Matteo Rossini
Learning Behavioral Representations of Human Mobility
Sep 11, 2020
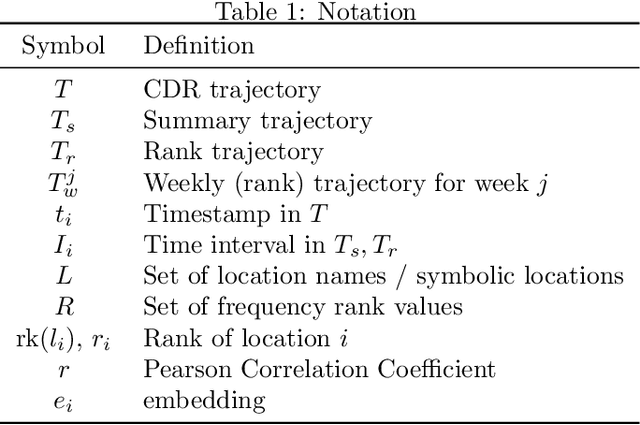

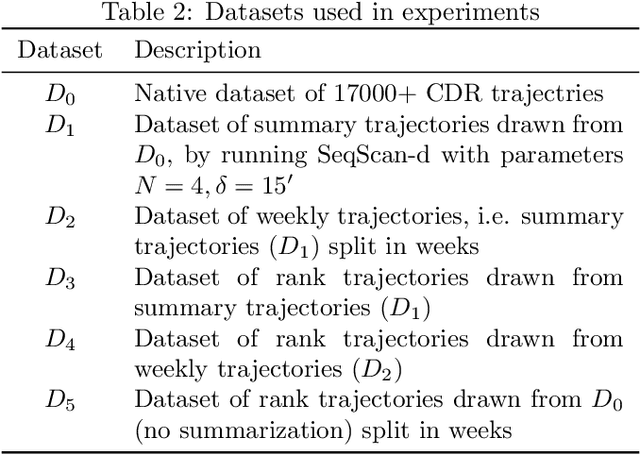
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the suitability of state-of-the-art representation learning methods to the analysis of behavioral similarity of moving individuals, based on CDR trajectories. The core of the contribution is a novel methodological framework, mob2vec, centered on the combined use of a recent symbolic trajectory segmentation method for the removal of noise, a novel trajectory generalization method incorporating behavioral information, and an unsupervised technique for the learning of vector representations from sequential data. Mob2vec is the result of an empirical study conducted on real CDR data through an extensive experimentation. As a result, it is shown that mob2vec generates vector representations of CDR trajectories in low dimensional spaces which preserve the similarity of the mobility behavior of individuals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge