Mohammad Jalili Torkamani
Boosting Accuracy and Interpretability in Multilingual Hate Speech Detection Through Layer Freezing and Explainable AI
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Sentiment analysis focuses on identifying the emotional polarity expressed in textual data, typically categorized as positive, negative, or neutral. Hate speech detection, on the other hand, aims to recognize content that incites violence, discrimination, or hostility toward individuals or groups based on attributes such as race, gender, sexual orientation, or religion. Both tasks play a critical role in online content moderation by enabling the detection and mitigation of harmful or offensive material, thereby contributing to safer digital environments. In this study, we examine the performance of three transformer-based models: BERT-base-multilingual-cased, RoBERTa-base, and XLM-RoBERTa-base with the first eight layers frozen, for multilingual sentiment analysis and hate speech detection. The evaluation is conducted across five languages: English, Korean, Japanese, Chinese, and French. The models are compared using standard performance metrics, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. To enhance model interpretability and provide deeper insight into prediction behavior, we integrate the Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) framework, which highlights the contribution of individual words to the models decisions. By combining state-of-the-art transformer architectures with explainability techniques, this work aims to improve both the effectiveness and transparency of multilingual sentiment analysis and hate speech detection systems.
Adaptive Edge-Cloud Inference for Speech-to-Action Systems Using ASR and Large Language Models
Dec 18, 2025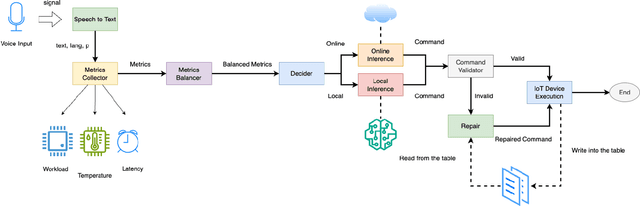
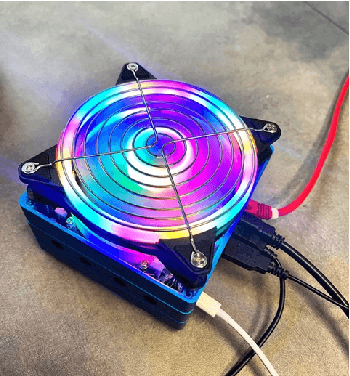

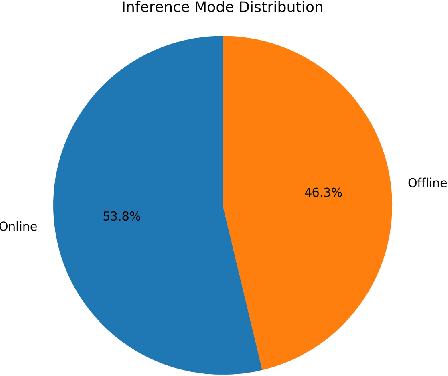
Abstract:Voice-based interaction has emerged as a natural and intuitive modality for controlling IoT devices. However, speech-driven edge devices face a fundamental trade-off between cloud-based solutions, which offer stronger language understanding capabilities at the cost of latency, connectivity dependence, and privacy concerns, and edge-based solutions, which provide low latency and improved privacy but are limited by computational constraints. This paper presents ASTA, an adaptive speech-to-action solution that dynamically routes voice commands between edge and cloud inference to balance performance and system resource utilization. ASTA integrates on-device automatic speech recognition and lightweight offline language-model inference with cloud-based LLM processing, guided by real-time system metrics such as CPU workload, device temperature, and network latency. A metric-aware routing mechanism selects the inference path at runtime, while a rule-based command validation and repair component ensures successful end-to-end command execution. We implemented our solution on an NVIDIA Jetson-based edge platform and evaluated it using a diverse dataset of 80 spoken commands. Experimental results show that ASTA successfully routes all input commands for execution, achieving a balanced distribution between online and offline inference. The system attains an ASR accuracy of 62.5% and generates executable commands without repair for only 47.5% of inputs, highlighting the importance of the repair mechanism in improving robustness. These results suggest that adaptive edge-cloud orchestration is a viable approach for resilient and resource-aware voice-controlled IoT systems.
Simulating a Bias Mitigation Scenario in Large Language Models
Sep 17, 2025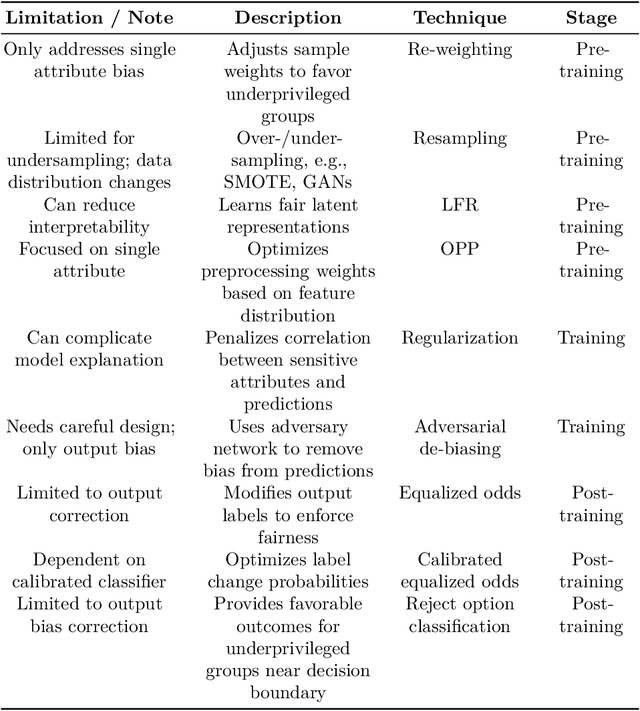
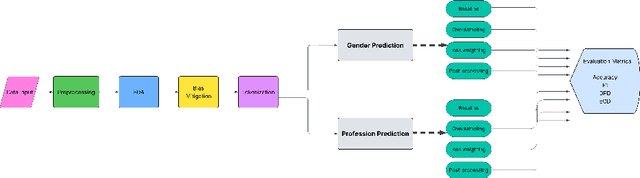
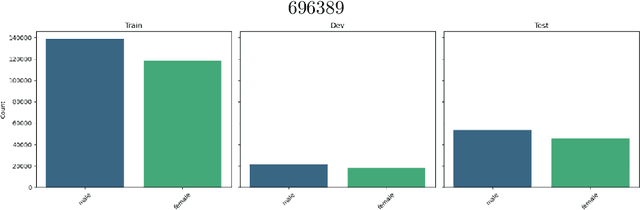
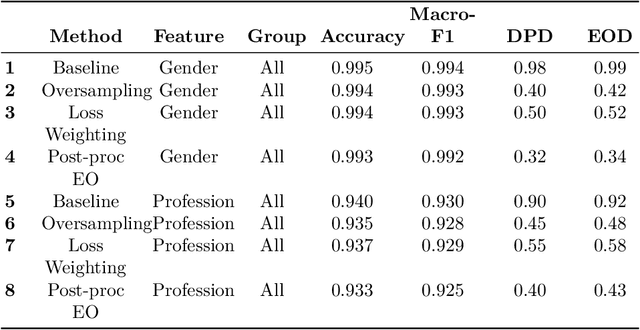
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have fundamentally transformed the field of natural language processing; however, their vulnerability to biases presents a notable obstacle that threatens both fairness and trust. This review offers an extensive analysis of the bias landscape in LLMs, tracing its roots and expressions across various NLP tasks. Biases are classified into implicit and explicit types, with particular attention given to their emergence from data sources, architectural designs, and contextual deployments. This study advances beyond theoretical analysis by implementing a simulation framework designed to evaluate bias mitigation strategies in practice. The framework integrates multiple approaches including data curation, debiasing during model training, and post-hoc output calibration and assesses their impact in controlled experimental settings. In summary, this work not only synthesizes existing knowledge on bias in LLMs but also contributes original empirical validation through simulation of mitigation strategies.
LLM-Driven Adaptive 6G-Ready Wireless Body Area Networks: Survey and Framework
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs) enable continuous monitoring of physiological signals for applications ranging from chronic disease management to emergency response. Recent advances in 6G communications, post-quantum cryptography, and energy harvesting have the potential to enhance WBAN performance. However, integrating these technologies into a unified, adaptive system remains a challenge. This paper surveys some of the most well-known Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) architectures, routing strategies, and security mechanisms, identifying key gaps in adaptability, energy efficiency, and quantum-resistant security. We propose a novel Large Language Model-driven adaptive WBAN framework in which a Large Language Model acts as a cognitive control plane, coordinating routing, physical layer selection, micro-energy harvesting, and post-quantum security in real time. Our review highlights the limitations of current heuristic-based designs and outlines a research agenda for resource-constrained, 6G-ready medical systems. This approach aims to enable ultra-reliable, secure, and self-optimizing WBANs for next-generation mobile health applications.
Kajal: Extracting Grammar of a Source Code Using Large Language Models
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Understanding and extracting the grammar of a domain-specific language (DSL) is crucial for various software engineering tasks; however, manually creating these grammars is time-intensive and error-prone. This paper presents Kajal, a novel approach that automatically infers grammar from DSL code snippets by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) through prompt engineering and few-shot learning. Kajal dynamically constructs input prompts, using contextual information to guide the LLM in generating the corresponding grammars, which are iteratively refined through a feedback-driven approach. Our experiments show that Kajal achieves 60% accuracy with few-shot learning and 45% without it, demonstrating the significant impact of few-shot learning on the tool's effectiveness. This approach offers a promising solution for automating DSL grammar extraction, and future work will explore using smaller, open-source LLMs and testing on larger datasets to further validate Kajal's performance.
ASSERTIFY: Utilizing Large Language Models to Generate Assertions for Production Code
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Production assertions are statements embedded in the code to help developers validate their assumptions about the code. They assist developers in debugging, provide valuable documentation, and enhance code comprehension. Current research in this area primarily focuses on assertion generation for unit tests using techniques, such as static analysis and deep learning. While these techniques have shown promise, they fall short when it comes to generating production assertions, which serve a different purpose. This preprint addresses the gap by introducing Assertify, an automated end-to-end tool that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) and prompt engineering with few-shot learning to generate production assertions. By creating context-rich prompts, the tool emulates the approach developers take when creating production assertions for their code. To evaluate our approach, we compiled a dataset of 2,810 methods by scraping 22 mature Java repositories from GitHub. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of few-shot learning by producing assertions with an average ROUGE-L score of 0.526, indicating reasonably high structural similarity with the assertions written by developers. This research demonstrates the potential of LLMs in automating the generation of production assertions that resemble the original assertions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge