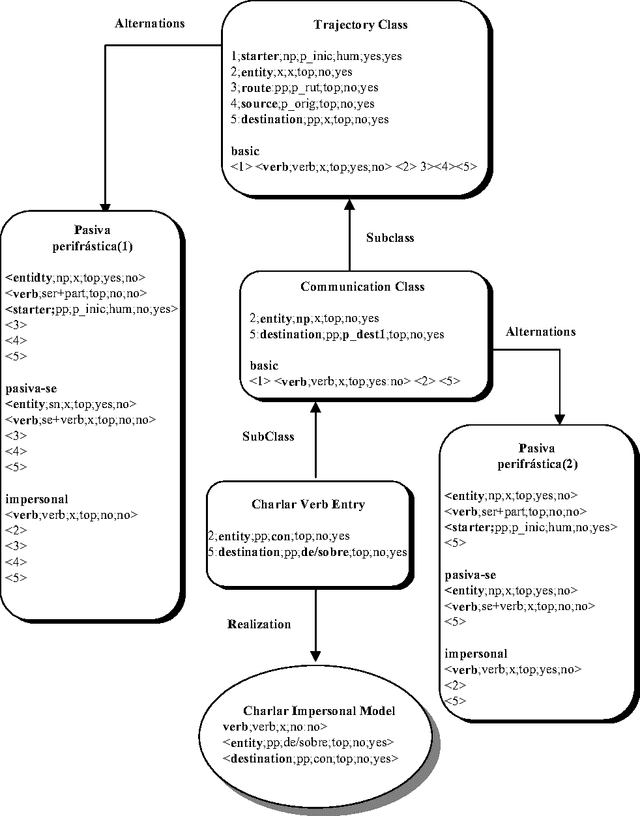

Abstract:The aim of this work is to explore new methodologies on Semantic Parsing for unrestricted texts. Our approach follows the current trends in Information Extraction (IE) and is based on the application of a verbal subcategorization lexicon (LEXPIR) by means of complex pattern recognition techniques. LEXPIR is framed on the theoretical model of the verbal subcategorization developed in the Pirapides project.
* 12 pages, extended version of the paper. Spanish version of the paper also available from authors home page
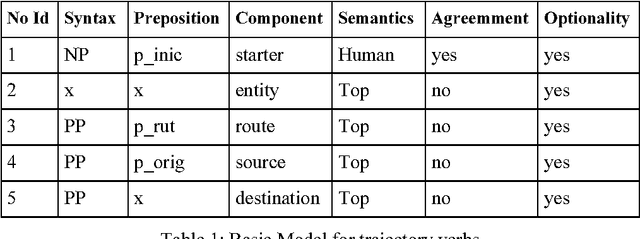
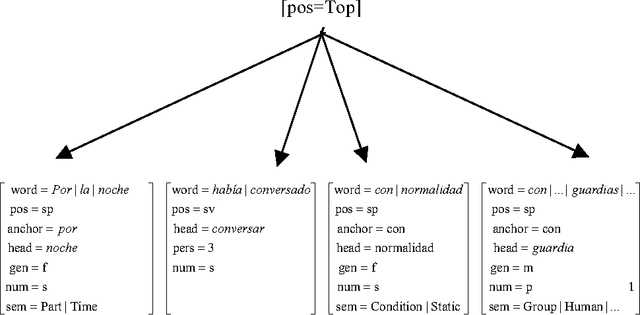
Using a Diathesis Model for Semantic Parsing
Jun 29, 2000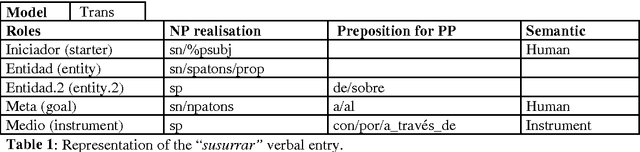
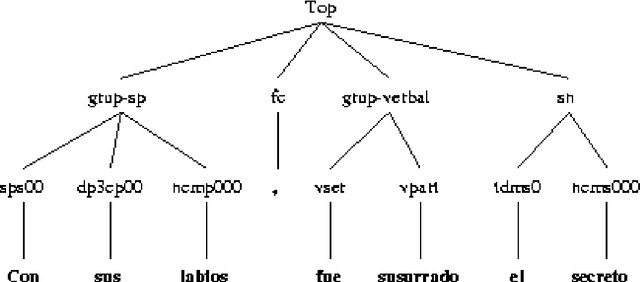
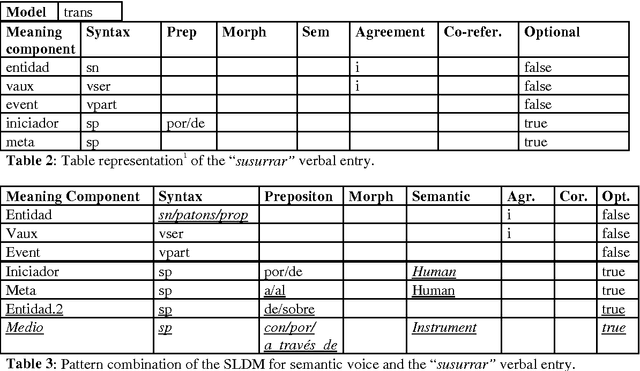
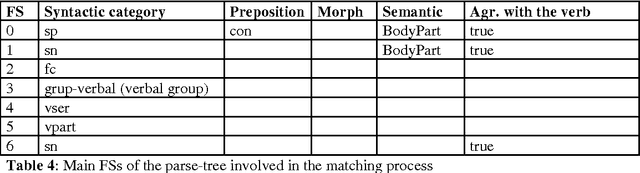
Abstract:This paper presents a semantic parsing approach for unrestricted texts. Semantic parsing is one of the major bottlenecks of Natural Language Understanding (NLU) systems and usually requires building expensive resources not easily portable to other domains. Our approach obtains a case-role analysis, in which the semantic roles of the verb are identified. In order to cover all the possible syntactic realisations of a verb, our system combines their argument structure with a set of general semantic labelled diatheses models. Combining them, the system builds a set of syntactic-semantic patterns with their own role-case representation. Once the patterns are build, we use an approximate tree pattern-matching algorithm to identify the most reliable pattern for a sentence. The pattern matching is performed between the syntactic-semantic patterns and the feature-structure tree representing the morphological, syntactical and semantic information of the analysed sentence. For sentences assigned to the correct model, the semantic parsing system we are presenting identifies correctly more than 73% of possible semantic case-roles.
* 8 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge