Mitchell Plyler
SENTRA: Selected-Next-Token Transformer for LLM Text Detection
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:LLMs are becoming increasingly capable and widespread. Consequently, the potential and reality of their misuse is also growing. In this work, we address the problem of detecting LLM-generated text that is not explicitly declared as such. We present a novel, general-purpose, and supervised LLM text detector, SElected-Next-Token tRAnsformer (SENTRA). SENTRA is a Transformer-based encoder leveraging selected-next-token-probability sequences and utilizing contrastive pre-training on large amounts of unlabeled data. Our experiments on three popular public datasets across 24 domains of text demonstrate SENTRA is a general-purpose classifier that significantly outperforms popular baselines in the out-of-domain setting.
Iterative Counterfactual Data Augmentation
Feb 25, 2025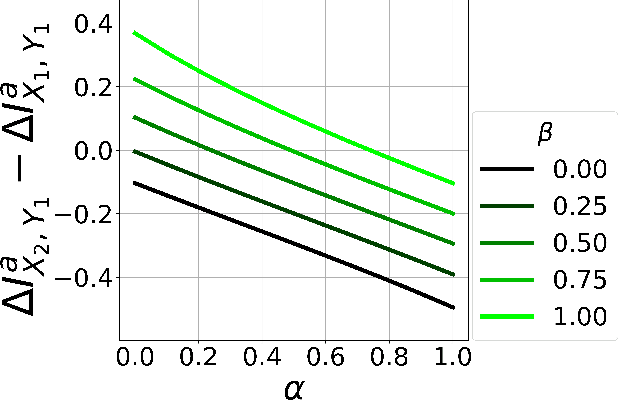
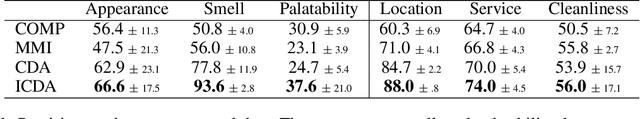
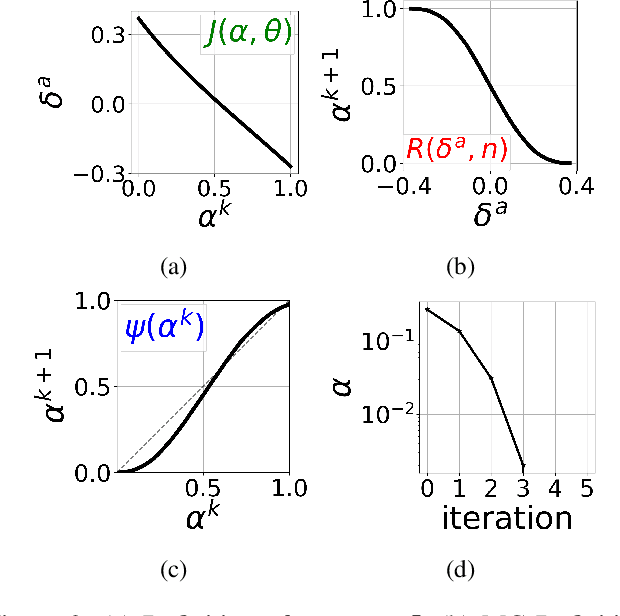
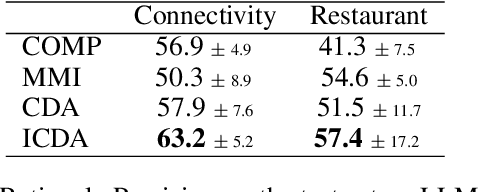
Abstract:Counterfactual data augmentation (CDA) is a method for controlling information or biases in training datasets by generating a complementary dataset with typically opposing biases. Prior work often either relies on hand-crafted rules or algorithmic CDA methods which can leave unwanted information in the augmented dataset. In this work, we show iterative CDA (ICDA) with initial, high-noise interventions can converge to a state with significantly lower noise. Our ICDA procedure produces a dataset where one target signal in the training dataset maintains high mutual information with a corresponding label and the information of spurious signals are reduced. We show training on the augmented datasets produces rationales on documents that better align with human annotation. Our experiments include six human produced datasets and two large-language model generated datasets.
Making a Difference One Rationale at a Time
Jan 13, 2022



Abstract:Rationales, snippets of extracted text that explain an inference, have emerged as a popular framework for interpretable natural language processing (NLP). Rationale models typically consist of two cooperating modules: a selector and a classifier with the goal of maximizing the mutual information (MMI) between the "selected" text and the document label. Despite their promises, MMI-based methods often pick up on spurious text patterns and result in models with nonsensical behaviors. In this work, we investigate whether counterfactual data augmentation (CDA), without human assistance, can improve the performance of the selector by lowering the mutual information between spurious signals and the document label. Our counterfactuals are produced in an unsupervised fashion using class-dependent generative models. From an information theoretic lens, we derive properties of the unaugmented dataset for which our CDA approach would succeed. The effectiveness of CDA is empirically evaluated by comparing against several baselines including an improved MMI-based rationale schema on two multi aspect datasets. Our results show that CDA produces rationales that better capture the signal of interest.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge