Miguel Cárdenas-Montes
Dynamic Price of Parking Service based on Deep Learning
Jan 11, 2022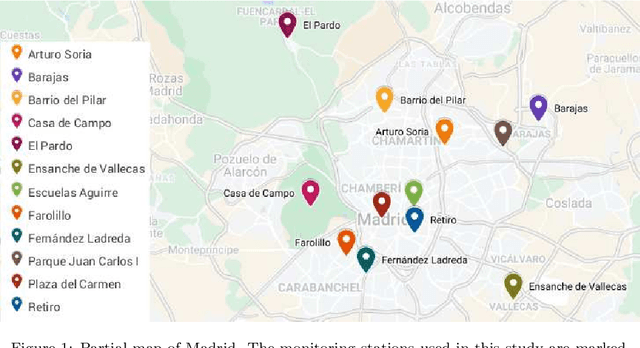
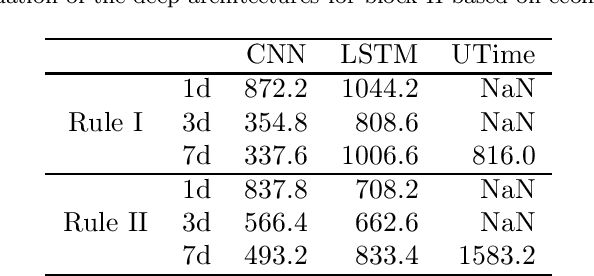
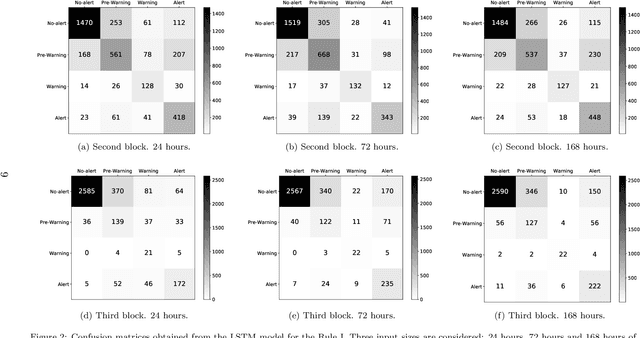
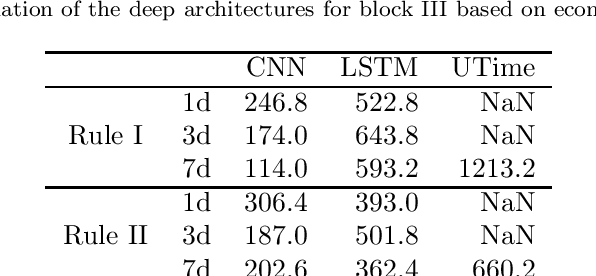
Abstract:The improvement of air-quality in urban areas is one of the main concerns of public government bodies. This concern emerges from the evidence between the air quality and the public health. Major efforts from government bodies in this area include monitoring and forecasting systems, banning more pollutant motor vehicles, and traffic limitations during the periods of low-quality air. In this work, a proposal for dynamic prices in regulated parking services is presented. The dynamic prices in parking service must discourage motor vehicles parking when low-quality episodes are predicted. For this purpose, diverse deep learning strategies are evaluated. They have in common the use of collective air-quality measurements for forecasting labels about air quality in the city. The proposal is evaluated by using economic parameters and deep learning quality criteria at Madrid (Spain).
Understanding the input-output relationship of neural networks in the time series forecasting radon levels at Canfranc Underground Laboratory
Mar 01, 2021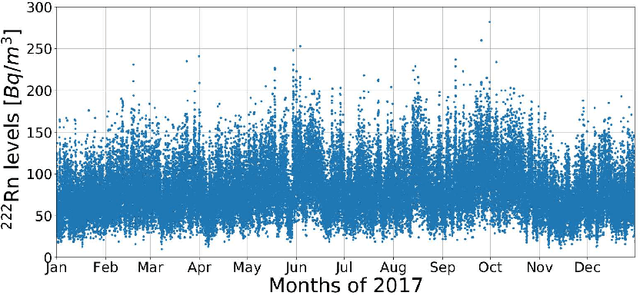
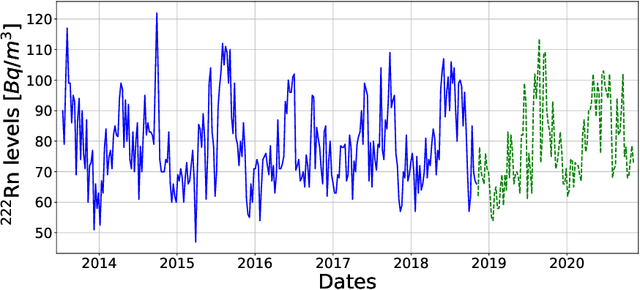
Abstract:Underground physics experiments such as dark matter direct detection need to keep control of the background contribution. Hosting these experiments in underground facilities helps to minimize certain background sources such as the cosmic rays. One of the largest remaining background sources is the radon emanated from the rocks enclosing the research facility. The radon particles could be deposited inside the detectors when they are opened to perform the maintenance operations. Therefore, forecasting the radon levels is a crucial task in an attempt to schedule the maintenance operations when radon level is minimum. In the past, deep learning models have been implemented to forecast the radon time series at the Canfranc Underground Laboratory (LSC), in Spain, with satisfactory results. When forecasting time series, the past values of the time series are taken as input variables. The present work focuses on understanding the relative contribution of these input variables to the predictions generated by neural networks. The results allow us to understand how the predictions of the time series depend on the input variables. These results may be used to build better predictors in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge