Maryam Imani
Region-Aware Deformable Convolutions
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce Region-Aware Deformable Convolution (RAD-Conv), a new convolutional operator that enhances neural networks' ability to adapt to complex image structures. Unlike traditional deformable convolutions, which are limited to fixed quadrilateral sampling areas, RAD-Conv uses four boundary offsets per kernel element to create flexible, rectangular regions that dynamically adjust their size and shape to match image content. This approach allows precise control over the receptive field's width and height, enabling the capture of both local details and long-range dependencies, even with small 1x1 kernels. By decoupling the receptive field's shape from the kernel's structure, RAD-Conv combines the adaptability of attention mechanisms with the efficiency of standard convolutions. This innovative design offers a practical solution for building more expressive and efficient vision models, bridging the gap between rigid convolutional architectures and computationally costly attention-based methods.
Classification of Heart Sounds Using Multi-Branch Deep Convolutional Network and LSTM-CNN
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a fast and cost-effective method for diagnosing cardiac abnormalities with high accuracy and reliability using low-cost systems in clinics. The primary limitation of automatic diagnosing of cardiac diseases is the rarity of correct and acceptable labeled samples, which can be expensive to prepare. To address this issue, two methods are proposed in this work. The first method is a unique Multi-Branch Deep Convolutional Neural Network (MBDCN) architecture inspired by human auditory processing, specifically designed to optimize feature extraction by employing various sizes of convolutional filters and audio signal power spectrum as input. In the second method, called as Long short-term memory-Convolutional Neural (LSCN) model, Additionally, the network architecture includes Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network blocks to improve feature extraction in the time domain. The innovative approach of combining multiple parallel branches consisting of the one-dimensional convolutional layers along with LSTM blocks helps in achieving superior results in audio signal processing tasks. The experimental results demonstrate superiority of the proposed methods over the state-of-the-art techniques. The overall classification accuracy of heart sounds with the LSCN network is more than 96%. The efficiency of this network is significant compared to common feature extraction methods such as Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) and wavelet transform. Therefore, the proposed method shows promising results in the automatic analysis of heart sounds and has potential applications in the diagnosis and early detection of cardiovascular diseases.
Deep Curriculum Learning for PolSAR Image Classification
Dec 26, 2021
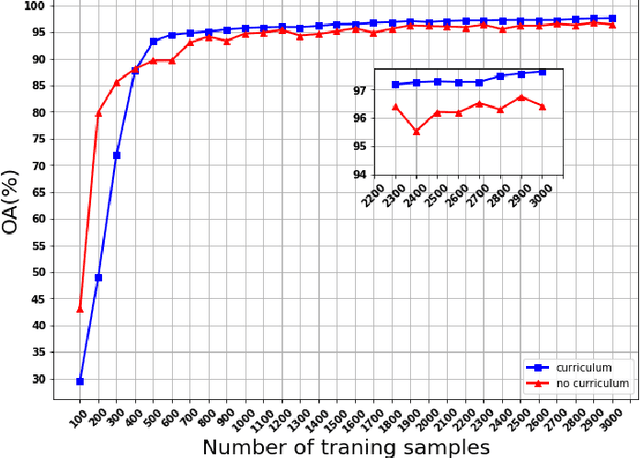
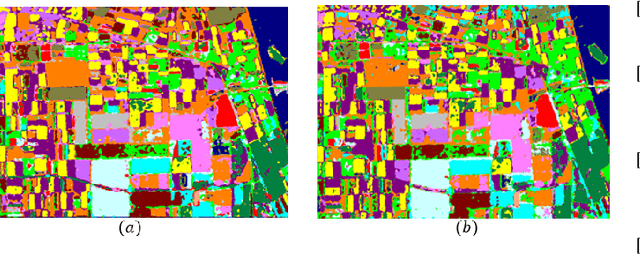
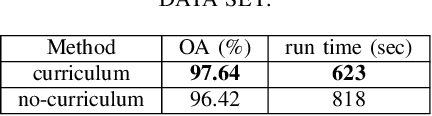
Abstract:Following the great success of curriculum learning in the area of machine learning, a novel deep curriculum learning method proposed in this paper, entitled DCL, particularly for the classification of fully polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) data. This method utilizes the entropy-alpha target decomposition method to estimate the degree of complexity of each PolSAR image patch before applying it to the convolutional neural network (CNN). Also, an accumulative mini-batch pacing function is used to introduce more difficult patches to CNN.Experiments on the widely used data set of AIRSAR Flevoland reveal that the proposed curriculum learning method can not only increase classification accuracy but also lead to faster training convergence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge