Maria Dyshel
Learning to Love Edge Cases in Formative Math Assessment: Using the AMMORE Dataset and Chain-of-Thought Prompting to Improve Grading Accuracy
Sep 26, 2024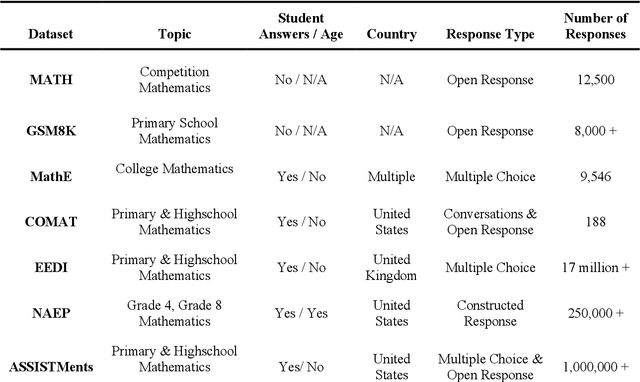
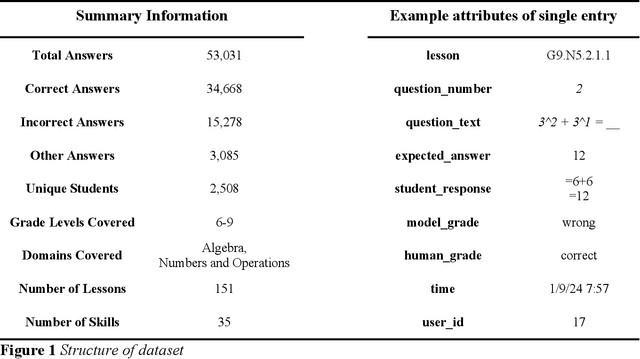


Abstract:This paper introduces AMMORE, a new dataset of 53,000 math open-response question-answer pairs from Rori, a learning platform used by students in several African countries and conducts two experiments to evaluate the use of large language models (LLM) for grading particularly challenging student answers. The AMMORE dataset enables various potential analyses and provides an important resource for researching student math acquisition in understudied, real-world, educational contexts. In experiment 1 we use a variety of LLM-driven approaches, including zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought prompting, to grade the 1% of student answers that a rule-based classifier fails to grade accurately. We find that the best-performing approach -- chain-of-thought prompting -- accurately scored 92% of these edge cases, effectively boosting the overall accuracy of the grading from 98.7% to 99.9%. In experiment 2, we aim to better understand the consequential validity of the improved grading accuracy, by passing grades generated by the best-performing LLM-based approach to a Bayesian Knowledge Tracing (BKT) model, which estimated student mastery of specific lessons. We find that relatively modest improvements in model accuracy at the individual question level can lead to significant changes in the estimation of student mastery. Where the rules-based classifier currently used to grade student, answers misclassified the mastery status of 6.9% of students across their completed lessons, using the LLM chain-of-thought approach this misclassification rate was reduced to 2.6% of students. Taken together, these findings suggest that LLMs could be a valuable tool for grading open-response questions in K-12 mathematics education, potentially enabling encouraging wider adoption of open-ended questions in formative assessment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge