Mohamad Farzan Sabahi
Assessing the applicability of common performance metrics for real-world infrared small-target detection
Jan 10, 2023Abstract:Infrared small target detection (IRSTD) is a challenging task in computer vision. During the last two decades, researchers' efforts are devoted to improving detection ability of IRSTDs. Despite the huge improvement in designing new algorithms, lack of extensive investigation of the evaluation metrics are evident. Therefore, in this paper, a systematic approach is utilized to: First, investigate the evaluation ability of current metrics; Second, propose new evaluation metrics to address shortcoming of common metrics. To this end, after carefully reviewing the problem, the required conditions to have a successful detection are analyzed. Then, the shortcomings of current evaluation metrics which include pre-thresholding as well as post-thresholding metrics are determined. Based on the requirements of real-world systems, new metrics are proposed. Finally, the proposed metrics are used to compare and evaluate four well-known small infrared target detection algorithms. The results show that new metrics are consistent with qualitative results.
Small Infrared Target Detection Using Absolute Directional Mean Difference Algorithm
Oct 07, 2018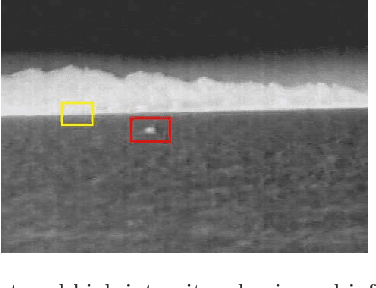
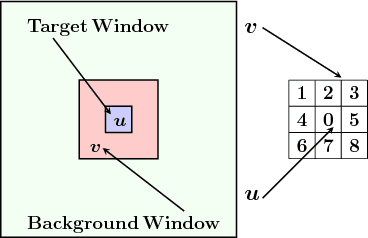
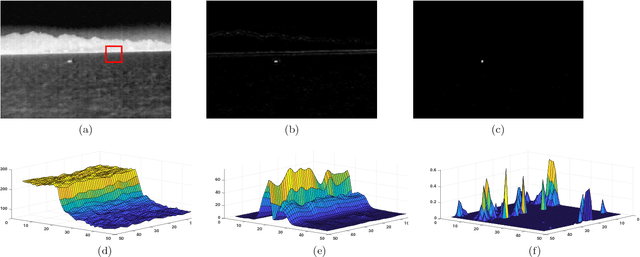

Abstract:Infrared small target detection in an infrared search and track (IRST) system is a challenging task. This situation becomes more complicated when high gray-intensity structural backgrounds appear in the field of view (FoV) of the infrared seeker. While the majority of the infrared small target detection algorithms neglect directional information, in this paper, a directional approach is presented to suppress structural backgrounds and develop more effective detection algorithm. To this end, a similar concept to the average absolute gray difference (AAGD) is utilized to construct a directional small target detection algorithm called absolute directional mean difference (ADMD). Also, an efficient implementation procedure is presented for the proposed algorithm. The proposed algorithm effectively enhances the target area and eliminates background clutter. Simulation results on real infrared images prove the significant effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge