Mariem Krichen
File Transfer Application For Sharing Femto Access
Apr 27, 2011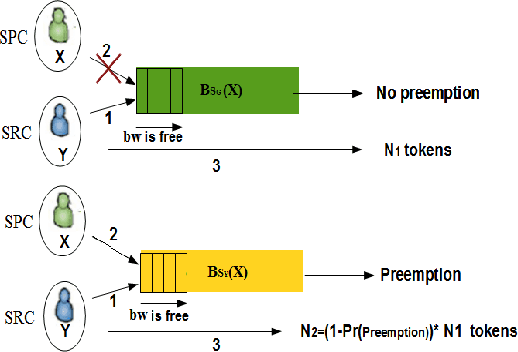
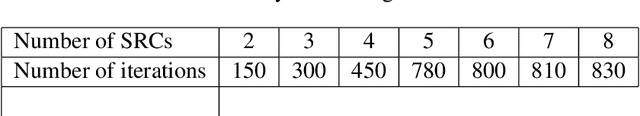
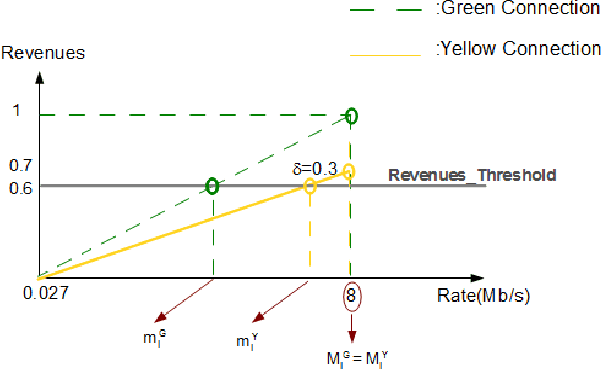
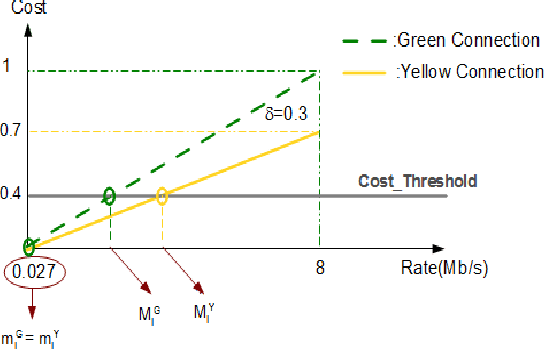
Abstract:In wireless access network optimization, today's main challenges reside in traffic offload and in the improvement of both capacity and coverage networks. The operators are interested in solving their localized coverage and capacity problems in areas where the macro network signal is not able to serve the demand for mobile data. Thus, the major issue for operators is to find the best solution at reasonable expanses. The femto cell seems to be the answer to this problematic. In this work (This work is supported by the COMET project AWARE. http://www.ftw.at/news/project-start-for-aware-ftw), we focus on the problem of sharing femto access between a same mobile operator's customers. This problem can be modeled as a game where service requesters customers (SRCs) and service providers customers (SPCs) are the players. This work addresses the sharing femto access problem considering only one SPC using game theory tools. We consider that SRCs are static and have some similar and regular connection behavior. We also note that the SPC and each SRC have a software embedded respectively on its femto access, user equipment (UE). After each connection requested by a SRC, its software will learn the strategy increasing its gain knowing that no information about the other SRCs strategies is given. The following article presents a distributed learning algorithm with incomplete information running in SRCs software. We will then answer the following questions for a game with $N$ SRCs and one SPC: how many connections are necessary for each SRC in order to learn the strategy maximizing its gain? Does this algorithm converge to a stable state? If yes, does this state a Nash Equilibrium and is there any way to optimize the learning process duration time triggered by SRCs software?
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge