Mitchell G. Newberry
Evolutionary forces in language change
Aug 02, 2016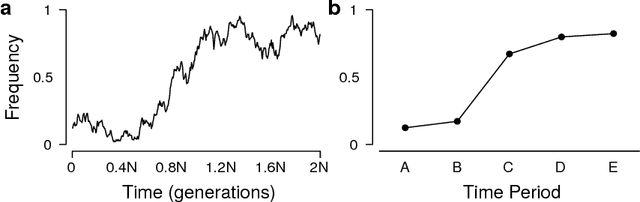
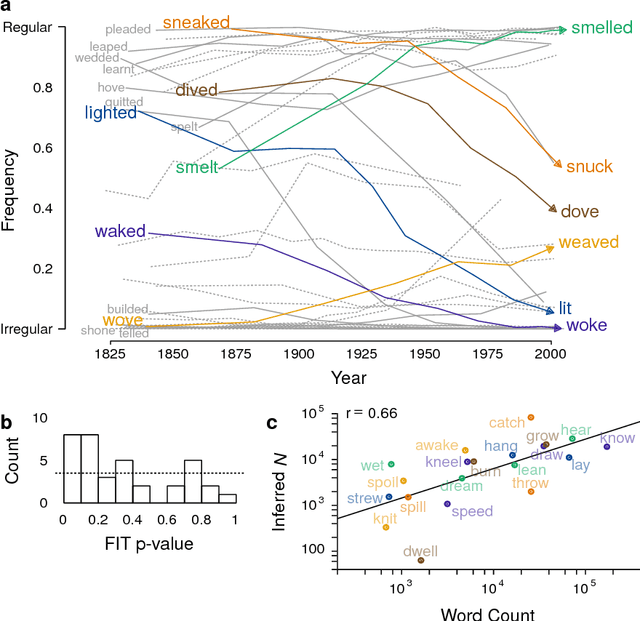
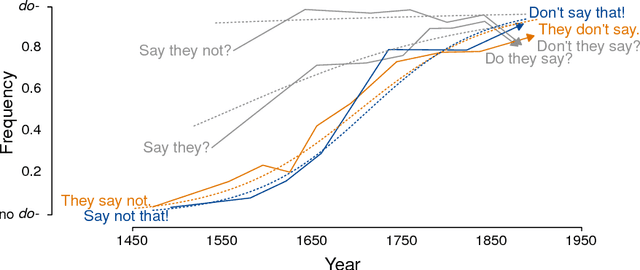
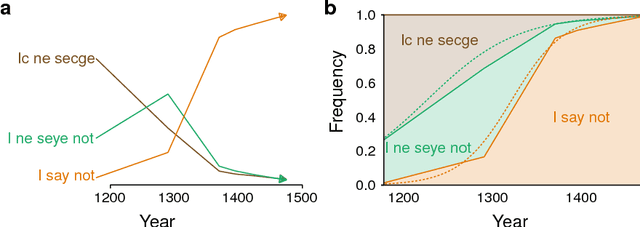
Abstract:Languages and genes are both transmitted from generation to generation, with opportunity for differential reproduction and survivorship of forms. Here we apply a rigorous inference framework, drawn from population genetics, to distinguish between two broad mechanisms of language change: drift and selection. Drift is change that results from stochasticity in transmission and it may occur in the absence of any intrinsic difference between linguistic forms; whereas selection is truly an evolutionary force arising from intrinsic differences -- for example, when one form is preferred by members of the population. Using large corpora of parsed texts spanning the 12th century to the 21st century, we analyze three examples of grammatical changes in English: the regularization of past-tense verbs, the rise of the periphrastic `do', and syntactic variation in verbal negation. We show that we can reject stochastic drift in favor of a selective force driving some of these language changes, but not others. The strength of drift depends on a word's frequency, and so drift provides an alternative explanation for why some words are more prone to change than others. Our results suggest an important role for stochasticity in language change, and they provide a null model against which selective theories of language evolution must be compared.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge