Mirko Hu
Simplex2Vec embeddings for community detection in simplicial complexes
Jun 21, 2019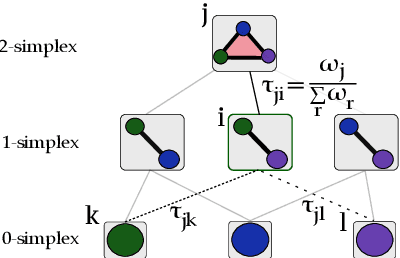
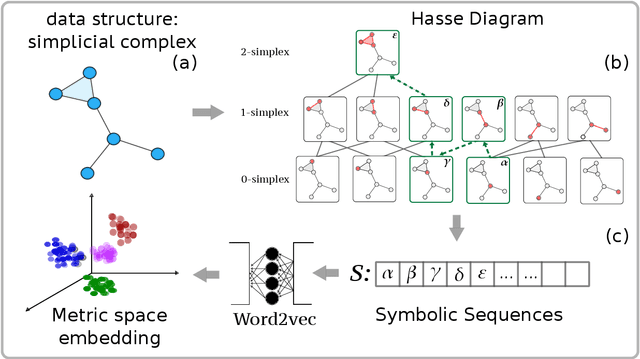
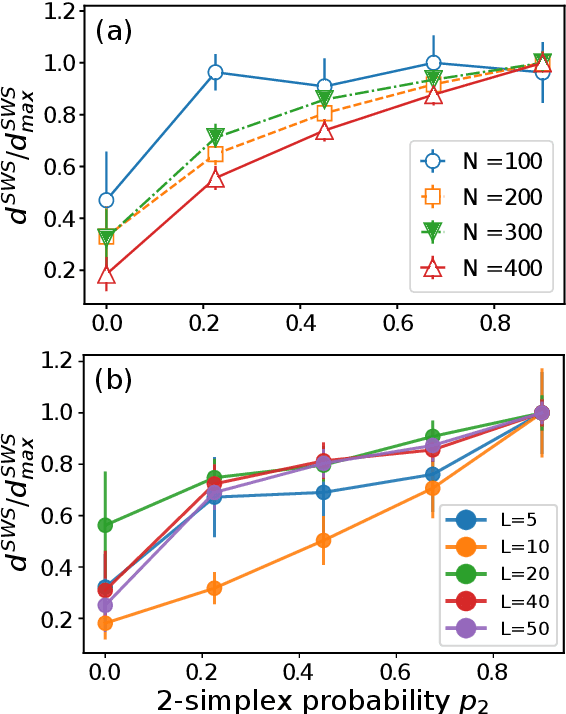
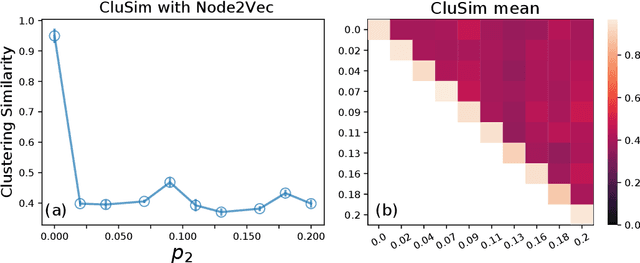
Abstract:Topological representations are rapidly becoming a popular way to capture and encode higher-order interactions in complex systems. They have found applications in disciplines as different as cancer genomics, brain function, and computational social science, in representing both descriptive features of data and inference models. While intense research has focused on the connectivity and homological features of topological representations, surprisingly scarce attention has been given to the investigation of the community structures of simplicial complexes. To this end, we adopt recent advances in symbolic embeddings to compute and visualize the community structures of simplicial complexes. We first investigate the stability properties of embedding obtained for synthetic simplicial complexes to the presence of higher order interactions. We then focus on complexes arising from social and brain functional data and show how higher order interactions can be leveraged to improve clustering detection and assess the effect of higher order interaction on individual nodes. We conclude delineating limitations and directions for extension of this work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge