Miguel Simão
Improving novelty detection with generative adversarial networks on hand gesture data
Apr 13, 2023



Abstract:We propose a novel way of solving the issue of classification of out-of-vocabulary gestures using Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) trained in the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) framework. A generative model augments the data set in an online fashion with new samples and stochastic target vectors, while a discriminative model determines the class of the samples. The approach was evaluated on the UC2017 SG and UC2018 DualMyo data sets. The generative models performance was measured with a distance metric between generated and real samples. The discriminative models were evaluated by their accuracy on trained and novel classes. In terms of sample generation quality, the GAN is significantly better than a random distribution (noise) in mean distance, for all classes. In the classification tests, the baseline neural network was not capable of identifying untrained gestures. When the proposed methodology was implemented, we found that there is a trade-off between the detection of trained and untrained gestures, with some trained samples being mistaken as novelty. Nevertheless, a novelty detection accuracy of 95.4% or 90.2% (depending on the data set) was achieved with just 5% loss of accuracy on trained classes.
Gesture Recognition from Skeleton Data for Intuitive Human-Machine Interaction
Aug 26, 2020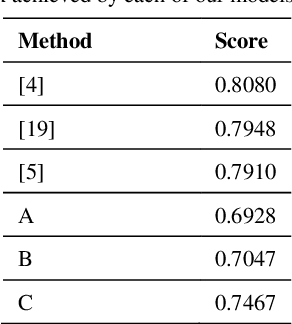
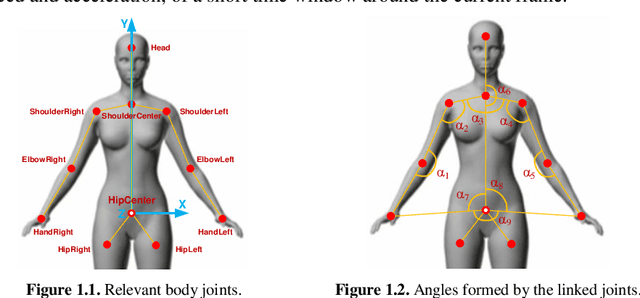
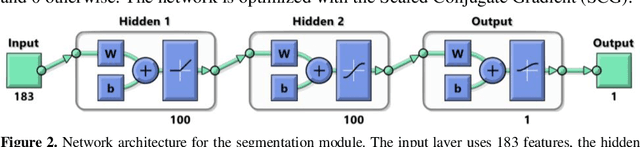
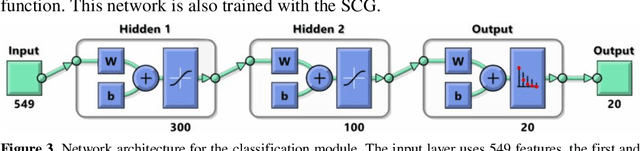
Abstract:Human gesture recognition has assumed a capital role in industrial applications, such as Human-Machine Interaction. We propose an approach for segmentation and classification of dynamic gestures based on a set of handcrafted features, which are drawn from the skeleton data provided by the Kinect sensor. The module for gesture detection relies on a feedforward neural network which performs framewise binary classification. The method for gesture recognition applies a sliding window, which extracts information from both the spatial and temporal dimensions. Then we combine windows of varying durations to get a multi-temporal scale approach and an additional gain in performance. Encouraged by the recent success of Recurrent Neural Networks for time series domains, we also propose a method for simultaneous gesture segmentation and classification based on the bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory cells, which have shown ability for learning the temporal relationships on long temporal scales. We evaluate all the different approaches on the dataset published for the ChaLearn Looking at People Challenge 2014. The most effective method achieves a Jaccard index of 0.75, which suggests a performance almost on pair with that presented by the state-of-the-art techniques. At the end, the recognized gestures are used to interact with a collaborative robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge