Mehdi Sookhak
Joint UAV-UGV Positioning and Trajectory Planning via Meta A3C for Reliable Emergency Communications
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Joint deployment of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) has been shown to be an effective method to establish communications in areas affected by disasters. However, ensuring good Quality of Services (QoS) while using as few UAVs as possible also requires optimal positioning and trajectory planning for UAVs and UGVs. This paper proposes a joint UAV-UGV-based positioning and trajectory planning framework for UAVs and UGVs deployment that guarantees optimal QoS for ground users. To model the UGVs' mobility, we introduce a road graph, which directs their movement along valid road segments and adheres to the road network constraints. To solve the sum rate optimization problem, we reformulate the problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) and propose a novel asynchronous Advantage Actor Critic (A3C) incorporated with meta-learning for rapid adaptation to new environments and dynamic conditions. Numerical results demonstrate that our proposed Meta-A3C approach outperforms A3C and DDPG, delivering 13.1\% higher throughput and 49\% faster execution while meeting the QoS requirements.
GraphTrafficGPT: Enhancing Traffic Management Through Graph-Based AI Agent Coordination
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) offer significant promise for intelligent traffic management; however, current chain-based systems like TrafficGPT are hindered by sequential task execution, high token usage, and poor scalability, making them inefficient for complex, real-world scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose GraphTrafficGPT, a novel graph-based architecture, which fundamentally redesigns the task coordination process for LLM-driven traffic applications. GraphTrafficGPT represents tasks and their dependencies as nodes and edges in a directed graph, enabling efficient parallel execution and dynamic resource allocation. The main idea behind the proposed model is a Brain Agent that decomposes user queries, constructs optimized dependency graphs, and coordinates a network of specialized agents for data retrieval, analysis, visualization, and simulation. By introducing advanced context-aware token management and supporting concurrent multi-query processing, the proposed architecture handles interdependent tasks typical of modern urban mobility environments. Experimental results demonstrate that GraphTrafficGPT reduces token consumption by 50.2% and average response latency by 19.0% compared to TrafficGPT, while supporting simultaneous multi-query execution with up to 23.0% improvement in efficiency.
FSM: FBS Set Management, An energy efficient multi-drone 3D trajectory approach in cellular networks
Feb 08, 2022

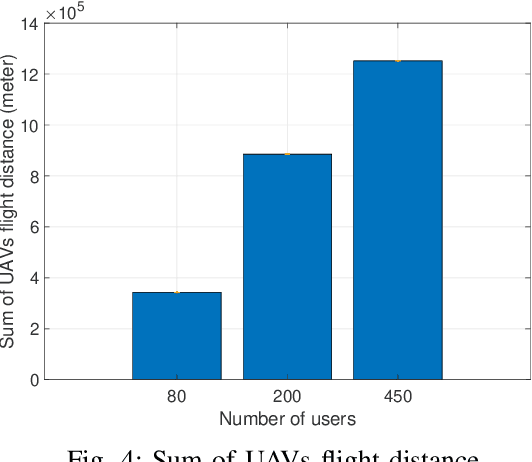
Abstract:In this paper, we consider a cellular network demand in an urban area. We aim to cover users and serve their required data rate in a period of time using a 5G cellular network. The type of considered UAV in this scenario is The Scout B- 330 UAV helicopter which can fly up to 3 km height. In these scenarios, to find the most proper trajectory of UAVs, we first must find the best positions of UAVs in different snapshots. We consider orthogonal frequency reuse to avoid interference between UAVs in the network. We also consider the number of communication channels constraint in intra cellular network. To find the optimum position of UAVs in each snapshot. We consider Non-Line of Sight (NLoS) path loss in these scenarios and aim to cover all users in each snapshot. To find the optimum trajectory of UAVs, we propose a mathematical model based on transportation problem to minimize the total distance tracked by UAVs. In each step we solve the proposed mathematical model for transiting UAVs between two snapshots. We also consider that users can be placed in different altitudes an their positions follows the Poison Point Process distribution and their mobility follows the random way point. The UAVs battery and flight limitations are also considered. To tackle the energy problem we introduce the Drone Cell Off (DCO) approach to avoid losing energy in idle hover mode.
Joint position and trajectory optimization of flying base station in 5G cellular networks, based on users' current and predicted location
Feb 08, 2022



Abstract:Nowadays, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have been significantly improved, and one of their most important applications is to provide temporary coverage for cellular users. Static Base Station cannot service all users due to temporary crashes because of temporary events such as ground BS breakdowns, bad weather conditions, natural disasters, transmission errors, etc., drones equipped with small cellular BS. The Drone Base Station is immediately sent to the target location and establishes the necessary communication links without requiring any predetermined infrastructure and covers that area. Finding the optimal location and the appropriate number (DBS) of drone-BS in this area is a challenge. Therefore, in this paper, the optimal location and optimal number of DBSs are distributed in the current state of the users and the subsequent user states determined by the prediction. Finally, the DBS transition is optimized from the current state to the predicted future locations. The simulation results show that the proposed method can provide acceptable coverage on the network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge