Maurizio Morisio
A Data-driven Neural Network Architecture for Sentiment Analysis
Jun 30, 2020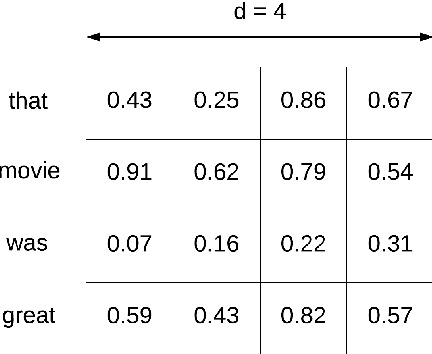
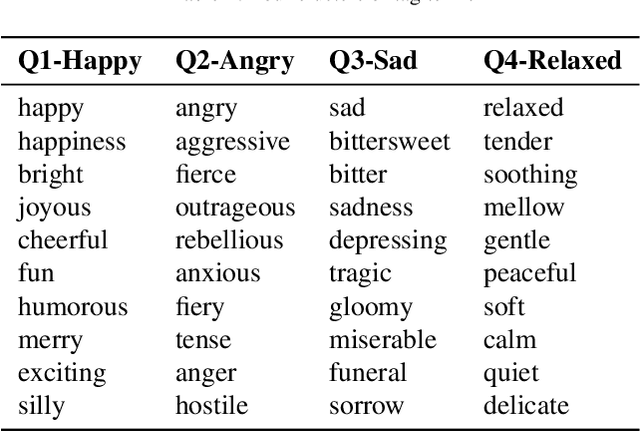
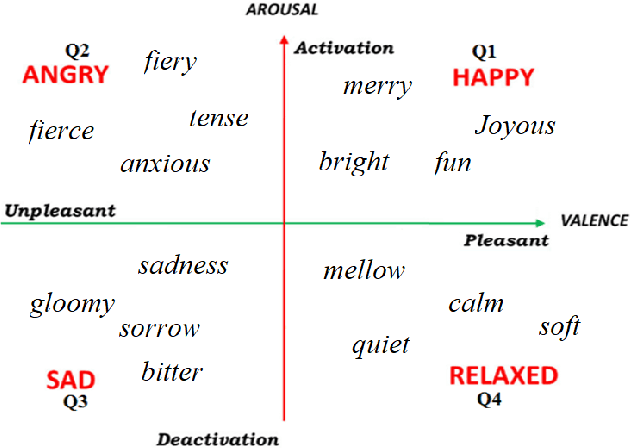
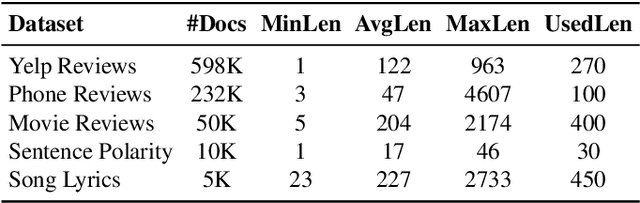
Abstract:The fabulous results of convolution neural networks in image-related tasks, attracted attention of text mining, sentiment analysis and other text analysis researchers. It is however difficult to find enough data for feeding such networks, optimize their parameters, and make the right design choices when constructing network architectures. In this paper we present the creation steps of two big datasets of song emotions. We also explore usage of convolution and max-pooling neural layers on song lyrics, product and movie review text datasets. Three variants of a simple and flexible neural network architecture are also compared. Our intention was to spot any important patterns that can serve as guidelines for parameter optimization of similar models. We also wanted to identify architecture design choices which lead to high performing sentiment analysis models. To this end, we conducted a series of experiments with neural architectures of various configurations. Our results indicate that parallel convolutions of filter lengths up to three are usually enough for capturing relevant text features. Also, max-pooling region size should be adapted to the length of text documents for producing the best feature maps. Top results we got are obtained with feature maps of lengths 6 to 18. An improvement on future neural network models for sentiment analysis, could be generating sentiment polarity prediction of documents using aggregation of predictions on smaller excerpt of the entire text.
* 18 pages, 4 tables, 7 figures
Quality of Word Embeddings on Sentiment Analysis Tasks
Mar 06, 2020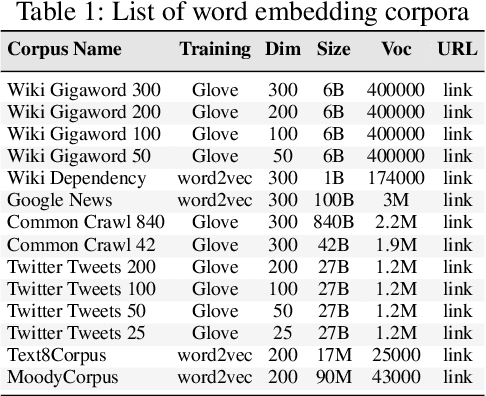
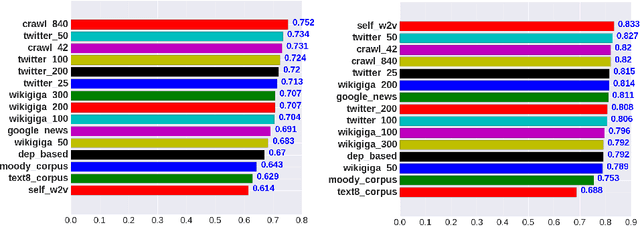
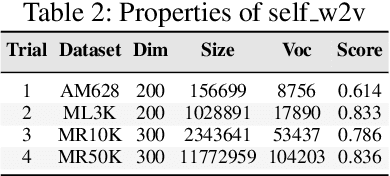
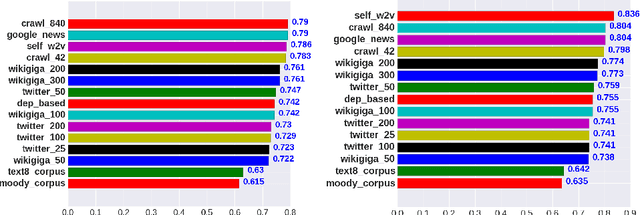
Abstract:Word embeddings or distributed representations of words are being used in various applications like machine translation, sentiment analysis, topic identification etc. Quality of word embeddings and performance of their applications depends on several factors like training method, corpus size and relevance etc. In this study we compare performance of a dozen of pretrained word embedding models on lyrics sentiment analysis and movie review polarity tasks. According to our results, Twitter Tweets is the best on lyrics sentiment analysis, whereas Google News and Common Crawl are the top performers on movie polarity analysis. Glove trained models slightly outrun those trained with Skipgram. Also, factors like topic relevance and size of corpus significantly impact the quality of the models. When medium or large-sized text sets are available, obtaining word embeddings from same training dataset is usually the best choice.
Word Embeddings for Sentiment Analysis: A Comprehensive Empirical Survey
Feb 02, 2019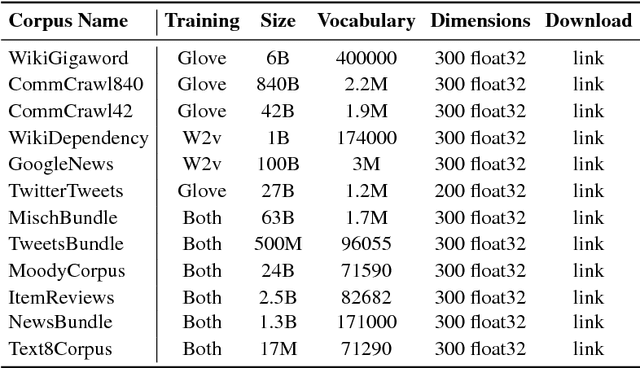
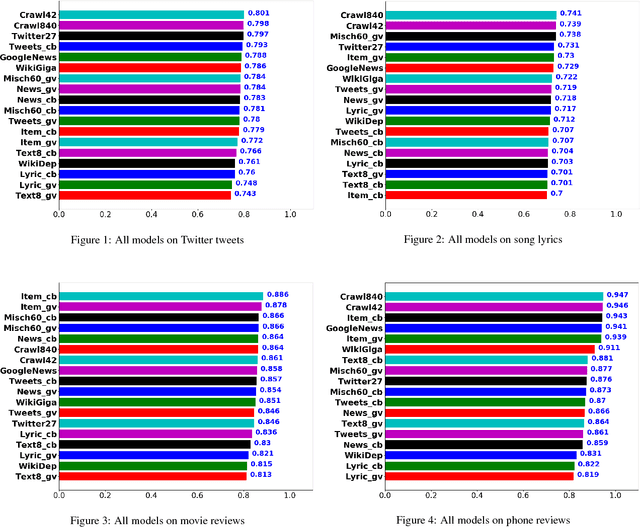
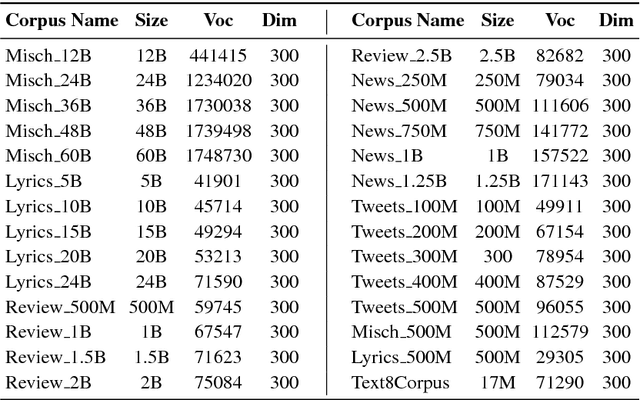
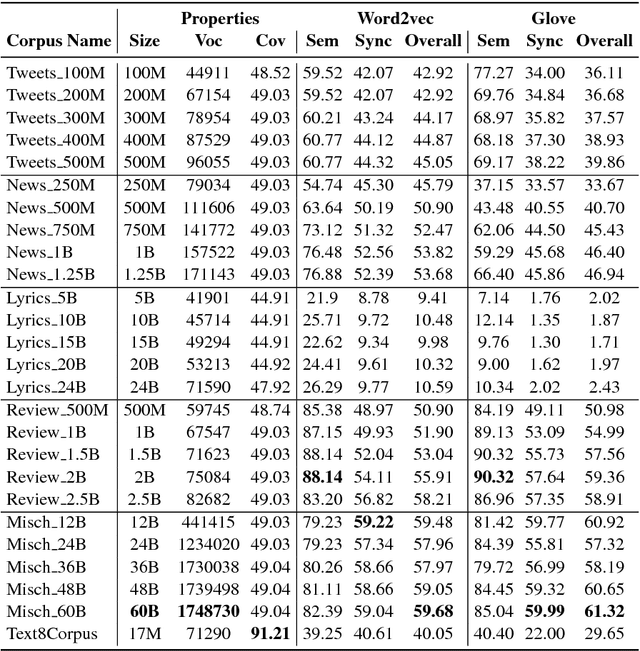
Abstract:This work investigates the role of factors like training method, training corpus size and thematic relevance of texts in the performance of word embedding features on sentiment analysis of tweets, song lyrics, movie reviews and item reviews. We also explore specific training or post-processing methods that can be used to enhance the performance of word embeddings in certain tasks or domains. Our empirical observations indicate that models trained with multithematic texts that are large and rich in vocabulary are the best in answering syntactic and semantic word analogy questions. We further observe that influence of thematic relevance is stronger on movie and phone reviews, but weaker on tweets and lyrics. These two later domains are more sensitive to corpus size and training method, with Glove outperforming Word2vec. "Injecting" extra intelligence from lexicons or generating sentiment specific word embeddings are two prominent alternatives for increasing performance of word embedding features.
Hybrid Recommender Systems: A Systematic Literature Review
Jan 12, 2019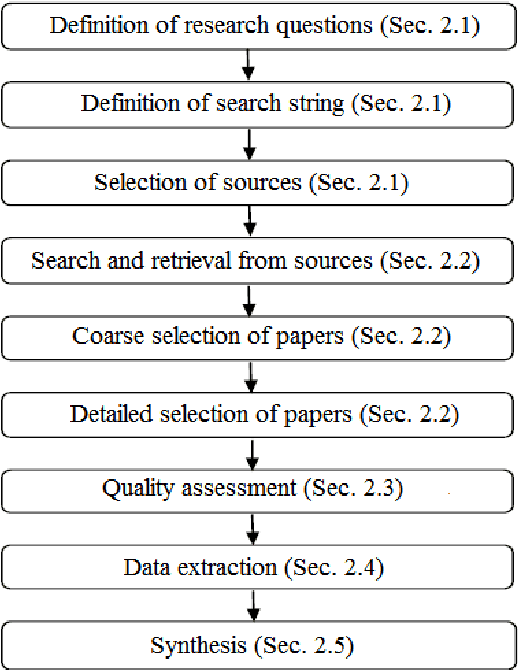
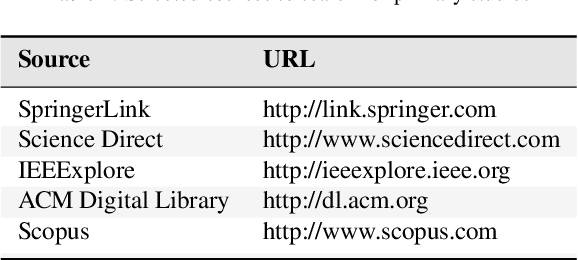
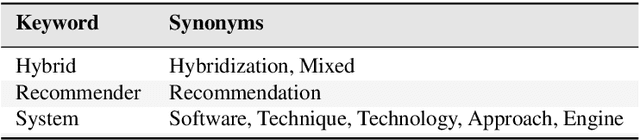
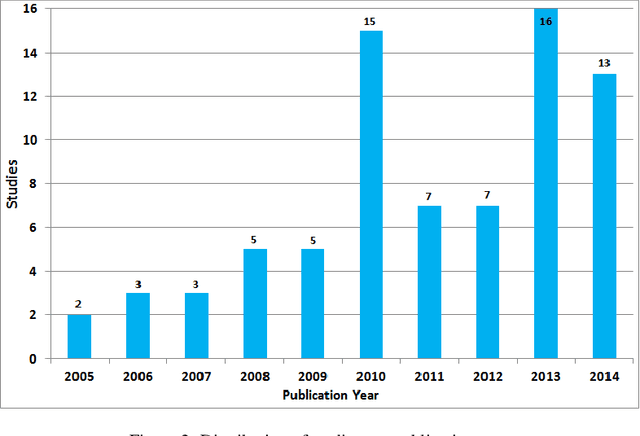
Abstract:Recommender systems are software tools used to generate and provide suggestions for items and other entities to the users by exploiting various strategies. Hybrid recommender systems combine two or more recommendation strategies in different ways to benefit from their complementary advantages. This systematic literature review presents the state of the art in hybrid recommender systems of the last decade. It is the first quantitative review work completely focused in hybrid recommenders. We address the most relevant problems considered and present the associated data mining and recommendation techniques used to overcome them. We also explore the hybridization classes each hybrid recommender belongs to, the application domains, the evaluation process and proposed future research directions. Based on our findings, most of the studies combine collaborative filtering with another technique often in a weighted way. Also cold-start and data sparsity are the two traditional and top problems being addressed in 23 and 22 studies each, while movies and movie datasets are still widely used by most of the authors. As most of the studies are evaluated by comparisons with similar methods using accuracy metrics, providing more credible and user oriented evaluations remains a typical challenge. Besides this, newer challenges were also identified such as responding to the variation of user context, evolving user tastes or providing cross-domain recommendations. Being a hot topic, hybrid recommenders represent a good basis with which to respond accordingly by exploring newer opportunities such as contextualizing recommendations, involving parallel hybrid algorithms, processing larger datasets, etc.
* 38 pages, 9 figures, 14 tables. The final authenticated version is available online at https://content.iospress.com/articles/intelligent-data-analysis/ida163209
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge