Martin Möddel
Resonant Inductive Coupling Network for Human-Sized Magnetic Particle Imaging
Dec 23, 2023Abstract:In Magnetic Particle Imaging, a field-free region is maneuvered throughout the field of view using a time-varying magnetic field known as the drive-field. Human-sized systems operate the drive-field in the kHz range and generate it by utilizing strong currents that can rise to the kA range within a coil called the drive field generator. Matching and tuning between a power amplifier, a band-pass filter and the drive-field generator is required. Here, for reasons of safety in future human scanners, a symmetrical topology and a transformer, called inductive coupling network is used. Our primary objectives are to achieve floating potentials to ensure patient safety, attaining high linearity and high gain for the resonant transformer. We present a novel systematic approach to the design of a loss-optimized resonant toroid with a D-shaped cross section, employing segmentation to adjust the inductance-to-resistance ratio while maintaining a constant quality factor. Simultaneously, we derive a specific matching condition of a symmetric transmit-receive circuit for magnetic particle imaging. The chosen setup filters the fundamental frequency and allows simultaneous signal transmission and reception. In addition, the decoupling of multiple drive field channels is discussed and the primary side of the transformer is evaluated for maximum coupling and minimum stray field. Two prototypes were constructed, measured, decoupled, and compared to the derived theory and to method-of-moment based simulations.
Generalized MPI Multi-Patch Reconstruction using Clusters of similar System Matrices
May 02, 2022


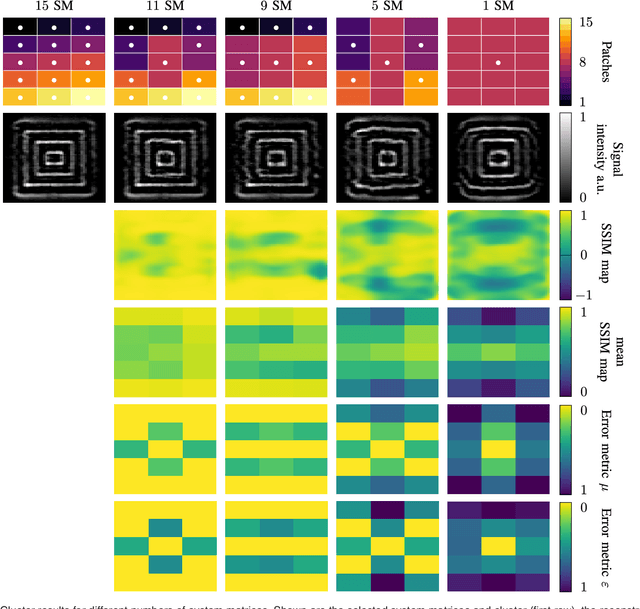
Abstract:The tomographic imaging method magnetic particle imaging (MPI) requires a multi-patch approach for capturing large field of views. This approach consists of a continuous or stepwise spatial shift of a small sub-volume of only few cubic centimeters size, which is scanned using one or multiple excitation fields in the kHz range. Under the assumption of ideal magnetic fields, the MPI system matrix is shift invariant and in turn a single matrix suffices for image reconstruction significantly reducing the calibration time and reconstruction effort. For large field imperfections, however, the method can lead to severe image artifacts. In the present work we generalize the efficient multi-patch reconstruction to work under non-ideal field conditions, where shift invariance holds only approximately for small shifts of the sub-volume. Patches are clustered based on a magnetic-field-based metric such that in each cluster the shift invariance holds in good approximation. The total number of clusters is the main parameter of our method and allows to trade off calibration time and image artifacts. The magnetic-field-based metric allows to perform the clustering without prior knowledge of the system matrices. The developed reconstruction algorithm is evaluated on a multi-patch measurement sequence with 15 patches, where efficient multi-patch reconstruction with a single calibration measurement leads to strong image artifacts. Analysis reveals that calibration measurements can be decreased from 15 to 11 with no visible image artifacts. A further reduction to 9 is possible with only slight degradation in image quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge