Mohamad Abdi
Automatic Mapping of Anatomical Landmarks from Free-Text Using Large Language Models: Insights from Llama-2
Oct 17, 2024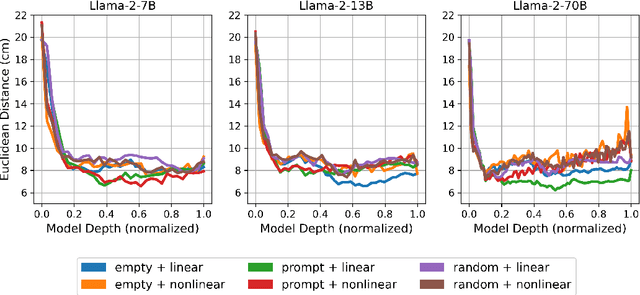
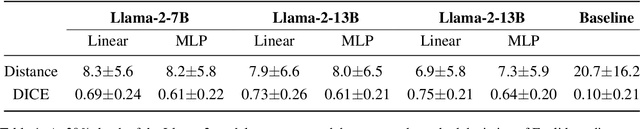
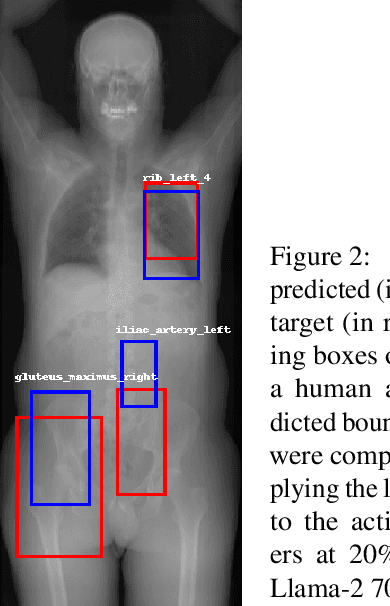
Abstract:Anatomical landmarks are vital in medical imaging for navigation and anomaly detection. Modern large language models (LLMs), like Llama-2, offer promise for automating the mapping of these landmarks in free-text radiology reports to corresponding positions in image data. Recent studies propose LLMs may develop coherent representations of generative processes. Motivated by these insights, we investigated whether LLMs accurately represent the spatial positions of anatomical landmarks. Through experiments with Llama-2 models, we found that they can linearly represent anatomical landmarks in space with considerable robustness to different prompts. These results underscore the potential of LLMs to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of medical imaging workflows.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge