Matthias Söllner
Supporting Cognitive and Emotional Empathic Writing of Students
May 31, 2021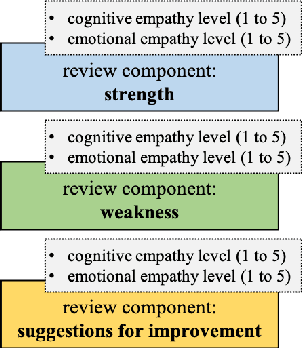

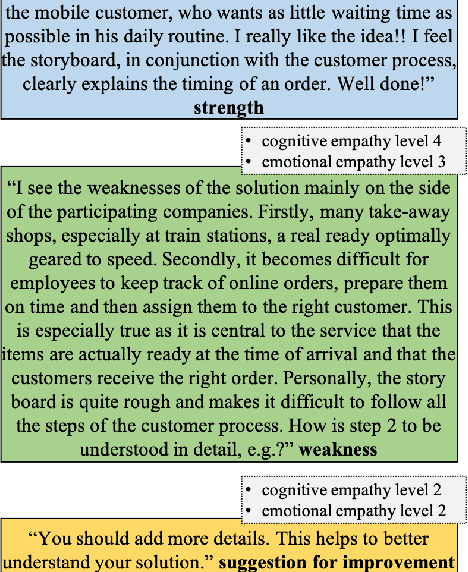
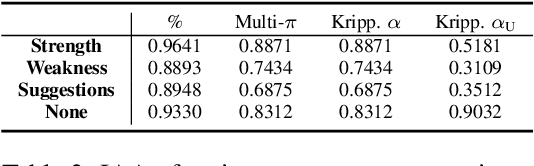
Abstract:We present an annotation approach to capturing emotional and cognitive empathy in student-written peer reviews on business models in German. We propose an annotation scheme that allows us to model emotional and cognitive empathy scores based on three types of review components. Also, we conducted an annotation study with three annotators based on 92 student essays to evaluate our annotation scheme. The obtained inter-rater agreement of {\alpha}=0.79 for the components and the multi-{\pi}=0.41 for the empathy scores indicate that the proposed annotation scheme successfully guides annotators to a substantial to moderate agreement. Moreover, we trained predictive models to detect the annotated empathy structures and embedded them in an adaptive writing support system for students to receive individual empathy feedback independent of an instructor, time, and location. We evaluated our tool in a peer learning exercise with 58 students and found promising results for perceived empathy skill learning, perceived feedback accuracy, and intention to use. Finally, we present our freely available corpus of 500 empathy-annotated, student-written peer reviews on business models and our annotation guidelines to encourage future research on the design and development of empathy support systems.
A Corpus for Argumentative Writing Support in German
Oct 26, 2020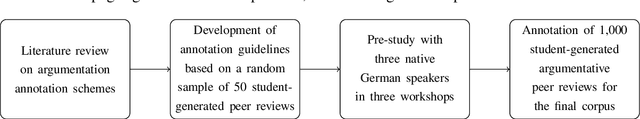



Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel annotation approach to capture claims and premises of arguments and their relations in student-written persuasive peer reviews on business models in German language. We propose an annotation scheme based on annotation guidelines that allows to model claims and premises as well as support and attack relations for capturing the structure of argumentative discourse in student-written peer reviews. We conduct an annotation study with three annotators on 50 persuasive essays to evaluate our annotation scheme. The obtained inter-rater agreement of $\alpha=0.57$ for argument components and $\alpha=0.49$ for argumentative relations indicates that the proposed annotation scheme successfully guides annotators to moderate agreement. Finally, we present our freely available corpus of 1,000 persuasive student-written peer reviews on business models and our annotation guidelines to encourage future research on the design and development of argumentative writing support systems for students.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge