Miroslav Purkrabek
BBoxMaskPose v2: Expanding Mutual Conditioning to 3D
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Most 2D human pose estimation benchmarks are nearly saturated, with the exception of crowded scenes. We introduce PMPose, a top-down 2D pose estimator that incorporates the probabilistic formulation and the mask-conditioning. PMPose improves crowded pose estimation without sacrificing performance on standard scenes. Building on this, we present BBoxMaskPose v2 (BMPv2) integrating PMPose and an enhanced SAM-based mask refinement module. BMPv2 surpasses state-of-the-art by 1.5 average precision (AP) points on COCO and 6 AP points on OCHuman, becoming the first method to exceed 50 AP on OCHuman. We demonstrate that BMP's 2D prompting of 3D model improves 3D pose estimation in crowded scenes and that advances in 2D pose quality directly benefit 3D estimation. Results on the new OCHuman-Pose dataset show that multi-person performance is more affected by pose prediction accuracy than by detection. The code, models, and data are available on https://MiraPurkrabek.github.io/BBox-Mask-Pose/.
SAM-pose2seg: Pose-Guided Human Instance Segmentation in Crowds
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Segment Anything (SAM) provides an unprecedented foundation for human segmentation, but may struggle under occlusion, where keypoints may be partially or fully invisible. We adapt SAM 2.1 for pose-guided segmentation with minimal encoder modifications, retaining its strong generalization. Using a fine-tuning strategy called PoseMaskRefine, we incorporate pose keypoints with high visibility into the iterative correction process originally employed by SAM, yielding improved robustness and accuracy across multiple datasets. During inference, we simplify prompting by selecting only the three keypoints with the highest visibility. This strategy reduces sensitivity to common errors, such as missing body parts or misclassified clothing, and allows accurate mask prediction from as few as a single keypoint. Our results demonstrate that pose-guided fine-tuning of SAM enables effective, occlusion-aware human segmentation while preserving the generalization capabilities of the original model. The code and pretrained models will be available at https://mirapurkrabek.github.io/BBox-Mask-Pose/.
BLANKET: Anonymizing Faces in Infant Video Recordings
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:Ensuring the ethical use of video data involving human subjects, particularly infants, requires robust anonymization methods. We propose BLANKET (Baby-face Landmark-preserving ANonymization with Keypoint dEtection consisTency), a novel approach designed to anonymize infant faces in video recordings while preserving essential facial attributes. Our method comprises two stages. First, a new random face, compatible with the original identity, is generated via inpainting using a diffusion model. Second, the new identity is seamlessly incorporated into each video frame through temporally consistent face swapping with authentic expression transfer. The method is evaluated on a dataset of short video recordings of babies and is compared to the popular anonymization method, DeepPrivacy2. Key metrics assessed include the level of de-identification, preservation of facial attributes, impact on human pose estimation (as an example of a downstream task), and presence of artifacts. Both methods alter the identity, and our method outperforms DeepPrivacy2 in all other respects. The code is available as an easy-to-use anonymization demo at https://github.com/ctu-vras/blanket-infant-face-anonym.
* Project website: https://github.com/ctu-vras/blanket-infant-face-anonym
Human Pose-Constrained UV Map Estimation
Jan 15, 2025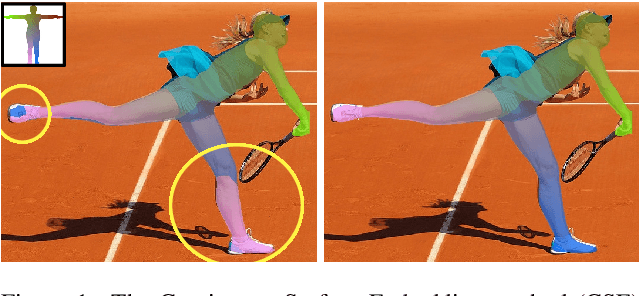
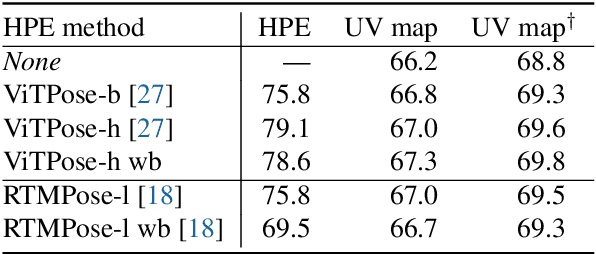

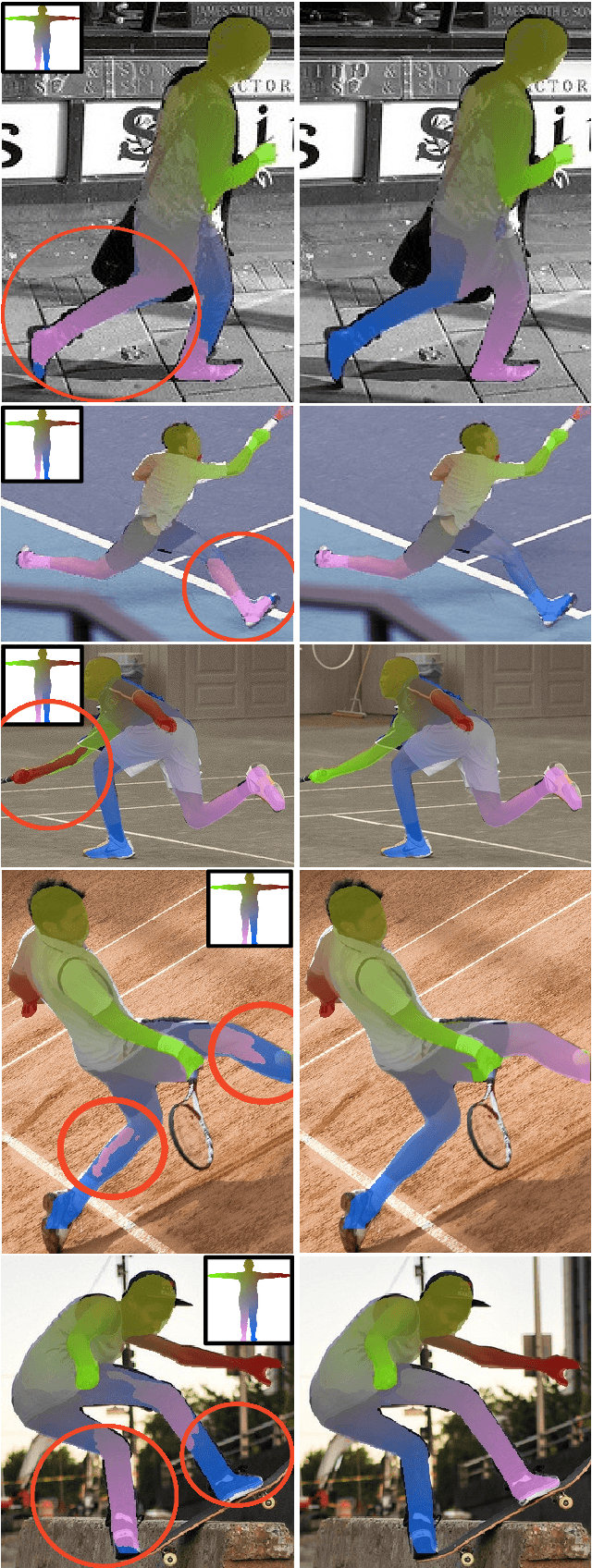
Abstract:UV map estimation is used in computer vision for detailed analysis of human posture or activity. Previous methods assign pixels to body model vertices by comparing pixel descriptors independently, without enforcing global coherence or plausibility in the UV map. We propose Pose-Constrained Continuous Surface Embeddings (PC-CSE), which integrates estimated 2D human pose into the pixel-to-vertex assignment process. The pose provides global anatomical constraints, ensuring that UV maps remain coherent while preserving local precision. Evaluation on DensePose COCO demonstrates consistent improvement, regardless of the chosen 2D human pose model. Whole-body poses offer better constraints by incorporating additional details about the hands and feet. Conditioning UV maps with human pose reduces invalid mappings and enhances anatomical plausibility. In addition, we highlight inconsistencies in the ground-truth annotations.
ProbPose: A Probabilistic Approach to 2D Human Pose Estimation
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Current Human Pose Estimation methods have achieved significant improvements. However, state-of-the-art models ignore out-of-image keypoints and use uncalibrated heatmaps as keypoint location representations. To address these limitations, we propose ProbPose, which predicts for each keypoint: a calibrated probability of keypoint presence at each location in the activation window, the probability of being outside of it, and its predicted visibility. To address the lack of evaluation protocols for out-of-image keypoints, we introduce the CropCOCO dataset and the Extended OKS (Ex-OKS) metric, which extends OKS to out-of-image points. Tested on COCO, CropCOCO, and OCHuman, ProbPose shows significant gains in out-of-image keypoint localization while also improving in-image localization through data augmentation. Additionally, the model improves robustness along the edges of the bounding box and offers better flexibility in keypoint evaluation. The code and models are available on https://mirapurkrabek.github.io/ProbPose/ for research purposes.
Detection, Pose Estimation and Segmentation for Multiple Bodies: Closing the Virtuous Circle
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Human pose estimation methods work well on separated people but struggle with multi-body scenarios. Recent work has addressed this problem by conditioning pose estimation with detected bounding boxes or bottom-up-estimated poses. Unfortunately, all of these approaches overlooked segmentation masks and their connection to estimated keypoints. We condition pose estimation model by segmentation masks instead of bounding boxes to improve instance separation. This improves top-down pose estimation in multi-body scenarios but does not fix detection errors. Consequently, we develop BBox-Mask-Pose (BMP), integrating detection, segmentation and pose estimation into self-improving feedback loop. We adapt detector and pose estimation model for conditioning by instance masks and use Segment Anything as pose-to-mask model to close the circle. With only small models, BMP is superior to top-down methods on OCHuman dataset and to detector-free methods on COCO dataset, combining the best from both approaches and matching state of art performance in both settings. Code is available on https://mirapurkrabek.github.io/BBox-Mask-Pose.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge