Montgomery Gole
Assessing how hyperparameters impact Large Language Models' sarcasm detection performance
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Sarcasm detection is challenging for both humans and machines. This work explores how model characteristics impact sarcasm detection in OpenAI's GPT, and Meta's Llama-2 models, given their strong natural language understanding, and popularity. We evaluate fine-tuned and zero-shot models across various sizes, releases, and hyperparameters. Experiments were conducted on the political and balanced (pol-bal) portion of the popular Self-Annotated Reddit Corpus (SARC2.0) sarcasm dataset. Fine-tuned performance improves monotonically with model size within a model family, while hyperparameter tuning also impacts performance. In the fine-tuning scenario, full precision Llama-2-13b achieves state-of-the-art accuracy and $F_1$-score, both measured at 0.83, comparable to average human performance. In the zero-shot setting, one GPT-4 model achieves competitive performance to prior attempts, yielding an accuracy of 0.70 and an $F_1$-score of 0.75. Furthermore, a model's performance may increase or decline with each release, highlighting the need to reassess performance after each release.
On Sarcasm Detection with OpenAI GPT-based Models
Dec 07, 2023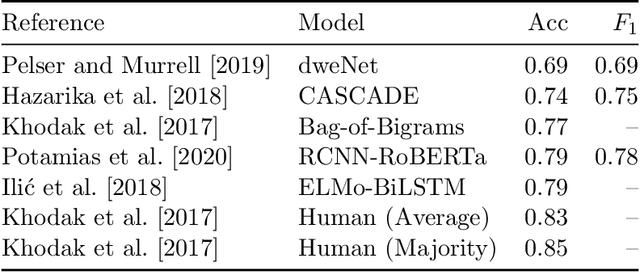

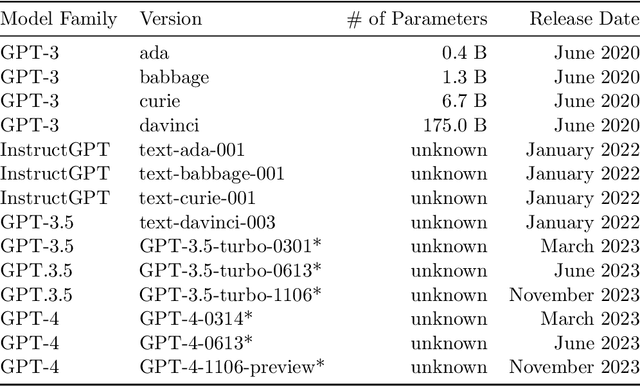
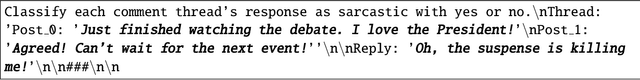
Abstract:Sarcasm is a form of irony that requires readers or listeners to interpret its intended meaning by considering context and social cues. Machine learning classification models have long had difficulty detecting sarcasm due to its social complexity and contradictory nature. This paper explores the applications of the Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT) models, including GPT-3, InstructGPT, GPT-3.5, and GPT-4, in detecting sarcasm in natural language. It tests fine-tuned and zero-shot models of different sizes and releases. The GPT models were tested on the political and balanced (pol-bal) portion of the popular Self-Annotated Reddit Corpus (SARC 2.0) sarcasm dataset. In the fine-tuning case, the largest fine-tuned GPT-3 model achieves accuracy and $F_1$-score of 0.81, outperforming prior models. In the zero-shot case, one of GPT-4 models yields an accuracy of 0.70 and $F_1$-score of 0.75. Other models score lower. Additionally, a model's performance may improve or deteriorate with each release, highlighting the need to reassess performance after each release.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge