Minxue Pan
A Bug or a Suggestion? An Automatic Way to Label Issues
Sep 03, 2019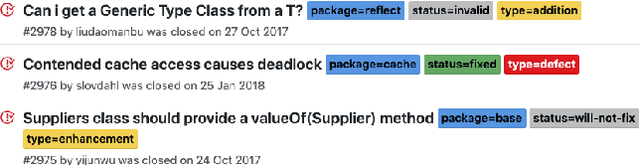
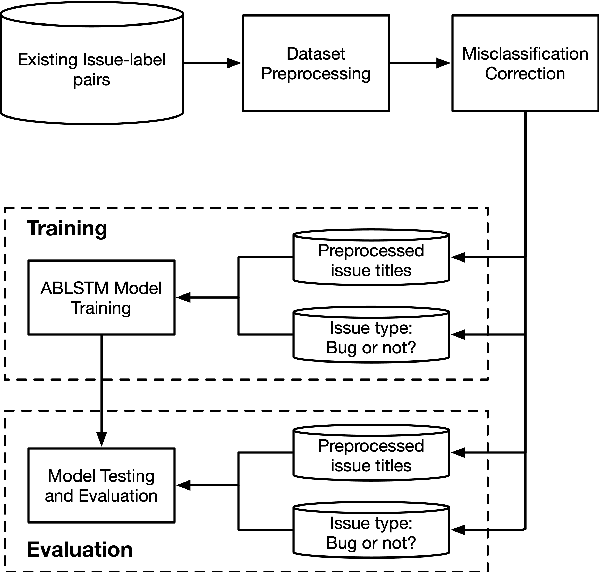
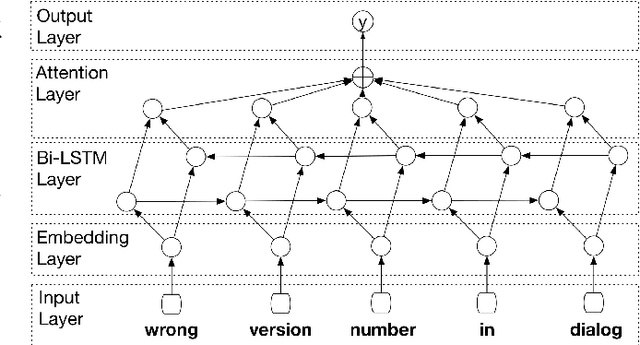
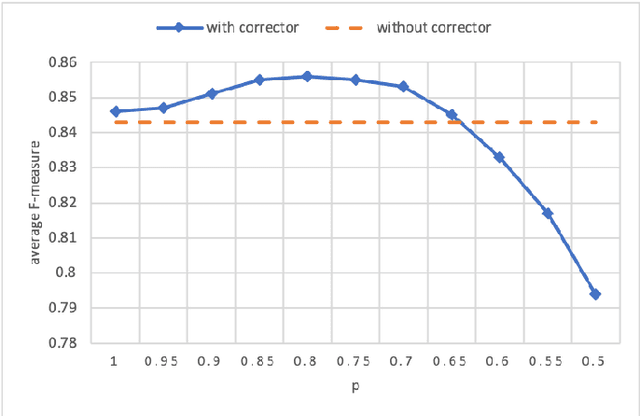
Abstract:More and more users and developers are using Issue Tracking Systems (ITSs) to report issues, including bugs, feature requests, enhancement suggestions, etc. Different information, however, is gathered from users when issues are reported on different ITSs, which presents considerable challenges for issue classification tools to work effectively across the ITSs. Besides, bugs often take higher priority when it comes to classifying the issues, while existing approaches to issue classification seldom focus on distinguishing bugs and the other non-bug issues, leading to suboptimal accuracy in bug identification. In this paper, we propose a deep learning-based approach to automatically identify bug-reporting issues across various ITSs. The approach implements the k-NN algorithm to detect and correct misclassifications in data extracted from the ITSs, and trains an attention-based bi-directional long short-term memory (ABLSTM) network using a dataset of over 1.2 million labelled issues to identify bug reports. Experimental evaluation shows that our approach achieved an F-measure of 85.6\% in distinguishing bugs and other issues, significantly outperforming the other benchmark and state-of-the-art approaches examined in the experiment.
PI-REC: Progressive Image Reconstruction Network With Edge and Color Domain
Mar 25, 2019



Abstract:We propose a universal image reconstruction method to represent detailed images purely from binary sparse edge and flat color domain. Inspired by the procedures of painting, our framework, based on generative adversarial network, consists of three phases: Imitation Phase aims at initializing networks, followed by Generating Phase to reconstruct preliminary images. Moreover, Refinement Phase is utilized to fine-tune preliminary images into final outputs with details. This framework allows our model generating abundant high frequency details from sparse input information. We also explore the defects of disentangling style latent space implicitly from images, and demonstrate that explicit color domain in our model performs better on controllability and interpretability. In our experiments, we achieve outstanding results on reconstructing realistic images and translating hand drawn drafts into satisfactory paintings. Besides, within the domain of edge-to-image translation, our model PI-REC outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods on evaluations of realism and accuracy, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge