Mertcan Cokbas
C2AL: Cohort-Contrastive Auxiliary Learning for Large-scale Recommendation Systems
Oct 02, 2025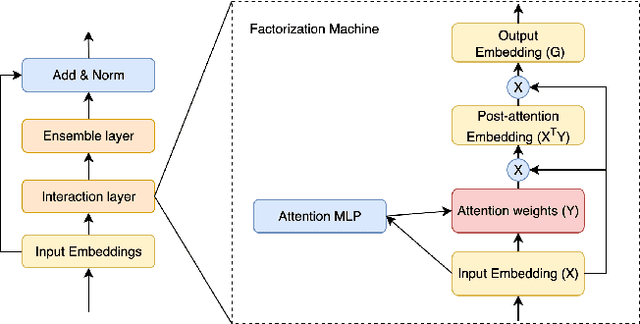
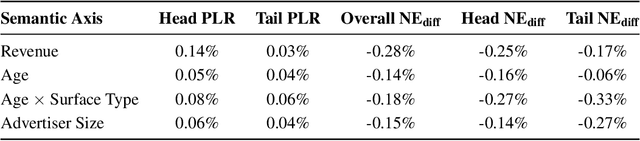
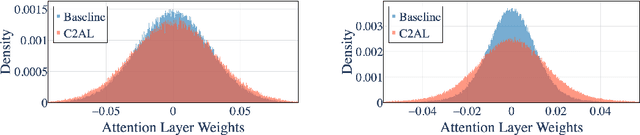

Abstract:Training large-scale recommendation models under a single global objective implicitly assumes homogeneity across user populations. However, real-world data are composites of heterogeneous cohorts with distinct conditional distributions. As models increase in scale and complexity and as more data is used for training, they become dominated by central distribution patterns, neglecting head and tail regions. This imbalance limits the model's learning ability and can result in inactive attention weights or dead neurons. In this paper, we reveal how the attention mechanism can play a key role in factorization machines for shared embedding selection, and propose to address this challenge by analyzing the substructures in the dataset and exposing those with strong distributional contrast through auxiliary learning. Unlike previous research, which heuristically applies weighted labels or multi-task heads to mitigate such biases, we leverage partially conflicting auxiliary labels to regularize the shared representation. This approach customizes the learning process of attention layers to preserve mutual information with minority cohorts while improving global performance. We evaluated C2AL on massive production datasets with billions of data points each for six SOTA models. Experiments show that the factorization machine is able to capture fine-grained user-ad interactions using the proposed method, achieving up to a 0.16% reduction in normalized entropy overall and delivering gains exceeding 0.30% on targeted minority cohorts.
Estimating Distances Between People using a Single Overhead Fisheye Camera with Application to Social-Distancing Oversight
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:Unobtrusive monitoring of distances between people indoors is a useful tool in the fight against pandemics. A natural resource to accomplish this are surveillance cameras. Unlike previous distance estimation methods, we use a single, overhead, fisheye camera with wide area coverage and propose two approaches. One method leverages a geometric model of the fisheye lens, whereas the other method uses a neural network to predict the 3D-world distance from people-locations in a fisheye image. To evaluate our algorithms, we collected a first-of-its-kind dataset using single fisheye camera, that comprises a wide range of distances between people (1-58 ft) and will be made publicly available. The algorithms achieve 1-2 ft distance error and over 95% accuracy in detecting social-distance violations.
Spatio-Visual Fusion-Based Person Re-Identification for Overhead Fisheye Images
Dec 22, 2022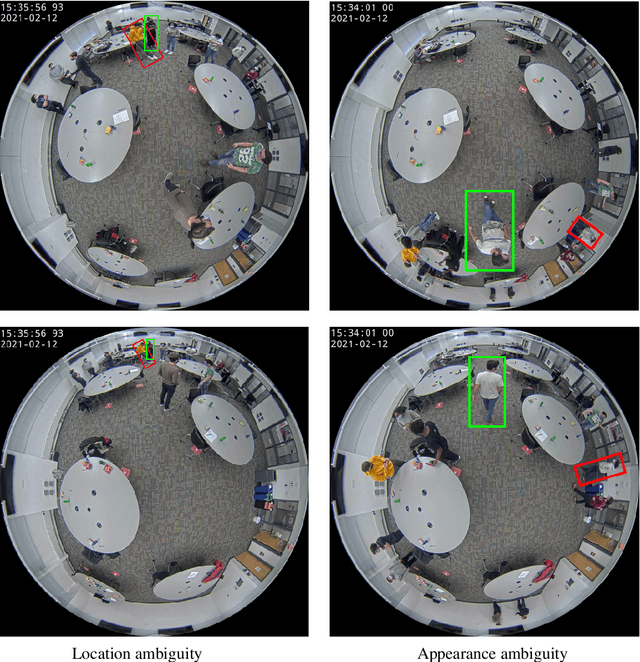

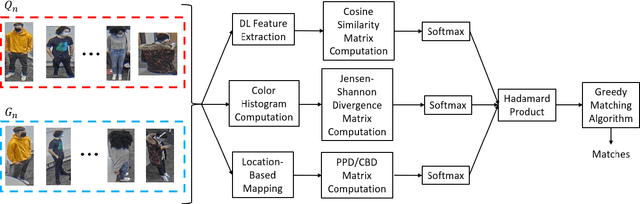
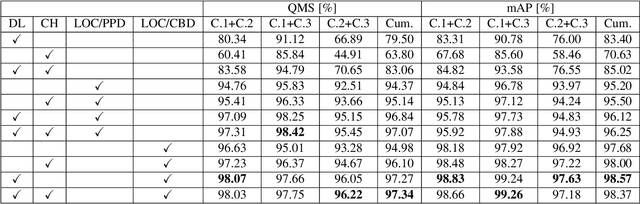
Abstract:Reliable and cost-effective counting of people in large indoor spaces is a significant challenge with many applications. An emerging approach is to deploy multiple fisheye cameras mounted overhead to monitor the whole space. However, due to the overlapping fields of view, person re-identificaiton (PRID) is critical for the accuracy of counting. While PRID has been thoroughly researched for traditional rectilinear cameras, few methods have been proposed for fisheye cameras and their performance is comparatively lower. To close this performance gap, we propose a multi-feature framework for fisheye PRID where we combine deep-learning, color-based and location-based features by means of novel feature fusion. We evaluate the performance of our framework for various feature combinations on FRIDA, a public fisheye PRID dataset. The results demonstrate that our multi-feature approach outperforms recent appearance-based deep-learning methods by almost 18% points and location-based methods by almost 3% points in accuracy.
FRIDA: Fisheye Re-Identification Dataset with Annotations
Oct 04, 2022
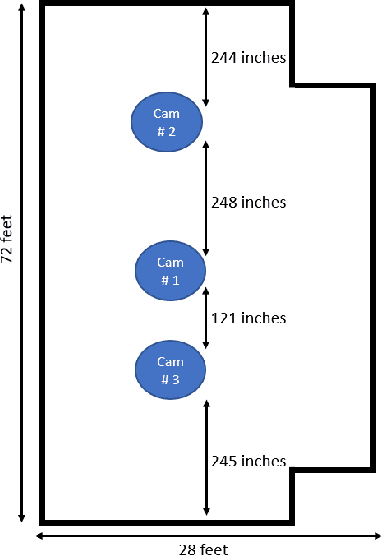
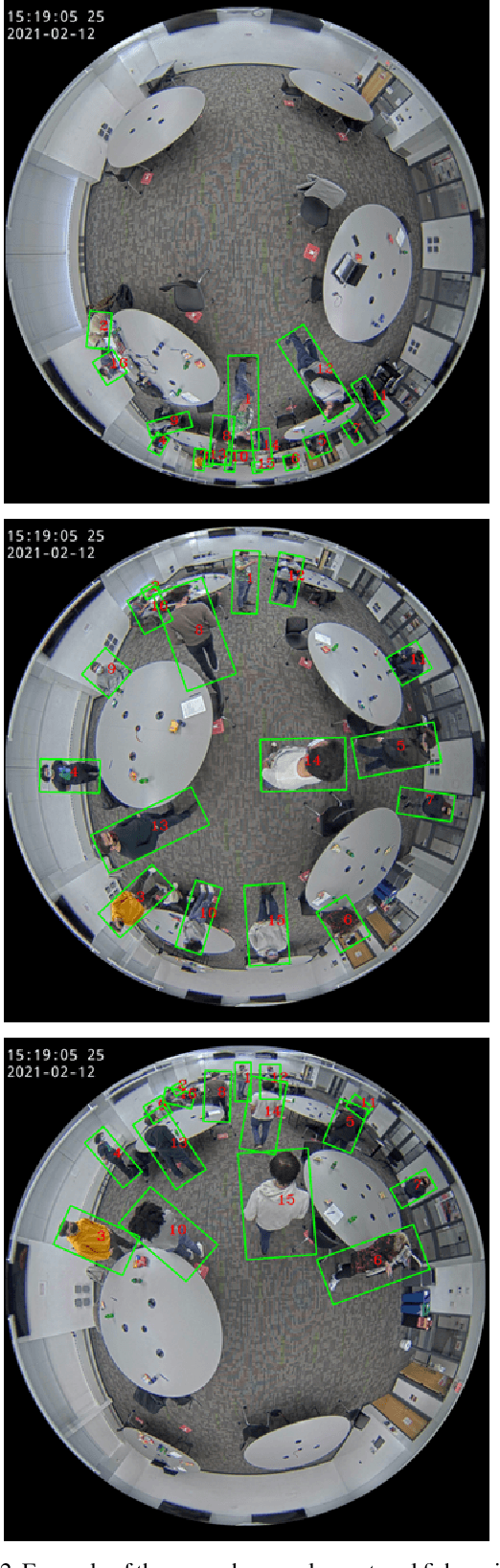

Abstract:Person re-identification (PRID) from side-mounted rectilinear-lens cameras is a well-studied problem. On the other hand, PRID from overhead fisheye cameras is new and largely unstudied, primarily due to the lack of suitable image datasets. To fill this void, we introduce the "Fisheye Re-IDentification Dataset with Annotations" (FRIDA), with 240k+ bounding-box annotations of people, captured by 3 time-synchronized, ceiling-mounted fisheye cameras in a large indoor space. Due to a field-of-view overlap, PRID in this case differs from a typical PRID problem, which we discuss in depth. We also evaluate the performance of 10 state-of-the-art PRID algorithms on FRIDA. We show that for 6 CNN-based algorithms, training on FRIDA boosts the performance by up to 11.64% points in mAP compared to training on a common rectilinear-camera PRID dataset.
Low-Resolution Overhead Thermal Tripwire for Occupancy Estimation
May 05, 2020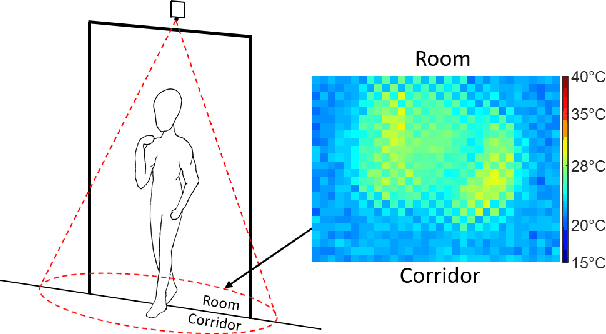
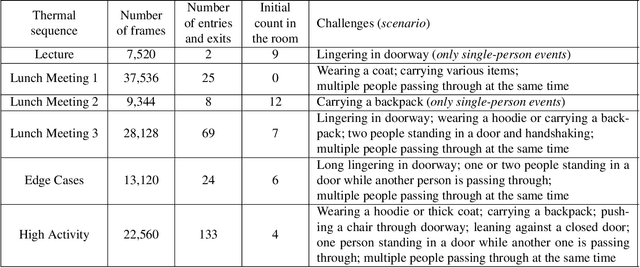
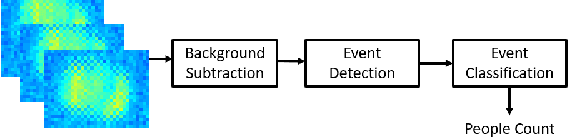
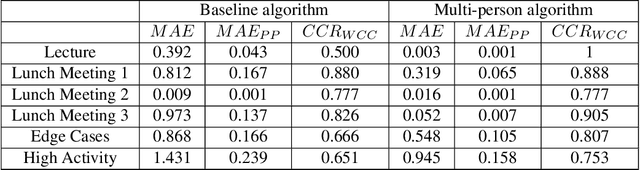
Abstract:Smart buildings use occupancy sensing for various tasks ranging from energy-efficient HVAC and lighting to space-utilization analysis and emergency response. We propose a people counting system which uses a low-resolution thermal sensor. Unlike previous people-counting systems based on thermal sensors, we use an overhead tripwire configuration at entryways to detect and track transient entries or exits. We develop two distinct people counting algorithms for this configuration. To evaluate our algorithms, we have collected and labeled a low-resolution thermal video dataset using the proposed system. The dataset, the first of its kind, is public and available for download. We also propose new evaluation metrics that are more suitable for systems that are subject to drift and jitter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge