Minoo Shayaninasab
Multi-Modal Emotion Recognition by Text, Speech and Video Using Pretrained Transformers
Feb 11, 2024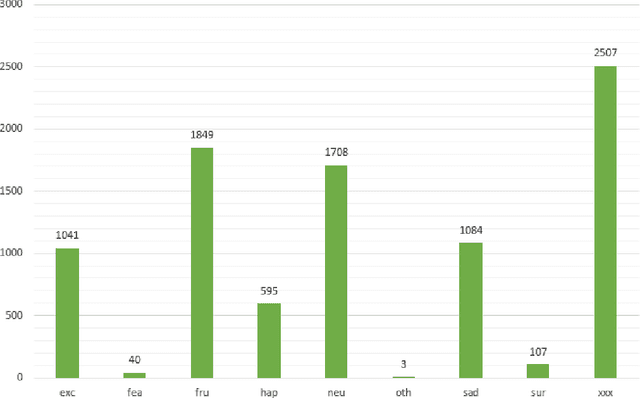
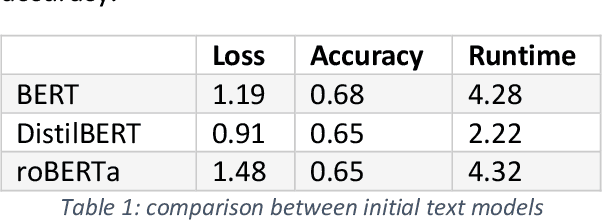
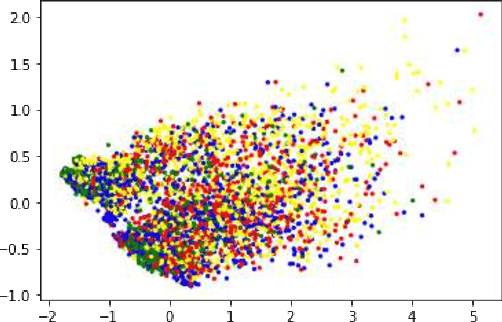
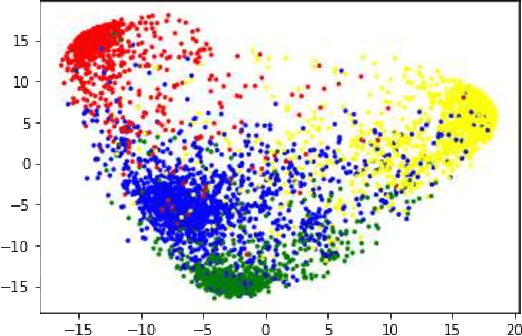
Abstract:Due to the complex nature of human emotions and the diversity of emotion representation methods in humans, emotion recognition is a challenging field. In this research, three input modalities, namely text, audio (speech), and video, are employed to generate multimodal feature vectors. For generating features for each of these modalities, pre-trained Transformer models with fine-tuning are utilized. In each modality, a Transformer model is used with transfer learning to extract feature and emotional structure. These features are then fused together, and emotion recognition is performed using a classifier. To select an appropriate fusion method and classifier, various feature-level and decision-level fusion techniques have been experimented with, and ultimately, the best model, which combines feature-level fusion by concatenating feature vectors and classification using a Support Vector Machine on the IEMOCAP multimodal dataset, achieves an accuracy of 75.42%. Keywords: Multimodal Emotion Recognition, IEMOCAP, Self-Supervised Learning, Transfer Learning, Transformer.
Persian Speech Emotion Recognition by Fine-Tuning Transformers
Feb 11, 2024Abstract:Given the significance of speech emotion recognition, numerous methods have been developed in recent years to create effective and efficient systems in this domain. One of these methods involves the use of pretrained transformers, fine-tuned to address this specific problem, resulting in high accuracy. Despite extensive discussions and global-scale efforts to enhance these systems, the application of this innovative and effective approach has received less attention in the context of Persian speech emotion recognition. In this article, we review the field of speech emotion recognition and its background, with an emphasis on the importance of employing transformers in this context. We present two models, one based on spectrograms and the other on the audio itself, fine-tuned using the shEMO dataset. These models significantly enhance the accuracy of previous systems, increasing it from approximately 65% to 80% on the mentioned dataset. Subsequently, to investigate the effect of multilinguality on the fine-tuning process, these same models are fine-tuned twice. First, they are fine-tuned using the English IEMOCAP dataset, and then they are fine-tuned with the Persian shEMO dataset. This results in an improved accuracy of 82% for the Persian emotion recognition system. Keywords: Persian Speech Emotion Recognition, shEMO, Self-Supervised Learning
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge