Martin Kodys
Privacy-Preserving Intrusion Detection using Convolutional Neural Networks
Apr 15, 2024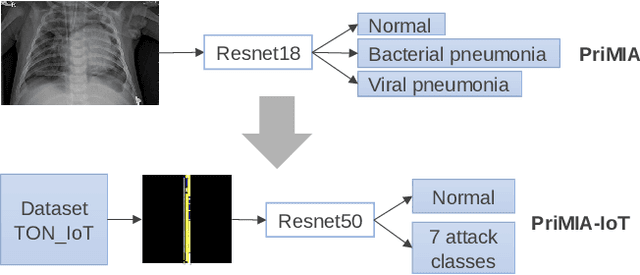

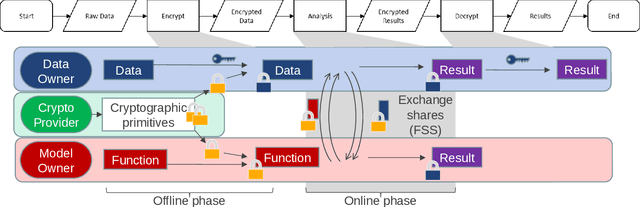
Abstract:Privacy-preserving analytics is designed to protect valuable assets. A common service provision involves the input data from the client and the model on the analyst's side. The importance of the privacy preservation is fuelled by legal obligations and intellectual property concerns. We explore the use case of a model owner providing an analytic service on customer's private data. No information about the data shall be revealed to the analyst and no information about the model shall be leaked to the customer. Current methods involve costs: accuracy deterioration and computational complexity. The complexity, in turn, results in a longer processing time, increased requirement on computing resources, and involves data communication between the client and the server. In order to deploy such service architecture, we need to evaluate the optimal setting that fits the constraints. And that is what this paper addresses. In this work, we enhance an attack detection system based on Convolutional Neural Networks with privacy-preserving technology based on PriMIA framework that is initially designed for medical data.
Intrusion Detection in Internet of Things using Convolutional Neural Networks
Nov 18, 2022



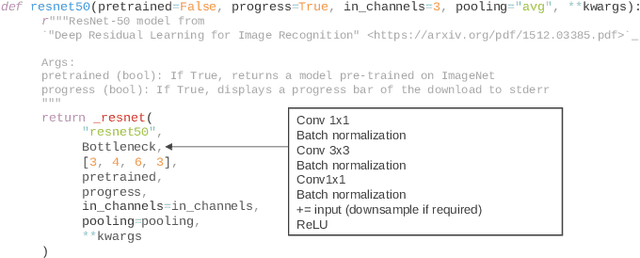
Abstract:Internet of Things (IoT) has become a popular paradigm to fulfil needs of the industry such as asset tracking, resource monitoring and automation. As security mechanisms are often neglected during the deployment of IoT devices, they are more easily attacked by complicated and large volume intrusion attacks using advanced techniques. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been used by the cyber security community in the past decade to automatically identify such attacks. However, deep learning methods have yet to be extensively explored for Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) specifically for IoT. Most recent works are based on time sequential models like LSTM and there is short of research in CNNs as they are not naturally suited for this problem. In this article, we propose a novel solution to the intrusion attacks against IoT devices using CNNs. The data is encoded as the convolutional operations to capture the patterns from the sensors data along time that are useful for attacks detection by CNNs. The proposed method is integrated with two classical CNNs: ResNet and EfficientNet, where the detection performance is evaluated. The experimental results show significant improvement in both true positive rate and false positive rate compared to the baseline using LSTM.
* Keywords: Cybersecurity, Intrusion Detection, IoT, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks; https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9647828
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge