Matteo Santilli
Distributed Adaptive and Resilient Control of Multi-Robot Systems with Limited Field of View Interactions
Dec 19, 2021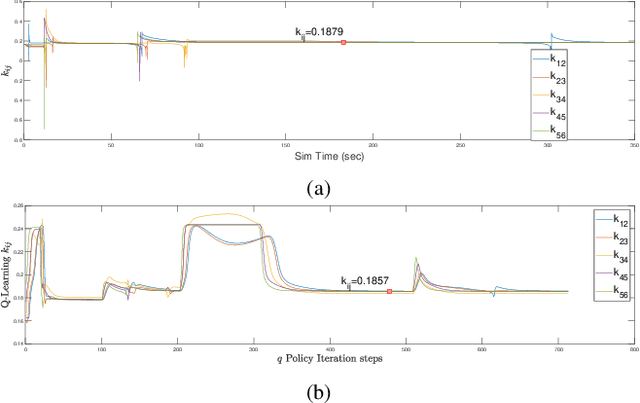
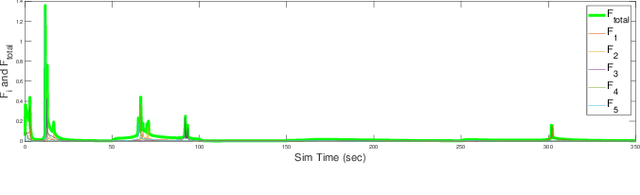
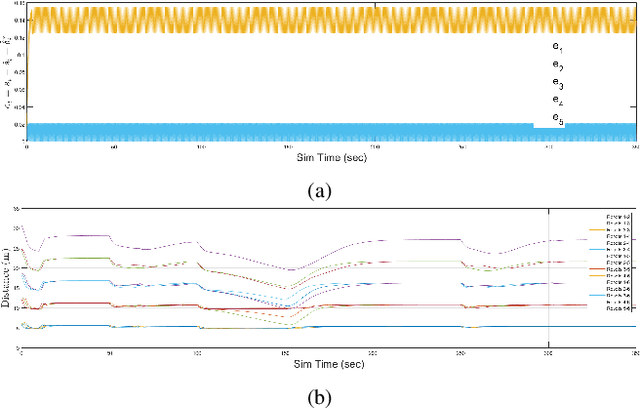
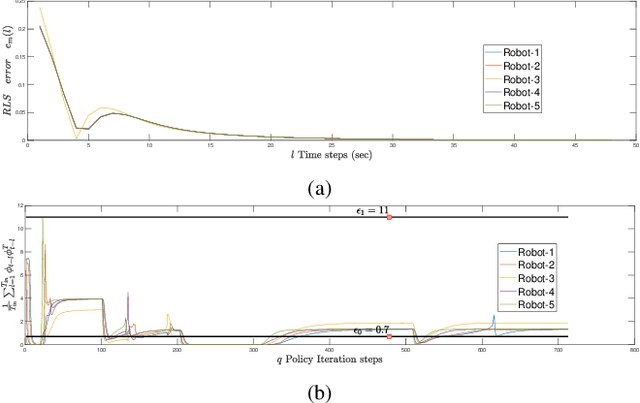
Abstract:In this paper, we consider two coupled problems for distributed multi-robot systems (MRSs) coordinating with limited field of view (FOV) sensors: adaptive tuning of interaction gains and rejection of sensor attacks. First, a typical shortcoming of distributed control frameworks (e.g., potential fields) is that the overall system behavior is highly sensitive to the gain assigned to relative interactions. Second, MRSs with limited FOV sensors can be more susceptible to sensor attacks aimed at their FOVs, and therefore must be resilient to such attacks. Based on these shortcomings, we propose a comprehensive solution that combines efforts in adaptive gain tuning and attack resilience to the problem of topology control for MRSs with limited FOVs. Specifically, we first derive an adaptive gain tuning scheme based on satisfying nominal pairwise interactions, which yields a dynamic balancing of interaction strengths in a robot's neighborhood. We then model additive sensor and actuator attacks (or faults) and derive H infinity control protocols by employing a static output-feedback technique, guaranteeing bounded L2 gains of the error induced by the attack (fault) signals. Finally, simulation results using ROS Gazebo are provided to support our theoretical findings.
Experimental Validation of Stable Coordination for Multi-Robot Systems with Limited Fields of View using a PortableMulti-Robot Testbed
Sep 16, 2019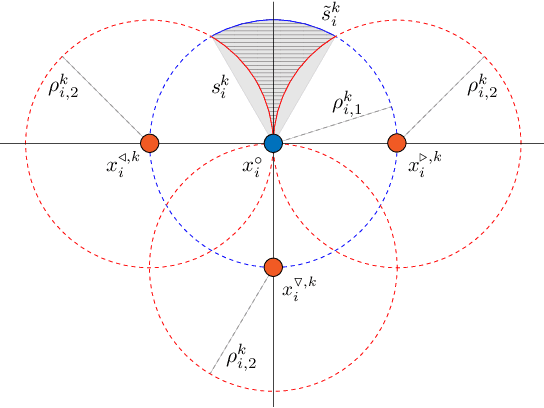
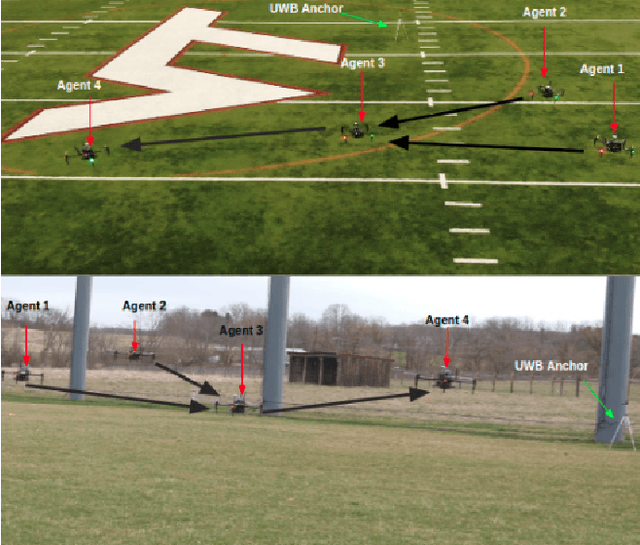
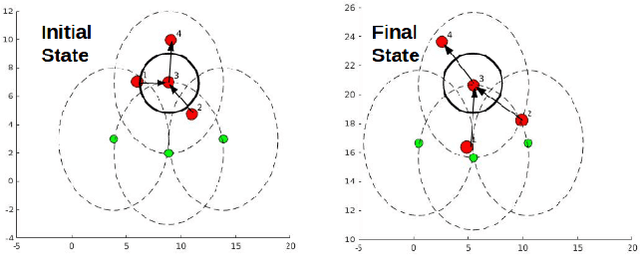
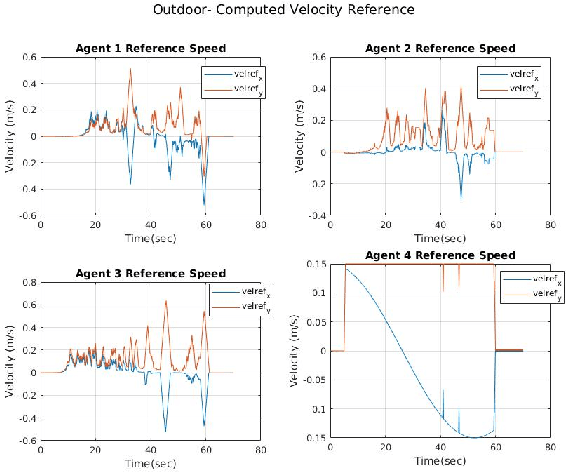
Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of stable coordinated motion in multi-robot systems with limited fields of view (FOVs). These problems arise naturally for multi-robot systems that interact based on sensing, such as our case study of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) each equipped with several cameras that are used for detecting neighboring UAVs. In this context, our contributions are: i) first, we derive a framework for studying stable motion and distributed topology control for multi-robot systems with limited FOVs; and ii) Then, we provide experimental results in indoor and challenging outdoor environments (e.g., with wind speeds up to 10 mph) with a team of UAVs to demonstrate the performance of the proposed control framework using a portable multi-robot experimental set-up.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge