Mitchell A. Nahmias
Noise Analysis of Photonic Modulator Neurons
Jul 17, 2019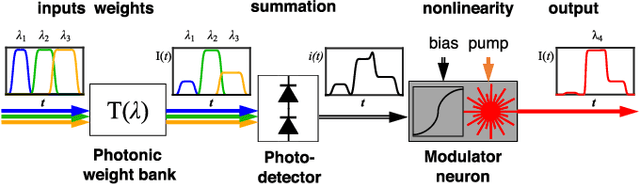
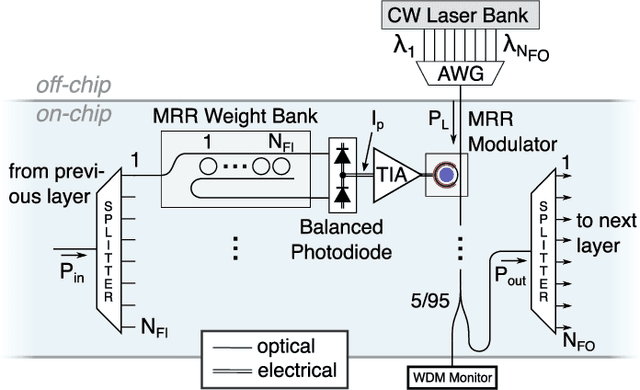
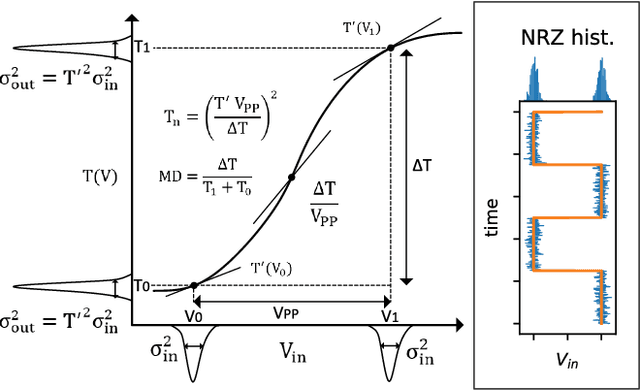
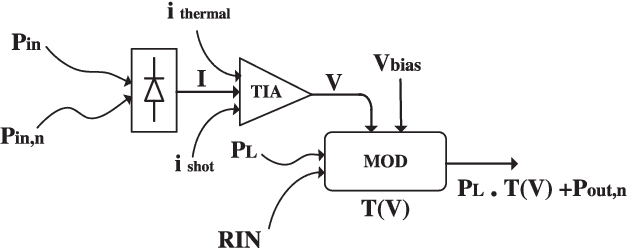
Abstract:Neuromorphic photonics relies on efficiently emulating analog neural networks at high speeds. Prior work showed that transducing signals from the optical to the electrical domain and back with transimpedance gain was an efficient approach to implementing analog photonic neurons and scalable networks. Here, we examine modulator-based photonic neuron circuits with passive and active transimpedance gains, with special attention to the sources of noise propagation. We find that a modulator nonlinear transfer function can suppress noise, which is necessary to avoid noise propagation in hardware neural networks. In addition, while efficient modulators can reduce power for an individual neuron, signal-to-noise ratios must be traded off with power consumption at a system level. Active transimpedance amplifiers may help relax this tradeoff for conventional p-n junction silicon photonic modulators, but a passive transimpedance circuit is sufficient when very efficient modulators (i.e. low C and low V-pi) are employed.
Neuromorphic Silicon Photonic Networks
Jun 12, 2017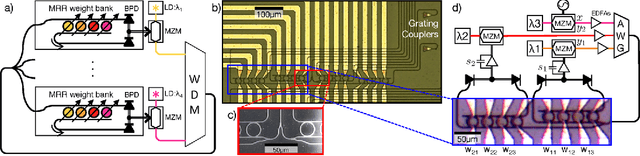
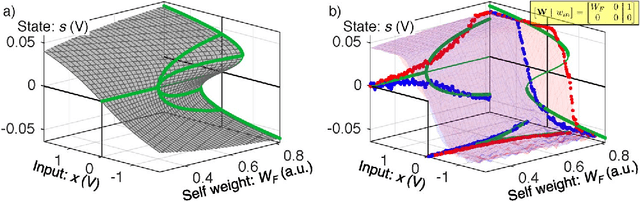
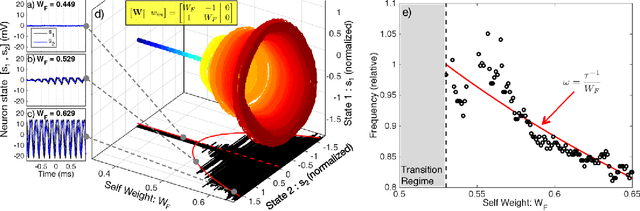
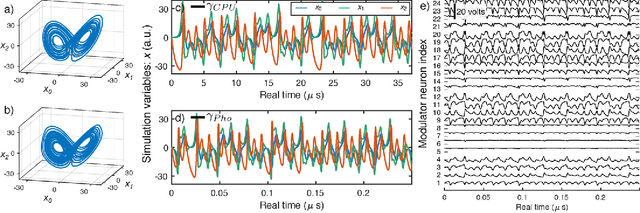
Abstract:Photonic systems for high-performance information processing have attracted renewed interest. Neuromorphic silicon photonics has the potential to integrate processing functions that vastly exceed the capabilities of electronics. We report first observations of a recurrent silicon photonic neural network, in which connections are configured by microring weight banks. A mathematical isomorphism between the silicon photonic circuit and a continuous neural network model is demonstrated through dynamical bifurcation analysis. Exploiting this isomorphism, a simulated 24-node silicon photonic neural network is programmed using "neural compiler" to solve a differential system emulation task. A 294-fold acceleration against a conventional benchmark is predicted. We also propose and derive power consumption analysis for modulator-class neurons that, as opposed to laser-class neurons, are compatible with silicon photonic platforms. At increased scale, Neuromorphic silicon photonics could access new regimes of ultrafast information processing for radio, control, and scientific computing.
* 12 pages, 4 figures, accepted in Scientific Reports
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge