Mohammad Abdullah Al Mamun
Classification of Short Segment Pediatric Heart Sounds Based on a Transformer-Based Convolutional Neural Network
Mar 30, 2024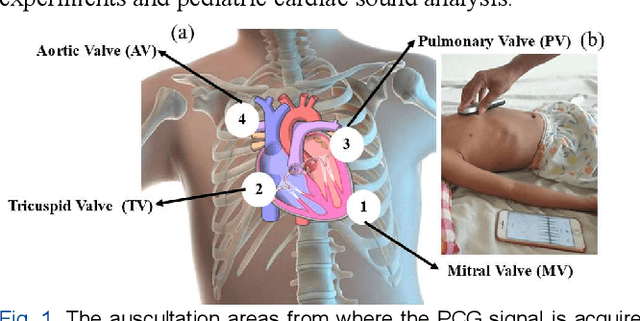
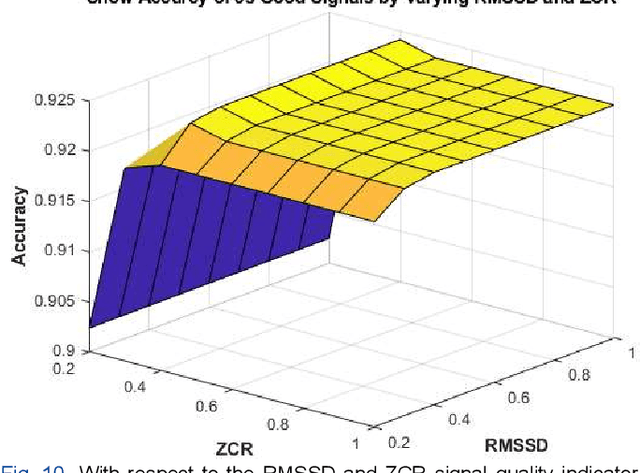
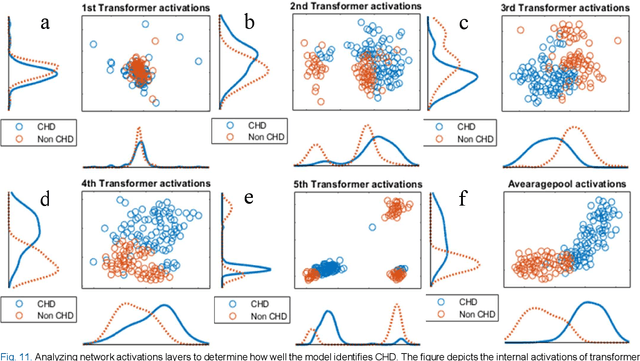
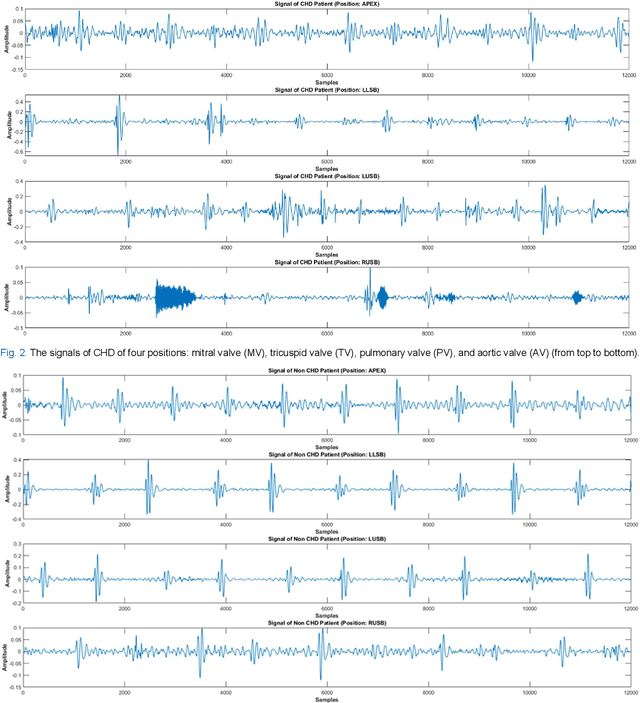
Abstract:Congenital anomalies arising as a result of a defect in the structure of the heart and great vessels are known as congenital heart diseases or CHDs. A PCG can provide essential details about the mechanical conduction system of the heart and point out specific patterns linked to different kinds of CHD. This study aims to investigate the minimum signal duration required for the automatic classification of heart sounds. This study also investigated the optimum signal quality assessment indicator (Root Mean Square of Successive Differences) RMSSD and (Zero Crossings Rate) ZCR value. Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs) based feature is used as an input to build a Transformer-Based residual one-dimensional convolutional neural network, which is then used for classifying the heart sound. The study showed that 0.4 is the ideal threshold for getting suitable signals for the RMSSD and ZCR indicators. Moreover, a minimum signal length of 5s is required for effective heart sound classification. It also shows that a shorter signal (3 s heart sound) does not have enough information to categorize heart sounds accurately, and the longer signal (15 s heart sound) may contain more noise. The best accuracy, 93.69%, is obtained for the 5s signal to distinguish the heart sound.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge