Md. Taimur Ahad
4IR Research Cell Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
A Novel Transfer Learning Approach for Mental Stability Classification from Voice Signal
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:This study presents a novel transfer learning approach and data augmentation technique for mental stability classification using human voice signals and addresses the challenges associated with limited data availability. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been employed to analyse spectrogram images generated from voice recordings. Three CNN architectures, VGG16, InceptionV3, and DenseNet121, were evaluated across three experimental phases: training on non-augmented data, augmented data, and transfer learning. This proposed transfer learning approach involves pre-training models on the augmented dataset and fine-tuning them on the non-augmented dataset while ensuring strict data separation to prevent data leakage. The results demonstrate significant improvements in classification performance compared to the baseline approach. Among three CNN architectures, DenseNet121 achieved the highest accuracy of 94% and an AUC score of 99% using the proposed transfer learning approach. This finding highlights the effectiveness of combining data augmentation and transfer learning to enhance CNN-based classification of mental stability using voice spectrograms, offering a promising non-invasive tool for mental health diagnostics.
A Semantic Segmentation Approach on Sweet Orange Leaf Diseases Detection Utilizing YOLO
Sep 10, 2024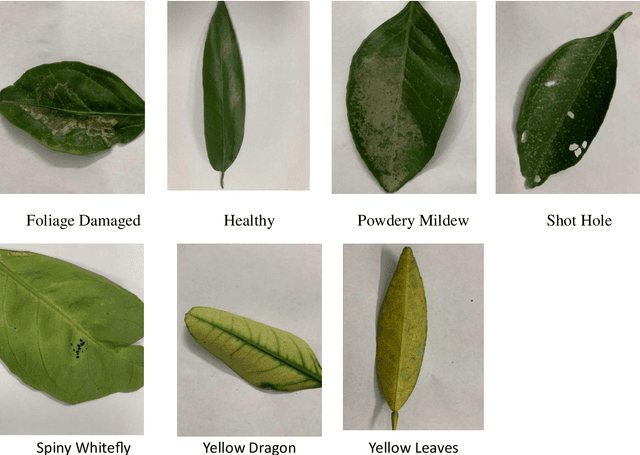
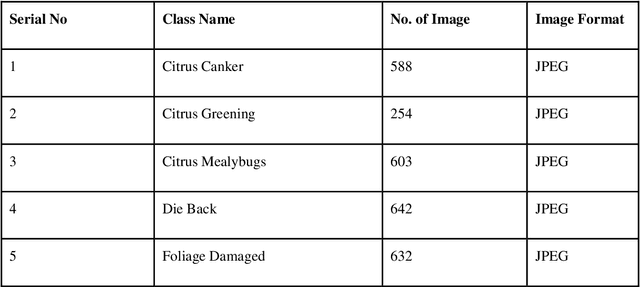
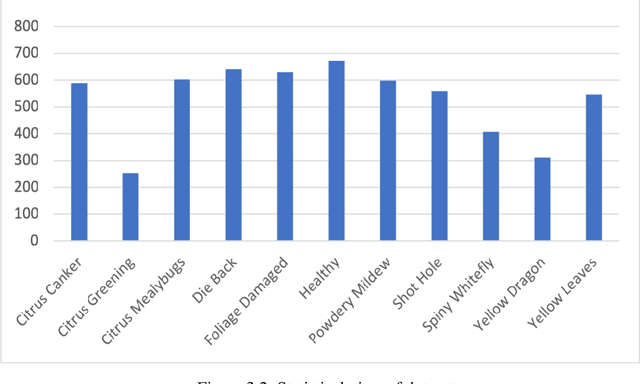
Abstract:This research introduces an advanced method for diagnosing diseases in sweet orange leaves by utilising advanced artificial intelligence models like YOLOv8 . Due to their significance as a vital agricultural product, sweet oranges encounter significant threats from a variety of diseases that harmfully affect both their yield and quality. Conventional methods for disease detection primarily depend on manual inspection which is ineffective and frequently leads to errors, resulting in delayed treatment and increased financial losses. In response to this challenge, the research utilized YOLOv8 , harnessing their proficiencies in detecting objects and analyzing images. YOLOv8 is recognized for its rapid and precise performance, while VIT is acknowledged for its detailed feature extraction abilities. Impressively, during both the training and validation stages, YOLOv8 exhibited a perfect accuracy of 80.4%, while VIT achieved an accuracy of 99.12%, showcasing their potential to transform disease detection in agriculture. The study comprehensively examined the practical challenges related to the implementation of AI technologies in agriculture, encompassing the computational demands and user accessibility, and offering viable solutions for broader usage. Moreover, it underscores the environmental considerations, particularly the potential for reduced pesticide usage, thereby promoting sustainable farming and environmental conservation. These findings provide encouraging insights into the application of AI in agriculture, suggesting a transition towards more effective, sustainable, and technologically advanced farming methods. This research not only highlights the efficacy of YOLOv8 within a specific agricultural domain but also lays the foundation for further studies that encompass a broader application in crop management and sustainable agricultural practices.
A study on deep feature extraction to detect and classify Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is a blood malignancy that mainly affects adults and children. This study looks into the use of deep learning, specifically Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), for the detection and classification of ALL. Conventional techniques for ALL diagnosis, such bone marrow biopsy, are costly and prone to mistakes made by hand. By utilising automated technologies, the research seeks to improve diagnostic accuracy. The research uses a variety of pre-trained CNN models, such as InceptionV3, ResNet101, VGG19, DenseNet121, MobileNetV2, and DenseNet121, to extract characteristics from pictures of blood smears. ANOVA, Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE), Random Forest, Lasso, and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) are a few of the selection approaches used to find the most relevant features after feature extraction. Following that, machine learning methods like Na\"ive Bayes, Random Forest, Support Vector Machine (SVM), and K-Nearest Neighbours (KNN) are used to classify these features. With an 87% accuracy rate, the ResNet101 model produced the best results, closely followed by DenseNet121 and VGG19. According to the study, CNN-based models have the potential to decrease the need for medical specialists by increasing the speed and accuracy of ALL diagnosis. To improve model performance, the study also recommends expanding and diversifying datasets and investigating more sophisticated designs such as transformers. This study highlights how well automated deep learning systems do medical diagnosis.
Machine Learning-Based Tea Leaf Disease Detection: A Comprehensive Review
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Tea leaf diseases are a major challenge to agricultural productivity, with far-reaching implications for yield and quality in the tea industry. The rise of machine learning has enabled the development of innovative approaches to combat these diseases. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for effective crop management. For predicting tea leaf disease, several automated systems have already been developed using different image processing techniques. This paper delivers a systematic review of the literature on machine learning methodologies applied to diagnose tea leaf disease via image classification. It thoroughly evaluates the strengths and constraints of various Vision Transformer models, including Inception Convolutional Vision Transformer (ICVT), GreenViT, PlantXViT, PlantViT, MSCVT, Transfer Learning Model & Vision Transformer (TLMViT), IterationViT, IEM-ViT. Moreover, this paper also reviews models like Dense Convolutional Network (DenseNet), Residual Neural Network (ResNet)-50V2, YOLOv5, YOLOv7, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Deep CNN, Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm (NSGA-II), MobileNetv2, and Lesion-Aware Visual Transformer. These machine-learning models have been tested on various datasets, demonstrating their real-world applicability. This review study not only highlights current progress in the field but also provides valuable insights for future research directions in the machine learning-based detection and classification of tea leaf diseases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge