Mohammad Tawhid Kawser
Performance Comparison Between VoLTE and non-VoLTE Voice Calls During Mobility in Commercial Deployment: A Drive Test-Based Analysis
Jul 23, 2023
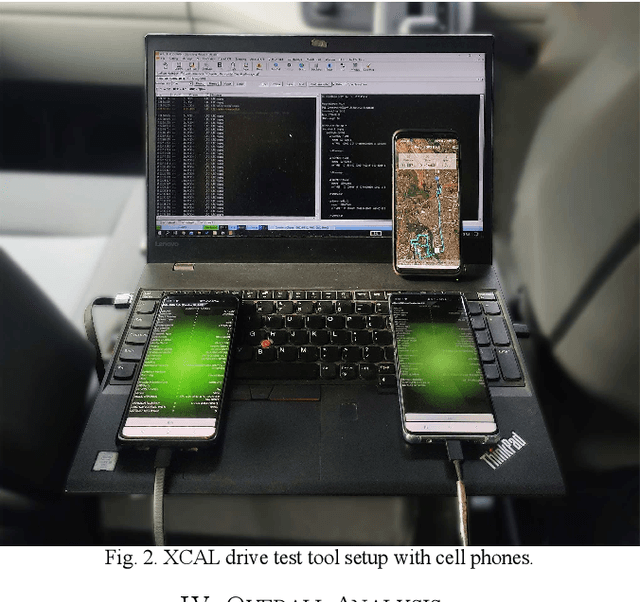
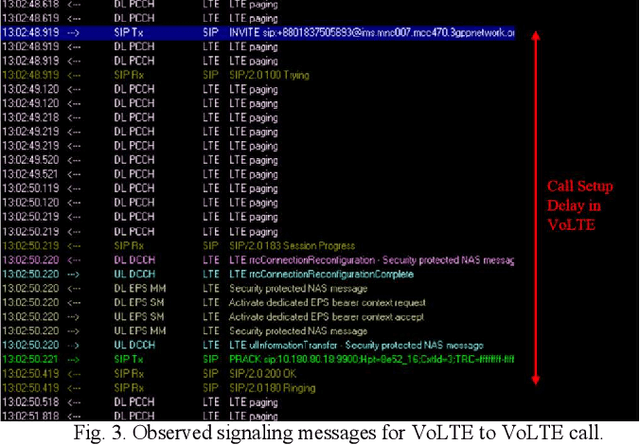
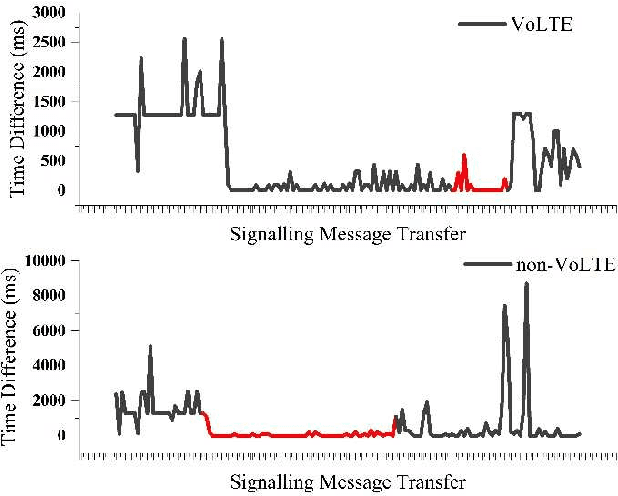
Abstract:The optimization of network performance is vital for the delivery of services using standard cellular technologies for mobile communications. Call setup delay and User Equipment (UE) battery savings significantly influence network performance. Improving these factors is vital for ensuring optimal service delivery. In comparison to traditional circuit-switched voice calls, VoLTE (Voice over LTE) technology offers faster call setup durations and better battery-saving performance. To validate these claims, a drive test was carried out using the XCAL drive test tool to collect real-time network parameter details in VoLTE and non-VoLTE voice calls. The findings highlight the analysis of real-time network characteristics, such as the call setup delay calculation, battery-saving performance, and DRX mechanism. The study contributes to the understanding of network optimization strategies and provides insights for enhancing the quality of service (QoS) in mobile communication networks. Examining VoLTE and non-VoLTE operations, this research highlights the substantial energy savings obtained by VoLTE. Specifically, VoLTE saves approximately 60.76% of energy before the Service Request and approximately 38.97% of energy after the Service Request. Moreover, VoLTE to VoLTE calls have a 72.6% faster call setup delay than non-VoLTE-based LTE to LTE calls, because of fewer signaling messages required. Furthermore, as compared to non-VoLTE to non-VoLTE calls, VoLTE to non-VoLTE calls offer an 18.6% faster call setup delay. These results showcase the performance advantages of VoLTE and reinforce its potential for offering better services in wireless communication networks.
Atmospheric Influence on the Path Loss at High Frequencies for Deployment of 5G Cellular Communication Networks
Jun 02, 2023

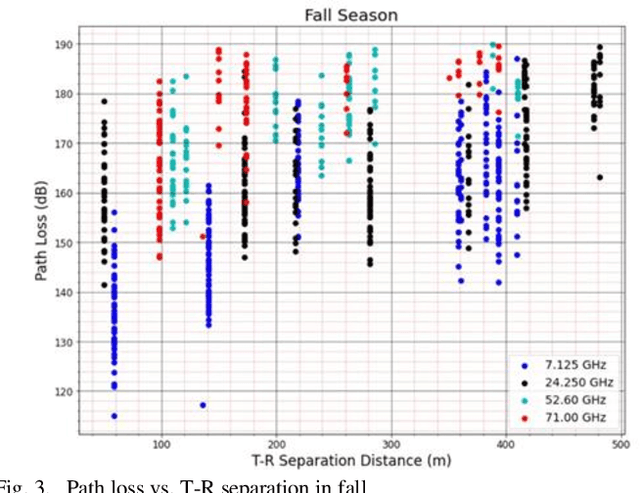

Abstract:Over the past few decades, the development of cellular communication technology has spanned several generations in order to add sophisticated features in the updated versions. Moreover, different high-frequency bands are considered for advanced cellular generations. The presence of updated generations like 4G and 5G is driven by the rising demand for a greater data rate and a better experience for end users. However, because 5G-NR operates at a high frequency and has significant propagation, atmospheric fluctuations like temperature, humidity, and rain rate might result in poorer signal reception, and higher path loss effects unlike the prior generation, which employed frequencies below 6 GHz. This paper makes an attempt to provide a comparative analysis about the influence of different relative atmospheric conditions on 5G cellular communication for various operating frequencies in any urban microcell (UMi) environment maintaining the real outdoor propagation conditions. In addition, the simulation dataset based on environmental factors has been validated by the prediction of path loss using multiple regression techniques. Consequently, this study also aims to address the performance analysis of regression techniques for stable estimations of path loss at high frequencies for different atmospheric conditions for 5G mobile generations due to various possible radio link quality issues and fluctuations in different seasons in South Asia. Furthermore, in comparison to contemporary studies, the Machine Learning models have outperformed in predicting the path loss for the four seasons in South Asian regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge