Mohamed Debbagh
Predictive Pattern Recognition Techniques Towards Spatiotemporal Representation of Plant Growth in Simulated and Controlled Environments: A Comprehensive Review
Dec 13, 2024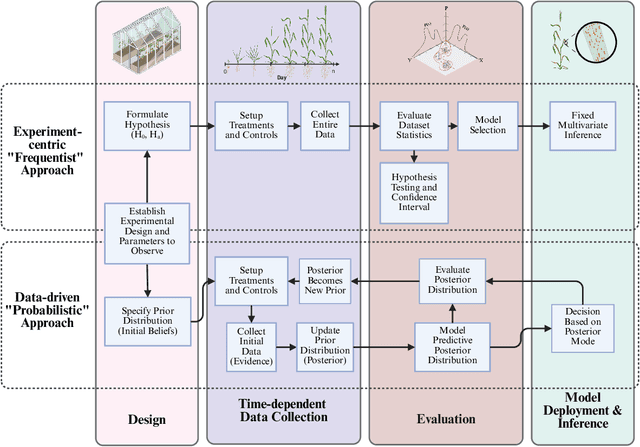
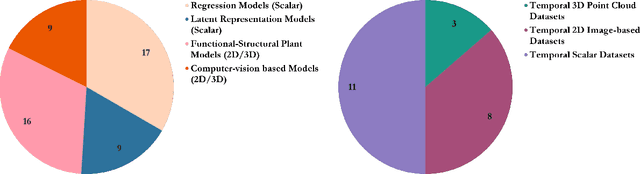
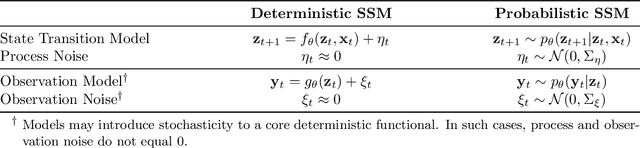
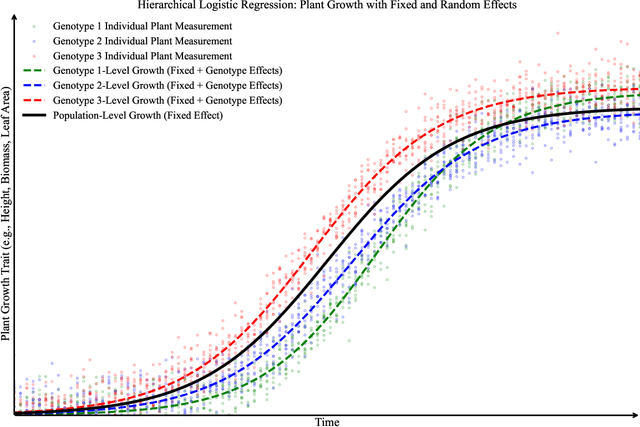
Abstract:Accurate predictions and representations of plant growth patterns in simulated and controlled environments are important for addressing various challenges in plant phenomics research. This review explores various works on state-of-the-art predictive pattern recognition techniques, focusing on the spatiotemporal modeling of plant traits and the integration of dynamic environmental interactions. We provide a comprehensive examination of deterministic, probabilistic, and generative modeling approaches, emphasizing their applications in high-throughput phenotyping and simulation-based plant growth forecasting. Key topics include regressions and neural network-based representation models for the task of forecasting, limitations of existing experiment-based deterministic approaches, and the need for dynamic frameworks that incorporate uncertainty and evolving environmental feedback. This review surveys advances in 2D and 3D structured data representations through functional-structural plant models and conditional generative models. We offer a perspective on opportunities for future works, emphasizing the integration of domain-specific knowledge to data-driven methods, improvements to available datasets, and the implementation of these techniques toward real-world applications.
Generative Plant Growth Simulation from Sequence-Informed Environmental Conditions
May 23, 2024Abstract:A plant growth simulation can be characterized as a reconstructed visual representation of a plant or plant system. The phenotypic characteristics and plant structures are controlled by the scene environment and other contextual attributes. Considering the temporal dependencies and compounding effects of various factors on growth trajectories, we formulate a probabilistic approach to the simulation task by solving a frame synthesis and pattern recognition problem. We introduce a Sequence-Informed Plant Growth Simulation framework (SI-PGS) that employs a conditional generative model to implicitly learn a distribution of possible plant representations within a dynamic scene from a fusion of low dimensional temporal sensor and context data. Methods such as controlled latent sampling and recurrent output connections are used to improve coherence in plant structures between frames of predictions. In this work, we demonstrate that SI-PGS is able to capture temporal dependencies and continuously generate realistic frames of a plant scene.
Neural Radiance Fields : A Review and Some Recent Developments
Apr 30, 2023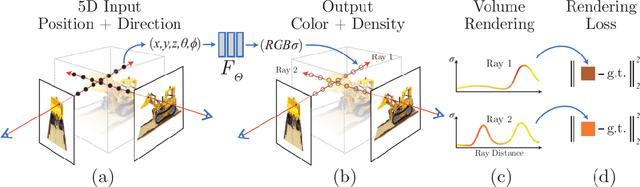
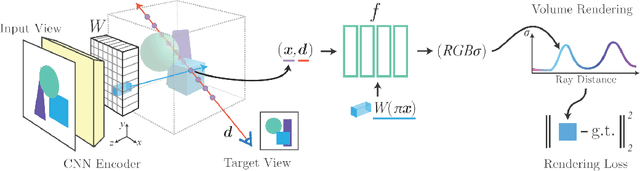
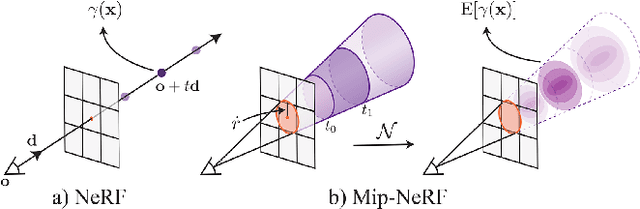
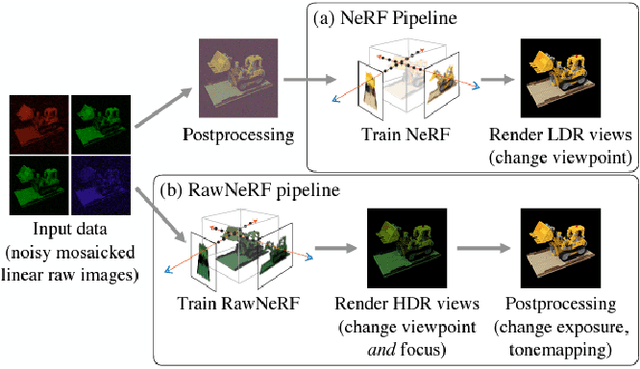
Abstract:Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) is a framework that represents a 3D scene in the weights of a fully connected neural network, known as the Multi-Layer Perception(MLP). The method was introduced for the task of novel view synthesis and is able to achieve state-of-the-art photorealistic image renderings from a given continuous viewpoint. NeRFs have become a popular field of research as recent developments have been made that expand the performance and capabilities of the base framework. Recent developments include methods that require less images to train the model for view synthesis as well as methods that are able to generate views from unconstrained and dynamic scene representations.
Learning Structured Output Representations from Attributes using Deep Conditional Generative Models
Apr 30, 2023



Abstract:Structured output representation is a generative task explored in computer vision that often times requires the mapping of low dimensional features to high dimensional structured outputs. Losses in complex spatial information in deterministic approaches such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) lead to uncertainties and ambiguous structures within a single output representation. A probabilistic approach through deep Conditional Generative Models (CGM) is presented by Sohn et al. in which a particular model known as the Conditional Variational Auto-encoder (CVAE) is introduced and explored. While the original paper focuses on the task of image segmentation, this paper adopts the CVAE framework for the task of controlled output representation through attributes. This approach allows us to learn a disentangled multimodal prior distribution, resulting in more controlled and robust approach to sample generation. In this work we recreate the CVAE architecture and train it on images conditioned on various attributes obtained from two image datasets; the Large-scale CelebFaces Attributes (CelebA) dataset and the Caltech-UCSD Birds (CUB-200-2011) dataset. We attempt to generate new faces with distinct attributes such as hair color and glasses, as well as different bird species samples with various attributes. We further introduce strategies for improving generalized sample generation by applying a weighted term to the variational lower bound.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge