Matthew C. Spencer
New User Event Prediction Through the Lens of Causal Inference
Jul 10, 2024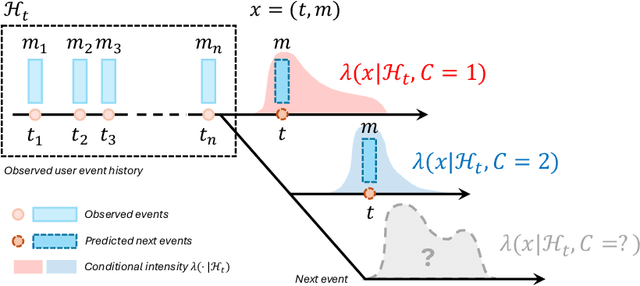
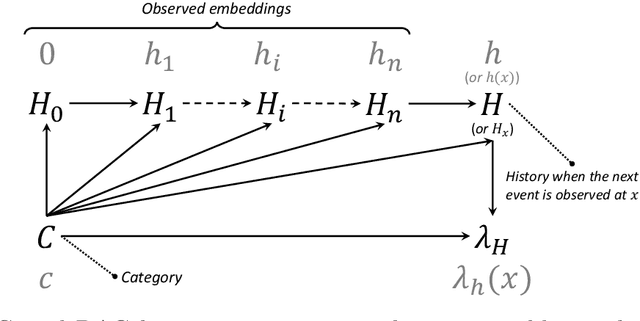
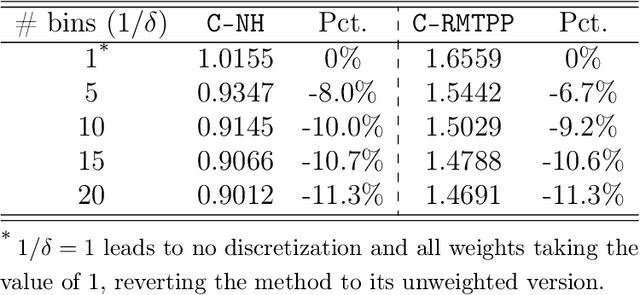
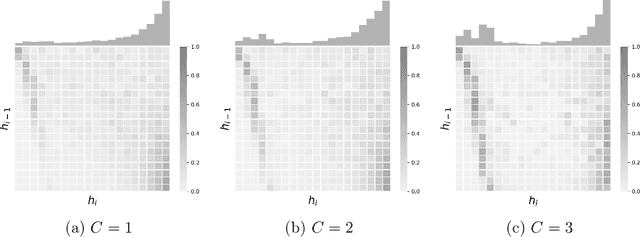
Abstract:Modeling and analysis for event series generated by heterogeneous users of various behavioral patterns are closely involved in our daily lives, including credit card fraud detection, online platform user recommendation, and social network analysis. The most commonly adopted approach to this task is to classify users into behavior-based categories and analyze each of them separately. However, this approach requires extensive data to fully understand user behavior, presenting challenges in modeling newcomers without historical knowledge. In this paper, we propose a novel discrete event prediction framework for new users through the lens of causal inference. Our method offers an unbiased prediction for new users without needing to know their categories. We treat the user event history as the ''treatment'' for future events and the user category as the key confounder. Thus, the prediction problem can be framed as counterfactual outcome estimation, with the new user model trained on an adjusted dataset where each event is re-weighted by its inverse propensity score. We demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed framework with a numerical simulation study and two real-world applications, including Netflix rating prediction and seller contact prediction for customer support at Amazon.
A Semi-supervised Multi-task Learning Approach to Classify Customer Contact Intents
Jun 10, 2021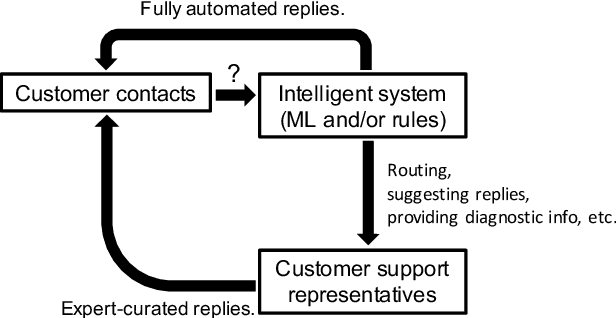

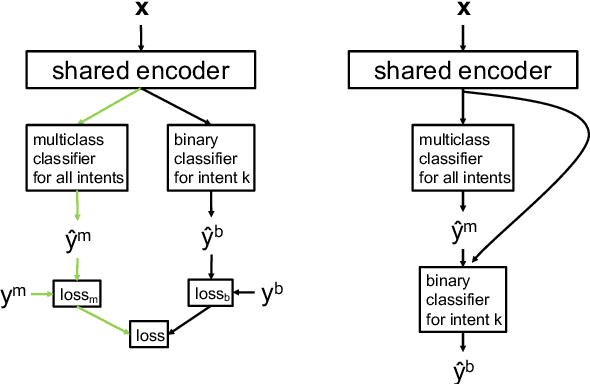

Abstract:In the area of customer support, understanding customers' intents is a crucial step. Machine learning plays a vital role in this type of intent classification. In reality, it is typical to collect confirmation from customer support representatives (CSRs) regarding the intent prediction, though it can unnecessarily incur prohibitive cost to ask CSRs to assign existing or new intents to the mis-classified cases. Apart from the confirmed cases with and without intent labels, there can be a number of cases with no human curation. This data composition (Positives + Unlabeled + multiclass Negatives) creates unique challenges for model development. In response to that, we propose a semi-supervised multi-task learning paradigm. In this manuscript, we share our experience in building text-based intent classification models for a customer support service on an E-commerce website. We improve the performance significantly by evolving the model from multiclass classification to semi-supervised multi-task learning by leveraging the negative cases, domain- and task-adaptively pretrained ALBERT on customer contact texts, and a number of un-curated data with no labels. In the evaluation, the final model boosts the average AUC ROC by almost 20 points compared to the baseline finetuned multiclass classification ALBERT model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge